Effects of endothelial progenitor cell transplantation on the expression of inflammatory factors in a rat model of acute lung injury caused by paraquat poisoning
-
摘要:
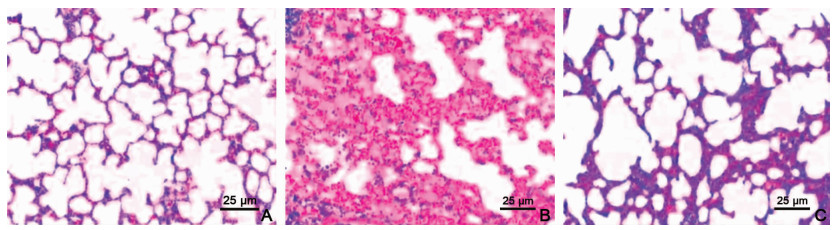
目的 分析内皮祖细胞移植对百草枯中毒所致急性肺损伤大鼠模型炎症因子表达的影响,为内皮祖细胞移植在临床中的应用提供参考。 方法 选取60只雄性SD大鼠作为实验动物,采取随机数字表法将大鼠分为对照组、百草枯组(模型组)和内皮祖细胞移植组(观察组),各20只,比较3组大鼠的肺组织损伤情况及血清炎性因子等指标的表达水平。 结果 3组大鼠的肺组织损伤评分和湿干重比比较差异有统计学意义(F=12.336、10.571,均P<0.05),模型组大鼠的肺组织损伤评分和湿干重比均高于观察组和对照组(均P<0.05),但观察组和对照组比较差异无统计学意义(均P>0.05);3组大鼠肺血清炎性因子表达水平比较差异有统计学意义(F=23.305、26.271、18.814、20.056,均P<0.05),观察组和模型组大鼠的血清炎性因子表达水平均高于对照组(均P<0.05),但观察组的血清炎性因子表达水平低于模型组(均P<0.05);3组大鼠的氧化应激指标比较差异有统计学意义(F=8.326、14.505,均P<0.05),模型组大鼠的丙二醛(MDA)明显高于观察组和对照组(均P<0.05),且超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)明显低于观察组和对照组(均P<0.05),但观察组和对照组氧化应激指标比较差异无统计学意义(均P>0.05)。 结论 内皮祖细胞移植可以降低百草枯中毒所致急性肺损伤大鼠模型炎症因子表达,具有较好的疗效。 Abstract:Objective To analyse the effect of endothelial progenitor cell transplantation on the expression of inflammatory factors in a rat model of acute lung injury caused by paraquat poisoning and to provide references for the clinical application of endothelial progenitor cell transplantation. Methods Sixty male SD rats were selected as experimental animals, and the rats were divided into the control group, paraquat group (model group) and endothelial progenitor cell transplantation group (observation group) by a random number table method. The tissue damage and expression level of serum inflammatory factors and other indicators were also compared. Results The lung tissue damage score and wet-dry weight ratio of the three groups of rats were significantly different (F=12.336, 10.571, all P < 0.05). The lung tissue damage score and wet-dry weight ratio of the model group were higher than those of the observation and control groups (all P < 0.05), but no significant difference was found between the observation and control groups (all P>0.05). The lung serum inflammatory factor expression levels of the three groups of rats were significantly different (F=23.305, 26.271, 18.814, 20.056, all P < 0.05), and the expression levels of the serum inflammatory factors in the observation and model groups were higher than those in the control group (all P < 0.05), but the expression level of the serum inflammatory factors in the observation group was lower than that in the model group (all P < 0.05). The oxidative stress indicators of the three groups of rats were significantly different (F=8.326, 14.505, all P < 0.05). The MDA of the model group was significantly higher than that of the observation and control groups (all P < 0.05), and SOD of the model group was significantly lower than that of the observation and control groups (all P < 0.05), but the observation and control groups had no significant difference in oxidative stress indicators (all P>0.05). Conclusion Endothelial progenitor cell transplantation can reduce the expression of inflammatory factors in a rat model of acute lung injury caused by paraquat poisoning, which has a definite effect. -
Key words:
- Endothelial progenitor cells /
- Paraquat /
- Acute lung injury /
- Inflammatory factors
-
表 1 3组大鼠肺组织损伤评分比较(x ±s,分)
组别 只数 肺组织损伤评分 观察组 20 1.36±0.33 模型组 20 10.03±0.75ab 对照组 20 0.59±0.11 F值 12.336 P值 0.015 注:与对照组比较,aP<0.05;与观察组比较,bP<0.05。 表 2 3组大鼠肺组织湿干重比比较(x ±s)
组别 只数 肺组织湿干重比 观察组 20 4.76±1.02 模型组 20 9.26±1.89ab 对照组 20 3.82±0.81 F值 10.571 P值 0.020 注:与对照组比较,aP<0.05;与观察组比较,bP<0.05。 表 3 3组大鼠的血清炎性因子表达水平比较(x ±s)
组别 只数 TNF-α(pg/mL) IL-6(ng/mL) IL-10(ng/mL) IL-1β(ng/mL) 观察组 20 126.34±12.23a 152.26±23.36a 85.71±5.62a 85.53±7.02a 模型组 20 202.34±25.82ab 352.18±52.71ab 95.54±12.79ab 142.23±18.83ab 对照组 20 42.11±4.32 80.22±4.45 47.18±2.36 57.31±4.09 F值 23.305 26.271 18.814 20.056 P值 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 注:与对照组比较,aP<0.05;与观察组比较,bP<0.05。 表 4 3组大鼠肺组织的氧化应激指标比较(x ±s)
组别 只数 MDA(nmol/mg) SOD(U/mg) 观察组 20 1.02±0.29 26.91±2.59 模型组 20 2.29±0.57ab 15.54±2.24ab 对照组 20 0.83±0.07 28.72±1.23 F值 8.326 14.505 P值 0.031 0.011 注:与对照组比较,aP<0.05;与观察组比较,bP<0.05。 -
[1] 黄铭, 黄伟. 大剂量氨溴索联合乙酰半胱氨酸在百草枯中毒肺纤维化患者早期应用中的疗效观察[J]. 中华全科医学, 2018, 16(12): 2098-2101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYQY201812042.htm [2] LIU M, XU H Y, ZHANG L, et al. Salvianolic acid B inhibits myofibroblast transdifferentiation in experimental pulmonary fibrosis via the up-regulation of Nrf2[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2018, 495(1): 325-331. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.11.014 [3] 陆元兰, 王瑜, 陈江华, 等. 5-氨基水杨酸激活Nrf2通路对百草枯中毒急性肺损伤的保护作用[J]. 医学研究生学报, 2018, 31(11): 1126-1130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLYB201811003.htm [4] 何招辉, 贺慧为, 卢院华, 等. 慢病毒介导VEGF165转染的内皮祖细胞移植可减轻大鼠ALI[J]. 中华危重病急救医学, 2017, 29(11): 1015-1020. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2017.11.011 [5] 李志, 陆爱珍, 张小媚, 等. 内皮祖细胞培养上清对高氧暴露新生大鼠肺结构的改善作用[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2017, 33(8): 1467-1474. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4718.2017.08.020 [6] 朱茂治, 祝禾辰, 陈传国, 等. KL-6粘糖蛋白在百草枯中毒致肺纤维化大鼠中的表达及意义[J]. 中华全科医学, 2017, 15(11): 1835-1838, 1999. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYQY201711006.htm [7] 吴燕生, 郁毅刚, 王健. 血必净注射液联合血液灌流对百草枯重度中毒患者致脏器损伤的保护作用研究[J]. 河北医学, 2017, 23(11): 1885-1888. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6233.2017.11.037 [8] 胡海霞, 吴扬, 臧秀贤, 等. 不同方式血液灌流对百草枯中毒患者血中毒物清除的研究[J]. 中华急诊医学杂志, 2016, 25(4): 499-502. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-0282.2016.04.021 [9] YAN B, CHEN F, XU L J, et al. HMGB1-TLR4-IL23-IL17A axis promotes paraquat-induced acute lung injury by mediating neutrophil infiltration in mice[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 597. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-00721-8 [10] 陈凤, 赫东芸, 闫百灵. 百草枯中毒致急性肺损伤的作用与机制研究[J]. 中国实验诊断学, 2018, 22(4): 668-669. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4287.2018.04.038 [11] 陈献, 吴雨径, 杜海科. 血浆吸附灌流联合血液滤过对急性百草枯中毒肺损伤的疗效及预后推断[J]. 天津医药, 2017, 45(12): 1312-1315. doi: 10.11958/20170696 [12] 刘振宁, 张立春, 沈海涛, 等. NLRP3/caspase-1信号通路在百草枯中毒致急性肺损伤过程中的作用[J]. 中国急救医学, 2016, 36(4): 358-362. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1949.2016.04.016 [13] 胡晓, 王煜, 沈海涛, 等. GW3965抑制p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路表达减轻百草枯致小鼠急性肺损伤[J]. 中华急诊医学杂志, 2018, 27(5): 507-512. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-0282.2018.05.010 [14] RURALI E, BASSETTI B, PERRUCCI G L, et al. BM ageing: Implication for cell therapy with EPCs[J]. Mech Ageing Dev, 2016, 159(16): 4-13. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000038821262410_2761.html [15] 冯韦韦, 吴爱兵, 王宏宾. 芹菜素对肝缺血-再灌注大鼠IL-1β、IL-6及TNF-α表达的影响[J]. 中华全科医学, 2019, 17(2): 183-185. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYQY201902006.htm [16] 赵燕凤, 张志群, 芦蕙, 等. PCT、白蛋白及IL-6水平检测在早产儿感染中的应用价值[J]. 中华全科医学, 2017, 15(1): 85-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYQY201701028.htm [17] 冯高科, THANH D N, 蒋学俊. 老年冠心病患者血液中Hcy、IL-6及BNP表达水平与冠心病病变程度的关系[J]. 中华全科医学, 2019, 17(10): 1644-1646. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYQY201910009.htm [18] 来涛, 左丽, 罗玉, 等. DENV-2感染的HUVECs与巨噬细胞相互作用对主要炎性细胞因子产生的影响[J]. 中华微生物学和免疫学杂志, 2019, 39(6): 432-439. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-5101.2019.06.005 [19] LI A, LI W, HAO F, et al. Early stage blood purification for paraquat poisoning: A multicenter retrospective study[J]. Blood Purif, 2016, 42(2): 93-99. doi: 10.1159/000445991 [20] 刘涛, 谢媛, 徐梦桐, 等. 沙利度胺对百草枯中毒ALI大鼠的保护作用及机制[J]. 中华危重病急救医学, 2017, 29(11): 977-981. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2017.11.004 -





 下载:
下载: