Analysis of the value of serum irisin in the diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome
-
摘要:
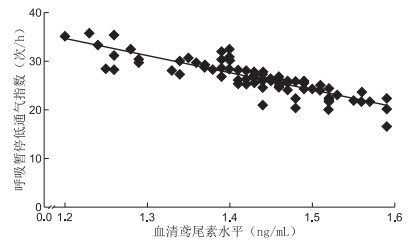
目的 探讨阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停综合征(obstructive sleep apnea syndrome,OSAS)程度与血清鸢尾素水平的相关性。 方法 选取2017年5月—2018年12月期间树兰(杭州)医院收治确诊的96例OSAS患者纳入OSAS组,并根据呼吸暂停低通气指数分为轻度30例、中度30例、重度36例;另选取30名健康体检者纳入对照组。采用多导睡眠监测仪检测呼吸暂停低通气指数、最低血氧饱和度及最长呼吸暂停时间,酶联免疫吸附法检测血清鸢尾素水平。 结果 OSAS组血清鸢尾素水平[(1.43±0.28)ng/mL]、最低血氧饱和度[(70.47±3.81)%]明显低于对照组[(2.82±0.54)ng/mL和(94.58±3.21)%],呼吸暂停低通气指数[(27.64±3.29)次/h] 明显多于对照组[(2.37±1.08)次/h],最长呼吸暂停时间[(37.45±4.23)s]明显长于对照组[(1.73±0.65)s],差异均有统计学意义(均P < 0.05)。随着病情的严重程度增加,血清鸢尾素水平、最低血氧饱和度降低,最长呼吸暂停时间升高。OSAS组呼吸暂停低通气指数、最长呼吸暂停时间均与血清鸢尾素水平呈负相关(r=-0.717、-0.765,均P < 0.05),最低血氧饱和度与血清鸢尾素水平呈正相关(r=0.747,P < 0.05)。以多导睡眠监测为金标准,血清鸢尾素诊断OSAS的敏感度为68.8%,特异度为93.3%。 结论 OSAS患者的血清鸢尾素水平与OSAS的病情程度有关,OSAS越严重,血清鸢尾素水平越低。 -
关键词:
- 阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停综合征 /
- 鸢尾素 /
- 呼吸暂停低通气指数 /
- 最低血氧饱和度 /
- 最长呼吸暂停时间
Abstract:Objective To investigate the correlation between the degree of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) and the level of irisin in serum. Methods Ninety-six OSAS patients diagnosed in Shulan (Hangzhou) Hospital from May 2017 to December 2018 were selected in the OSAS group, and according to the apnea hypopnea index, they were divided into mild (30 cases), moderate (30 cases) and severe (36 cases), another 30 healthy people were selected as the control group. The indexes of apnea hypopnea, the lowest oxygen saturation and the longest time of apnea were measured by polysomnography. The level of serum irisin was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Results The serum irisin level [(1.43±0.28) ng/mL], the lowest oxygen saturation [(70.47±3.81)%] in the OSAS group were significantly lower than those in the control group [(2.82±0.54) ng/mL and (94.58±3.21)%], the apnea hypopnea index [(27.64±3.29) times/h], the longest apnea time [(37.45±4.23) s] were significantly higher than those in the control group [(2.37±1.08) times/h and (1.73±0.65) s], the difference was statistically significant (all P < 0.05). With the increase of the severity of the disease, the level of serum irisin, the lowest oxygen saturation and the longest apnea time decreased. In the OSAS group, the index of apnea hypopnea and the longest time of apnea were negatively correlated with the level of serum irisin (r=-0.717, -0.765; all P < 0.05), and the lowest oxygen saturation was positively correlated with the level of serum irisin (r=0.747, P < 0.05). According to the gold standard of polysomnography, the sensitivity and specificity of irisin in the diagnosis of OSAS were 68.8% and 93.3%, respectively. Conclusion The serum irisin level of OSAS patients is related to the severity of OSAS. The more severe OSAS, the lower the serum irisin level. -
表 1 OSAS组与对照组一般资料比较
组别 例数 性别
(男/女,例)年龄
(x±s,岁)体重指数
(x±s)OSAS组 96 63/33 46.4±8.6 26.2±3.6 对照组 30 20/10 45.2±8.4 25.7±3.3 统计量 0.011a 0.671b 0.677b P值 0.916 0.504 0.500 注:a为χ2值,b为t值。 表 2 OSAS组与对照组血清鸢尾素水平及临床相关指标比较(x±s)
组别 例数 血清鸢尾素水平
(ng/mL)呼吸暂停低通气
指数(次/h)最低血氧饱
和度(%)最长呼吸暂停
时间(s)OSAS组 96 1.43±0.28 27.64±3.29 70.47±3.81 37.45±4.23 对照组 30 2.82±0.54 2.37±1.08 94.58±3.21 1.73±0.65 t值 18.560 41.280 31.340 45.960 P值 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 表 3 不同程度OSAS组血清鸢尾素水平及临床相关指标比较(x±s)
组别 例数 血清鸢尾素水平
(ng/mL)最低血氧饱
和度(%)最长呼吸暂停
时间(s)轻度OSAS组 30 1.83±0.03 86.25±2.21 25.37±1.58 中度OSAS组 30 1.05±0.03a 74.63±3.69a 34.26±4.09a 重度OSAS组 36 0.54±0.04ab 61.24±4.95ab 43.22±5.37ab F值 11 173.235 327.822 149.164 P值 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 注:与轻度OSAS组比较,aP < 0.05;与中度OSAS组比较,bP < 0.05。 -
[1] 王贺, 王莲地, 阳琰, 等. 2型糖尿病合并骨质疏松患者血清25羟维生素D、鸢尾素水平观察及其与骨密度的关系[J]. 中国糖尿病杂志, 2018, 26(7): 569-572. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6187.2018.07.008 [2] MAHGOUB M O, D'SOUZA C, AL DARMAKI R S M H, et al. An update on the role of irisin in the regulation of endocrine and metabolic functions[J]. Peptides, 2018, 104: 15-23. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2018.03.018 [3] 中华医学会呼吸病学分会睡眠呼吸障碍学组. 阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征诊治指南(2011年修订版)[J]. 中华结核和呼吸杂志, 2012, 35(1): 162-165. [4] 许亚慧, 刘凤娟, 王立生, 等. 阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征与心血管疾病相关性的研究进展[J]. 临床肺科杂志, 2019, 24(7): 1329-1332. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6663.2019.07.043 [5] KHATTAK H K, HAYAT F, PAMBOUKIAN S V, et al. Obstructive sleep apnea in heart failure: review of prevalence, treatment with continuous positive airway pressure, and prognosis[J]. Tex Heart Inst J, 2018, 45(3): 151-161. doi: 10.14503/THIJ-15-5678 [6] 钟水生, 胡琼力, 李志刚, 等. 合并阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停综合征的脑梗死患者血清皮质醇水平的测定[J]. 中华神经医学杂志, 2018, 17(8): 796-801. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-8925.2018.08.007 [7] 贺群, 李明晖. 阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征程度与血压变异性和血清瘦素相关性研究[J]. 中华全科医学, 2017, 15(2): 258-260. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYQY201702023.htm [8] 蔡文灿, 李彤, 刘彦明, 等. 阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停综合征患者血清Nesfatin-1水平变化及临床意义[J]. 中国医药导报, 2019, 16(28): 162-165. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYCY201928041.htm [9] KANG Y S, KIM J C, KIM J S, et al. Effects of swimming exercise on serum irisin and bone fndc5 in rat models of high-fat diet-induced osteoporosis[J]. J Sports Sci Med, 2019, 18(4): 596-603. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31827343 [10] HUH J Y, PANAGIOTOU G, MOUGIOS V, et al. FNDC5 and irisin in humans: I. Predictors of circulating concentrations in serum and plasma and Ⅱ. mRNA expression and circulating concentrations in response to weight loss and exercise[J]. Metabolism, 2012, 61(12): 1725-1738. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2012.09.002 [11] GIZAW M, ANANDAKUMAR P, DEBELA T. A review on the role of irisin in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. J Pharmacopuncture, 2017, 20(4): 235-242. http://www.journal.ac/scholar/v20n4/pdf/DHOCBS_2017_v20n4_235.pdf [12] LOURENCO M V, FROZZA R L, DE FREITAS G B, et al. Exercise-linked FNDC5/irisin rescues synaptic plasticity and memory defects in Alzheimer's models[J]. Nat Med, 2019, 25(1): 165-175. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0275-4 [13] LACEDONIA D, CARPAGNANO G E, PATRICELLI G, et al. Prevalence of comorbidities in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, overlap syndrome and obesity hypoventilation syndrome[J]. Clin Respir J, 2018, 12(5): 1905-1911. doi: 10.1111/crj.12754 [14] 赵淑玲, 张杰. 体质量管理对肥胖相关性阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征患者的影响[J]. 新疆医科大学学报, 2019, 42(8): 1037-1040. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5551.2019.08.016 [15] 栗宇, 崔晶, 任继平, 等. 肥胖指标在阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征筛查中的应用[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2019, 26(4): 211-214. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-EBYT201904013.htm -





 下载:
下载: