Expression of miR-30b and miR-96 in endometrial carcinoma and their relationship with prognosis
-
摘要:
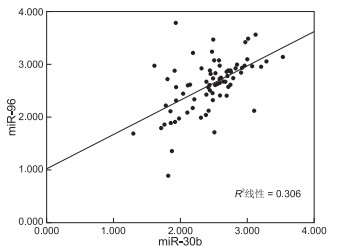
目的 检测子宫内膜癌(endometrial cancer,EC)患者外周血单个核细胞(peripheral blood mononuclear cell,PBMC)miR-30b、miR-96水平,探究其与临床病理及预后的关系。 方法 选择2012年10月—2014年8月温州市中西医结合医院收治的EC患者及门诊健康体检者(对照组)各76例,荧光定量PCR检测PBMC中miR-30b、miR-96水平,Pearson法分析二者相关性,Kaplan-Meier法分析二者与5年生存率的关系;Cox分析不良预后的危险因素。 结果 EC患者PBMC中miR-30b、miR-96水平均高于对照组(t=21.913、24.188,均P<0.05),二者呈正相关(r=0.553,P<0.05),均与病理分级、FIGO分期、肌层浸润及淋巴结转移有关(均P<0.05)。miR-30b高表达者5年总生存率(16.13%)低于低表达者(66.67%,χ2=16.890,P<0.05);miR-96高表达者5年总生存率(18.18%)低于低表达者(67.44%,χ2=16.307,P<0.05)。miR-30b、miR-96、FIGO分期、淋巴结转移是预后的影响因素(HR=2.861, 95% CI: 1.427~5.736;HR=1.973, 95% CI: 1.462~2.663;HR=2.235, 95% CI: 1.491~3.350;HR=2.439, 95% CI: 1.365~4.358;均P<0.05)。 结论 PMBC中miR-30b、miR-96高表达,与EC患者病理分级、FIGO分期、肌层浸润、淋巴结转移及5年生存率有关,是影响预后的独立危险因素。 Abstract:Objective The levels of miR-30b and miR-96 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) in patients with endometrial carcinoma (EC) were detected to explore their relationship with clinicopathology and prognosis. Methods A total of 76 EC patients and healthy outpatients(control group)admitted to Wenzhou hospital of integrated traditional Chinese and western medicine were selected. The expression levels of miR-30b and miR-96 in PBMC were detected by fluorescence quantitative PCR, the correlation was analyzed by Pearson method, the relationships between miR-30b and miR-96 expression levels in PBMC and 5-year survival rate of EC patients were analyzed by Kaplan-Meier method, and the risk factors affecting the prognosis of EC patients were analyzed by Cox regression. Results The expression levels of miR-30b and miR-96 in PBMC of EC patients were higher than those of control group (t=21.913, 24.188, all P < 0.05). They were positively correlated (r=0.553, P < 0.05), and correlated with pathological grade, FIGO stage, depth of muscle invasion and lymph node metastasis (P < 0.05). The 5-year overall survival rate of patients with high expression of miR-30b (16.13%) was lower than that of patients with low expression (66.67%, χ2=16.890, P < 0.05). The 5-year overall survival rate of patients with high expression of miR-96 (18.18%) was lower than that of patients with low expression (67.44%, χ2=16.307, P < 0.05). Levels of miR-30b and miR-96, FIGO stage and lymph node metastasis in PMBC were independent risk factors affecting the prognosis of EC patients (HR=2.861, 95% CI: 1.427-5.736; HR=1.973, 95% CI: 1.462-2.663; HR=2.235, 95% CI: 1.491-3.350; HR=2.439, 95% CI: 1.365-4.358; all P < 0.05). Conclusion The miR-30b and miR-96 are highly expressed in PMBC, which are related to pathological grade, FIGO stage, muscle invasion, lymph node metastasis and 5-year survival rate of EC patients, and are independent risk factors for adverse prognosis of EC patients. -
Key words:
- Endometrial cancer /
- MicroRNA-30b /
- MicroRNA-96
-
表 1 EC患者与对照组PBMC中miR-30b、miR-96表达水平比较(x±s)
组别 例数 miR-30b miR-96 对照组 76 1.12±0.21 1.06±0.19 EC组 76 2.46±0.49 2.57±0.51 t值 21.913 24.188 P值 <0.001 <0.001 表 2 PBMC中miR-30b、miR-96表达水平与EC患者临床病理参数的关系[例(%)]
项目 例数 miR-30b χ2值 P值 miR-96 χ2值 P值 高表达(31例) 低表达(45例) 高表达(33例) 低表达(43例) 年龄(岁) <55 52 18(34.62) 34(65.38) 1.853 0.173 19(36.54) 33(63.46) 2.350 0.125 ≥55 24 13(54.17) 11(45.83) 14(58.33) 10(41.67) BMI ≥24 39 16(41.03) 23(58.97) 0.036 0.849 19(48.72) 20(51.28) 0.526 0.468 <24 37 15(40.54) 22(59.46) 14(37.84) 23(62.16) 月经周期(d) ≥30 23 10(43.48) 13(56.52) 0.004 0.952 11(47.83) 12(52.17) 0.067 0.796 <30 53 21(39.62) 32(60.38) 22(41.51) 31(58.49) 病理类型 Ⅰ型 67 27(40.30) 40(59.70) 0.015 0.902 30(44.78) 37(55.22) 0.085 0.770 Ⅱ型 9 4(44.44) 5(55.56) 3(33.33) 6(66.67) 病理分级(级) 1+2 61 19(31.15) 42(68.85) 9.960 0.002 22(36.07) 39(63.93) 5.374 0.020 3 15 12(80.00) 3(20.00) 11(73.33) 4(26.67) FIGO分期(期) Ⅰ+Ⅱ 61 18(29.51) 43(70.49) 14.006 < 0.001 19(31.15) 42(68.85) 16.504 <0.001 Ⅲ+Ⅳ 15 13(86.67) 2(13.33) 14(93.33) 1(6.67) 肌层浸润深度 <1/2 55 17(30.91) 38(69.09) 6.633 0.010 17(30.91) 38(39.09) 10.908 0.001 ≥1/2 21 14(66.67) 7(33.33) 16(76.19) 5(23.81) 淋巴结转移 有 14 12(85.71) 2(14.29) 12.151 < 0.001 13(92.86) 1(7.14) 14.694 <0.001 无 62 19(30.65) 43(69.35) 20(32.26) 42(67.74) 表 3 EC患者预后影响因素的赋值情况
项目 赋值 年龄 年龄≥55岁=1,年龄<55岁=0 miR-30b >2.46=1,≤2.46=0 miR-96 >2.57=1,≤2.57=0 病理分级 1+2级=0,3级=1 FIGO分期 Ⅰ+Ⅱ期=0,Ⅲ+Ⅳ期=1 肌层浸润 <1/2=1,≥1/2=0 结局 死亡=1,截尾=0 淋巴结转移 有转移=1,无转移=0 BMI ≥24=1,<24=0 月经周期 ≥30 d=1,<30 d=0 病理类型 Ⅰ型=1,Ⅱ型=0 表 4 EC患者预后影响的单因素分析
自变量 B Wald χ2 SE P值 HR值 95% CI 年龄 0.434 1.145 0.406 0.365 1.544 0.904~2.637 miR-30b 1.425 5.376 0.615 <0.001 4.158 1.875~9.221 miR-96 1.377 6.432 0.543 <0.001 3.964 1.483~10.596 病理分级 1.229 5.725 0.514 <0.001 3.417 1.619~7.212 FIGO分期 1.038 9.072 0.345 <0.001 2.823 1.742~4.575 肌层浸润 0.656 4.631 0.305 0.024 1.928 1.257~2.957 淋巴结转移 1.153 7.496 0.421 <0.001 3.169 2.114~4.751 BMI 0.445 1.431 0.372 0.296 0.641 0.277~1.482 月经周期 0.075 0.418 0.116 0.519 1.078 0.593~1.961 病理类型 0.185 0.727 0.217 0.428 0.831 0.418~1.652 表 5 EC患者预后影响的多因素Cox回归分析
自变量 B Wald χ2 SE P值 HR值 95% CI miR-30b 1.051 5.476 0.499 0.001 2.861 1.427~5.736 miR-96 0.682 4.915 0.307 0.020 1.973 1.462~2.663 病理分级 0.427 1.736 0.324 0.084 1.533 0.886~2.652 FIGO分期 0.804 5.153 0.354 0.005 2.235 1.491~3.350 肌层浸润 0.348 1.352 0.299 0.164 1.416 0.893~2.245 淋巴结转移 0.892 4.486 0.421 0.011 2.439 1.365~4.358 -
[1] 郭玉霞, 郑绘霞. ING4在子宫内膜癌中的表达及意义[J]. 山西医科大学学报, 2018, 49(7): 859-861. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXYX201807024.htm [2] ZHANG K, LI H Y, YAN Y, et al. Identification of key genes and pathways between type Ⅰ and type Ⅱ endometrial cancer using bioinformatics analysis[J]. Oncol Lett, 2019, 18(3): 2464-2476. http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/sp/ol/2019/00000018/00000003/art00039 [3] WANG Q, ZHU W. MicroRNA-873 inhibits the proliferation and invasion of endometrial cancer cells by directly targeting hepatoma-derived growth factor[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2019, 18(2): 1291-1298. http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/sp/etm/2019/00000018/00000002/art00055 [4] VAN SINDEREN M, GRIFFITHS M, MENKHORST E, et al. Restoration of microRNA-29c in type Ⅰ endometrioid cancer reduced endometrial cancer cell growth[J]. Oncol Lett, 2019, 18(3): 2684-2693. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/334328349_Restoration_of_microRNA-29c_in_type_I_endometrioid_cancer_reduced_endometrial_cancer_cell_growth [5] 周辉芳, 谢英, 孙殿兴. miR-30b的生物学功能研究进展[J]. 解放军医药杂志, 2019, 31(8): 108-111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBGF201908027.htm [6] ZHANG K, WANG Y W, WANG Y Y, et al. Identification of microRNA biomarkers in the blood of breast cancer patients based on microRNA profiling[J]. Gene, 2017, 619(1): 10-20. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Ya_Wen_Wang/publication/315731133_Identification_of_microRNA_biomarkers_in_the_blood_of_breast_cancer_patients_based_on_microRNA_profiling/links/58eafcccaca2729d8cd59cbc/Identification-of-microRNA-biomarkers-in-the-blood-of-breast-cancer-patients-based-on-microRNA-profiling.pdf [7] JAYARAMAN M, RADHAKRISHNAN R, MATHEWS C A, et al. Identification of novel diagnostic and prognostic miRNA signatures in endometrial cancer[J]. Genes Cancer, 2017, 8(5-6): 566-576. doi: 10.18632/genesandcancer.144 [8] DENNY L, QUINN M. FIGO cancer report 2015[J]. Int J Gynaecol Obstet, 2015, 131(2): 75. [9] 周琦, 吴小华, 刘继红, 等. 子宫内膜癌诊断与治疗指南(第四版)[J]. 中国实用妇科与产科杂志, 2018, 34(8): 880-886. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSF201808016.htm [10] 许富, 崔德威. miR-30b的生物学功能研究进展[J]. 医学理论与实践, 2016, 29(11): 1434-1436. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXLL201611017.htm [11] LI Q, ZHANG X, LI N, et al. miR-30b inhibits cancer cell growth, migration, and invasion by targeting homeobox A1 in esophageal cancer[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2017, 485(2): 506-512. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.02.016 [12] XU J, LV H, ZHANG B, et al. miR-30b-5p acts as a tumor suppressor microRNA in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. J Thorac Dis, 2019, 11(7): 3015-3029. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2019.07.50 [13] QI Z, ZHANG B, ZHANG J, et al. MicroRNA-30b inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cell growth by targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor[J]. Neoplasma, 2018, 65(2): 192-200. doi: 10.4149/neo_2018_170217N118 [14] WU L, PU X X, WANG Q Z, et al. miR-96 induces cisplatin chemoresistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells by downregulating SAMD9[J]. Oncol Lett, 2016, 11(2): 945-952. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.4000 [15] 刘敏娟, 黄郁馨, 冯婉琴, 等. miR-96靶向血管生成素-1基因对子宫内膜异位症子宫内膜干细胞增殖的影响[J]. 广东医学, 2018, 39(23): 3448-3453. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9448.2018.23.002 -





 下载:
下载: