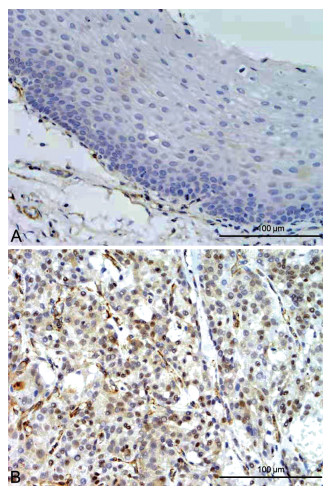
Expression of SOX6 in oral mucoepidermoid carcinoma and its clinical significance
-
摘要:
目的 检测转录因子性别决定区Y-box 6(SOX6)在唾液腺黏液表皮样癌组织及癌旁正常组织中的表达情况,并探究其表达的差异与临床病理特征及患者预后的关系。 方法 采用免疫组化EnVision法检测55例唾液腺黏液表皮样癌及相应癌旁正常组织中SOX6蛋白的表达情况,应用统计学方法分析SOX6的表达情况与唾液腺黏液表皮样癌患者的临床病理特征(性别、年龄、病理分级、TNM分期、淋巴结转移)及其预后的关系。 结果 黏液表皮样癌组织中SOX6阳性表达率为62.3%(37/55),其相应癌旁正常组织的阳性表达率为36.4%(20/55),黏液表皮样癌组织中SOX6阳性表达率明显高于其相应癌旁正常组织(P < 0.05)。在黏液表皮样癌中,SOX6表达阳性率的差异与病理分级和临床分期相关(均P < 0.05)。随着唾液腺黏液表皮样癌患者病理分级的降低、TNM分期的升高,SOX6阳性表达率明显升高。但患者性别、年龄与SOX6阳性表达率的高低间的差异无统计学意义(均P>0.05)。统计分析结果示,SOX6阴性组的5年生存期较阳性组长,差异有统计学意义,SOX6的高表达与患者不良预后有明显的相关性(P < 0.05),SOX6可能是影响唾液腺黏液表皮样癌患者的独立预后因素。 结论 SOX6在唾液腺黏液表皮样癌组织中呈高表达,其可能在唾液腺黏液表皮样癌发生、发展过程中扮演着重要角色,这为唾液腺黏液表皮样癌的治疗及预后评估提供一定的参考依据。 -
关键词:
- 黏液表皮样癌 /
- 转录因子性别决定区Y-box 6 /
- 免疫组织化学 /
- 预后
Abstract:Objective To detect the expression of transcription factor sex-determining region Y-box 6 (SOX6) in mucoepidermoid carcinoma (MEC) of salivary gland and adjacent normal tissues, as well as to explore the relationship between the expression difference and clinicopathological features and prognosis of patients. Methods The immunohistochemical EnVision method was used to detect the expression of SOX6 protein in 55 cases of salivary gland mucoepidermoid carcinoma and the corresponding normal tissues adjacent to the cancer. The relationship between the expression of SOX6 and the clinicopathological characteristics (gender, age, pathological grade, TNM staging, and lymph-node metastasis) and prognosis of salivary gland mucoepidermoid carcinoma was analysed by statistical methods. Results The positive expression rate of SOX6 in mucoepidermoid carcinoma was 62.3% (37/55), and the positive expression rate of SOX6 in the corresponding normal tissues adjacent to the cancer was 36.4% (20/55). The positive expression rate of SOX6 in mucoepidermoid carcinoma was significantly higher than that of the corresponding normal tissues (P < 0.05). The difference of SOX6 expression in mucoepidermoid carcinoma was related to pathological grade and clinical stage (all P < 0.05). With decreased pathological grade of MEC patients and increased TNM stage, the expression of SOX6 increased. But there was no statistical significance between gender, age and SOX6 positive expression rate (all P>0.05). The results of statistical analysis showed that the five-year survival time of the SOX6 negative group was longer than that of the positive group, and the difference was statistically significant. The high expression of SOX6 was significantly correlated with the poor prognosis of patients (P < 0.05). SOX6 may be an independent prognostic factor in patients with mucoepidermoid carcinoma of salivary gland. Conclusion SOX6 is highly expressed in MEC tissues and may play an important role in the occurrence of MEC, which has certain reference value for the treatment and diagnosis of MEC. -
表 1 MEC中SOX6的表达与临床病理参数的关系
[例(%)] 临床特征 例数 SOX6表达 χ2值 P值 - + 性别 男性 27 10(37.0) 17(63.0) 0.447 0.504 女性 28 8(28.6) 20(71.4) 年龄 ≤45岁 29 9(31.0) 20(69.0) 0.080 0.778 >45岁 26 9(34.6) 17(65.4) 淋巴结转移 无 33 14(42.4) 19(57.6) 3.524 0.061 有 22 4(18.2) 18(81.8) 病理分级 高分化 25 12(48.0) 13(52.0) 4.856 0.028 低/中分化 30 6(20.0) 24(80.0) TNM分期 Ⅰ+Ⅱ期 20 10(50.0) 10(50.0) 4.259 0.039 Ⅲ+Ⅳ期 35 8(22.9) 27(77.1) 表 2 影响MEC患者5年生存率的COX单因素回归分析
因素 B SE Wald χ2 P值 HR(95% CI) 性别 0.147 0.45 0.107 0.743 1.159(0.480~2.796) 年龄 -0.355 0.456 0.603 0.437 0.701(0.287~1.716) 淋巴结转移 0.237 0.45 0.277 0.599 1.267(0.525~3.061) 病理分级 1.051 0.517 4.128 0.042 2.860(1.038~7.882) TNM分期 1.284 0.627 4.186 0.041 3.610(1.055~12.348) SOX6表达 1.801 0.747 5.816 0.016 6.056(1.401~26.176) 表 3 影响MEC患者5年生存率的COX多因素回归分析
因素 B SE Wald χ2 P值 HR(95% CI) 性别 -0.223 0.482 0.215 0.643 0.800(0.311~2.056) 年龄 -0.097 0.502 0.037 0.847 0.908(0.339~2.427) 淋巴结转移 -0.658 0.511 1.661 0.198 0.518(0.19~1.409) 病理分级 0.421 0.589 0.512 0.474 1.524(0.481~4.828) TNM分期 1.184 0.724 2.676 0.102 3.269(0.791~13.511) SOX6表达 1.591 0.777 4.195 0.041 4.907(1.071~22.483) -
[1] 王张嵩, 谢舒乐, 张汉卿, 等. 2456例唾液腺肿瘤临床病理分析[J]. 口腔疾病防治, 2020, 28(5): 298-302. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDYB202005007.htm [2] 罗佳, 杨艳, 杨森. 唾液腺黏液表皮样癌的预后及影响因素分析[J]. 口腔医学, 2017, 37(1): 65-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KQYX201701015.htm [3] XU Y R, YANG W X. SOX-mediated molecular crosstalk during the progression of tumorigenesis[J]. Semin Cell Dev Biol, 2017, 63(29): 23-34. [4] LI Y, XIAO M, GUO F. The role of Sox6 and Netrin-1 in ovarian cancer cell growth, invasiveness, and angiogenesis[J]. Tumour Biol, 2017, 39(5): 1010428317705508. doi: 10.1177/1010428317705508 [5] 陈路遥, 张旭. SoxD家族基因与肿瘤发生发展关系的研究进展[J]. 解放军医学院学报, 2016, 37(10): 1103-1105, 1119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-5227.2016.10.023 [6] MATSE J H, BHAROS W K, VEERMAN E C I, et al. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma-associated expression of MUC5AC, MUC5B and mucin-type carbohydrate antigen sialylTn in the parotid gland[J]. Arch Oral Biol, 2017, 82: 121-126. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2017.06.010 [7] SIEGEL R, NAISHADHAM D, JEMAL A. Cancer statistics, 2018[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 63(1): 11-30. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30207593?utm_source=research-news&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=research-news [8] 韩呈武, 杨强, 宋秦伟. 胰腺癌组织中干细胞转录因子Sox2及Oct4的表达及意义[J]. 临床与实验病理学杂志, 2019, 35(11): 1300-1303, 1309. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LSBL201911011.htm [9] 余露, 颜梦然, 罗文婷, 等. SOX10在毛细胞型星形细胞瘤和室管膜肿瘤鉴别诊断中的应用[J]. 临床与实验病理学杂志, 2019, 35(9): 1032-1035. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LSBL201909007.htm [10] JIANG L, YANG H, CHEN T B, et al. Identification of HMG-box family establishes the significance of SOX6 in the malignant progression of glioblastoma[J]. Aging(Albany NY), 2020, 12(9): 8084-8106. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/341282355_Identification_of_HMG-box_family_establishes_the_significance_of_SOX6_in_the_malignant_progression_of_glioblastoma [11] 巨虎, 肖宗宇, 张广华, 等. SOX6基因对H2O2诱导的星形胶质细胞损伤的机制[J]. 中国比较医学杂志, 2020, 30(1): 88-93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7856.2020.01.014 [12] 刘恩令, 周玉秀, 王立群, 等. 过表达SOX6基因对卵巢癌SKOV3细胞增殖、凋亡的影响及其机制[J]. 山东医药, 2018, 58(20): 39-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2018.20.012 [13] JIANG W L, YUAN Q Y, JIANG Y Y, et al. Identification of Sox6 as a regulator of pancreatic cancer development[J]. Cell Mol Med, 2018, 22(3): 1864-1872. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13470 [14] CHEN L Y, XIE Y P, MA X, et al. SOX6 represses tumor growth of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by HMG domain-dependent regulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling[J]. Mol Carcinog, 2020, 59(10): 1159-1173. doi: 10.1002/mc.23246 [15] ZHOU C G, HU C, WANG B, et al. Curcumin suppresses cell proliferation, migration, and invasion through modulating miR-21-5p/SOX6 axis in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Biother Radiopharm, 2020, 10: 1089. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/343496822_Curcumin_Suppresses_Cell_Proliferation_Migration_and_Invasion_Through_Modulating_miR-21-5p_SOX6_Axis_in_Hepatocellular_Carcinoma [16] 付真睿, 盛飞, 张昌文, 等. SOX6在膀胱癌发生发展中的作用及相关机制[J]. 天津医科大学学报, 2019, 25(4): 373-377. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJYK201904016.htm [17] CHEN Y, SONG Y, MI Y, et al. microRNA-499a promotes the progression and chemoresistance of cervical cancer cells by targeting SOX6[J]. Apoptosis, 2020, 25(3-4): 205-216. doi: 10.1007/s10495-019-01588-y [18] 黄伟钊, 吴颖猛, 胡荣贵, 等. 食管癌组织中miR-1269a、SOX6的表达变化及意义[J]. 山东医药, 2020, 60(19): 9-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYY202019003.htm -





 下载:
下载: