Exploration of internal medicine education system with community characteristics
-
摘要:
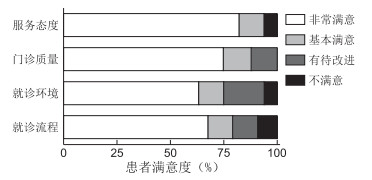
目的 以常见慢性病糖尿病为载体建立起有社区特色的内科学教育体系,来强化和提高社区全科医生在内分泌代谢病等慢性病方面的诊治水平,提高糖尿病患者的治疗达标率。 方法 2018年2月—2019年1月,针对社区全科医师实际需求,上海市虹口区2家三级甲等医院内分泌代谢科医师作为导师对辖区内8家社区卫生服务中心开展有社区特色的内科学教育,通过内分泌代谢科专科医师面向社区全科医师进行理论授课;学以致用,导师对糖尿病防治骨干全科医师进行临床带教;年度培训考核,患者满意度调查,建立教育体系,分析成效;区卫生和计划生育委员会“公共卫生与妇幼保健科”协同社区分管部门进行院际协调、工作监督,以确保工作顺利开展。 结果 1年期间12位内分泌专科医师共进行了96场讲座,培训社区医护约3 000余人次。8家社区“糖尿病专病门诊”从“无”到“有”,其中9位导师分别与各社区糖尿病防治骨干全科医师对接共同坐诊,受到患者好评,患者的建议聚焦在希望增加专病门诊次数,频率由1次/月增加至1次/1~2周,以及提高向三甲医院的转诊效率。参加理论授课的220位社区全科医师全部考核通过(85.01±3.86)分,其中参加临床带教的16名糖尿病防治骨干全科医师成绩优异(87.25±3.72)分。 结论 建立有社区特色的内科学教育体系,尤其对糖尿病防治骨干全科医师的培养,明显提高了社区对糖尿病及其并发症、合并症的规范化诊疗水平,有较高社区使用价值。将进一步提升带教内涵及质量,完善考勤、考核机制。 Abstract:Objective Medical education with community characteristics is established by taking diabetes mellitus as the carrier of common chronic diseases, so as to strengthen and improve the community's diagnosis and treatment of chronic diseases. Methods From February 2018 to January 2019, according to the actual needs of community general practitioners of 8 community health service centers, endocrinologists of two Class A tertiary hospitals in Hongkou District of Shanghai carried out theoretical lecturing for the general practitioners. Tutors gave the key general practitioners clinical teaching. Annual training assessment, patient satisfaction survey, education system establishment and effect analysis were carried out. The "public health and maternal and child health section" of the District Health and Family Planning Commission cooperated with the community departments in charge to carry out inter hospital coordination and work supervision, so as to ensure the development of the work. Results During one year, 12 endocrinologists gave 96 lectures and trained more than 3 000 medical staff of community. The community diabetes clinic of 8 community health service centers went from "none" to "yes", 9 tutors and key general practitioners for diabetes prevention and treatment visited together and were praised by the patients; patients' suggestions focus on increasing the frequency from once per month to once or twice per week, improving the efficiency of referral to Class A tertiary hospital. All community general practitioners passed the assessment (85.01±3.86), among which 16 key general practitioners for diabetes prevention and treatment had excellent performance (87.25±3.72), there was difference between groups (P=0.028). Conclusion The establishment of community characteristic internal medicine education in the community, especially the tutorial system for the cultivation of key general practitioners for diabetes prevention and treatment, obviously improve the standard diagnosis and treatment level of diabetes (including complications and complications) in the community, which has a high community value-in-use. Further improving the connotation and quality of teaching and improve the attendance and assessment mechanism, then twice as much can be accomplished with half the effort. -
Key words:
- Community general practitioners /
- Tutor teaching /
- Education system
-
表 1 理论培训课程——糖尿病系列讲座
培训课程 讲座题目 培训
频次考核
类型糖尿病的血糖管理 糖尿病血糖的监测与管理 8 问答题 特殊人群的血糖管理 8 问答题 高血糖的危害及治疗 8 问答题 糖尿病急性并发症的管理 糖尿病酮症酸中毒 8 问答题 糖尿病慢性并发症的管理 糖尿病肾病防治 8 问答题 糖尿病足基层筛查培训 8 问答题 糖尿病周围神经病变的筛查、诊断与治疗 8 问答题 糖尿病心血管疾病的防治 8 问答题 糖尿病合并症的管理 糖尿病患者高尿酸血症的防治 8 问答题 糖尿病患者血压管理 8 问答题 糖尿病患者的血脂管理 8 问答题 糖尿病与骨质疏松 8 问答题 -
[1] OGURTSOVA K, DA ROCHA FERNANDES J D, HUANG Y, et al. IDF diabetes atlas: global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2017, 128: 40-50. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2017.03.024 [2] WANG L, GAO P, ZHANG M, et al. Prevalence and ethnic pattern of diabetes and prediabetes in China in 2013[J]. JAMA, 2017, 317(24): 2515-2523. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.7596 [3] 中华医学会糖尿病学分会. 中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2017年版)[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志, 2018, 10(1): 4-67. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-5809.2018.01.003 [4] 宁光. 中国糖尿病防治的现状及展望[J]. 中国科学: 生命科学, 2018, 48(8): 810-811. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JCXK201808002.htm [5] 王卫庆, 王桂侠, 王颜刚, 等. 国家标准化代谢性疾病管理中心建设规范及管理指南[J]. 中华内分泌代谢杂志, 2019, 35(11): 907-908, 926. [6] 国务院. 全国医疗卫生服务体系规划纲要(2015-2020年)[Z]. (2015-03-30)[2020-02-01]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2015-03/30/content_9560.htm. [7] 国务院办公厅. 国务院办公厅关于推进分级诊疗制度建设的指导意见[Z]. (2015-09-11)[2020-02-01]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2015-09/11/content_10158.htm. [8] 唐立健, 李欣怡, 乜金茹. 分级诊疗制度下居民就诊意向及相关因素分析[J]. 现代医药卫生, 2020, 36(2): 195-197, 202. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5519.2020.02.011 [9] 高琴, 杨丽霞, 罗秀琼, 等. 分级诊疗的现状与思考[J]. 现代医药卫生, 2018, 34(8): 1273-1274. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5519.2018.08.056 [10] 教育部, 民政部, 科技部, 等. 教育部等九部门关于进一步推进社区教育发展的意见[Z]. (2016-07-08)[2020-02-01]. http://www.moe.gov.cn/srcsite/A07/zcs_cxsh/201607/t20160725_272872.html. [11] 蔡淳, 程旻娜, 贾伟平. 糖尿病分级诊疗和全程健康管理服务的策略与实践[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志, 2018, 10(12): 765-768. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-5809.2018.12.002 [12] 杨森, 王朝昕, 金花, 等. 基于利益相关者的上海市分级诊疗现状系统评价[J]. 中国全科医学, 2018, 21(22): 2672-2678. doi: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2018.22.006 [13] 戴慧敏, 刘伟, 吴培红, 等. 2型糖尿病"全科-专科"分级诊疗协作管理模式及开展现状研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2018, 21(10): 1188-1192. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2018.10.009 [14] 张丹. 我国糖尿病教育的现状及存在的问题[J]. 现代医学与健康研究电子杂志, 2018, 2(22): 109-110. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYJD201822050.htm [15] 马玉春. 健康教育对社区慢性病患者知识及行为的影响研究[J]. 河北医学, 2016, 22(9): 1583-1584. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6233.2016.09.079 -





 下载:
下载: