Mangiferin relieves Staphylococcus aureus-induced pneumonia by inhibiting the NF-κB signalling pathway
-
摘要:
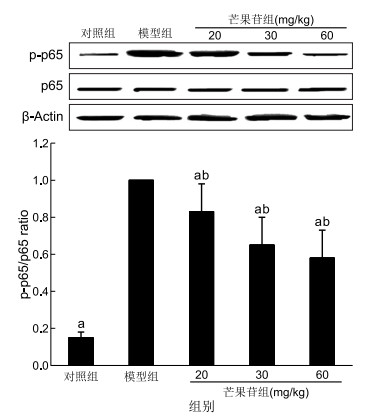
目的 探究芒果苷对金黄色葡萄球菌诱导的肺炎的影响及对NF-κB信号通路的作用。 方法 将50只Balb/c雄性小鼠采用随机数字法分为5组,每组10只:分别为对照组、金黄色葡萄球菌组、芒果苷(15、30、60 mg/kg)组。金黄色葡萄球菌诱导造模1 h后,芒果苷组给予腹腔注射芒果苷。12 h后,收集各组肺泡灌洗液、小鼠肺组织。测定各组肺泡灌洗液TNF-α和IL-1β水平,各组肺组织湿干比(W/D)和肺髓过氧化物酶(MPO)活性,肺组织p65水平。 结果 相比于模型组,低、中、高剂量芒果苷能有效降低TNF-α、IL-1β、W/D、MPO水平(均P < 0.05),并呈计量依赖性。高剂量组TNF-α、IL-1β、W/D、MPO分别为(3.25±0.52)ng/mL、(3.53±0.65)ng/mL、7.16±0.34、(3.15±0.61)U/g,显著低于模型组的(5.28±0.93)ng/mL、(6.63±0.85)ng/mL、10.55±0.92、(6.74±0.85)U/g(t=6.025,P < 0.001;t=9.161,P < 0.001;t=10.930,P < 0.001;t=10.850,P < 0.001)。机理研究显示芒果苷可有效下调金黄色葡萄球菌诱导的p-p65。 结论 芒果苷可通过抑制NF-κB信号通路改善金黄色葡萄球菌诱导的小鼠肺炎。 Abstract:Objective This study aimed to investigate the effect of mangiferin on Staphylococcus aureus-induced pneumonia and on the NF-κB signalling pathway. Methods Fifty Balb/c male mice were randomly divided into five groups by the random number method, with 10 mice in each group: control group, S. aureus group and mangiferin (15, 30 and 60 mg/kg) group. After 1 h of S. aureus-induced modelling, the mangiferin group was given intraperitoneal injection of mangiferin. After 12 h, the alveolar lavage fluid and lung tissues of each group were collected. The TNF-α and IL-1β levels of alveolar lavage fluid, wet-to-dry ratio (W/D), activity of pulmonary myeloperoxidase (MPO) and the p65 level of lung tissue were measured. Results Compared with the model group, low, middle and high dose of mangiferin could effectively reduce TNF-α, IL-1β, W/D and MPO in a quantitative manner (all P < 0.05). The TNF-α, IL-1β, W/D and MPO of the high-dose mangiferin group were (3.25±0.52) ng/mL, (3.53±0.65) ng/mL, 7.16±0.34 and (3.15±0.61) U/g, respectively, which were significantly lower than those of the model group[(5.28±0.93) ng/mL, (6.63±0.85) ng/mL, 10.55±0.92, (6.74±0.85) U/g, t=6.025, P < 0.001; t=9.161, P < 0.001; t=10.930, P < 0.001; t=10.850, P < 0.001]. Mechanism research showed that mangiferin could effectively down-regulate p-p65 induced by S. aureus. Conclusion Mangiferin could improve S. aureus-induced pneumonia in mice by inhibiting the NF-κB signalling pathway. -
Key words:
- Mangiferin /
- Pneumonia /
- Staphylococcus aureus /
- Pulmonary myeloperoxidase /
- Nuclear factor-κB
-
表 1 各组小鼠TNF-α和IL-1β比较(x ±s, ng/mL)
组别 只数 TNF-α 1L-1β 对照组 10 0.22±0.07a 0.12±0.03a 模型组 10 5.28±0.93 6.63±0.85 芒果苷低剂量 10 4.10±0.87ab 5.12±0.93ab 芒果苷中剂量 10 3.81±0.72ab 4.13±0.72ab 芒果苷高剂量 10 3.25±0.52ab 3.53±0.65ab F值 74.020 115.700 P值 < 0.001 < 0.001 注:与模型组比较,aP < 0.05;与对照组比较,bP < 0.05。 表 2 各组小鼠W/D比较(x ±s)
组别 只数 W/D 对照组 10 5.51±0.54a 模型组 10 10.55±0.92 芒果苷低剂量 10 8.72±0.83ab 芒果苷中剂量 10 7.53±0.72ab 芒果苷高剂量 10 7.16±0.34ab F值 71.580 P值 < 0.001 注:与模型组比较,aP < 0.05;与对照组比较,bP < 0.05。 表 3 各组小鼠MPO比较(x ±s, U/g)
组别 只数 MPO 对照组 10 0.32±0.05a 模型组 10 6.74±0.85 芒果苷低剂量 10 5.33±0.93ab 芒果苷中剂量 10 3.74±0.52ab 芒果苷高剂量 10 3.15±0.61ab F值 132.300 P值 < 0.001 注:与模型组比较,aP < 0.05;与对照组比较,bP < 0.05。 -
[1] 陈丹, 齐颖. 乳果糖联合益生菌对老年重症肺炎患者肠道微生态的影响[J]. 中华全科医学, 2019, 17(4): 666-669. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYQY201904040.htm [2] 肖燕燕, 李建宁, 蒋雪梅. 超声在常见肺部疾病诊断中的应用[J]. 中国中西医结合影像学杂志, 2020, 18(3): 316-320. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0512.2020.03.030 [3] 黄佳伟, 鲁娴娴, 崔海燕, 等. PM2.5通过NF-κB/NLRP3途径促进金黄色葡萄球菌肺炎的研究[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2019, 14(5): 133-143. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STDL201905012.htm [4] GAO H, KANG N, HU C, et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 exerts anti-inflammatory effects in vitro and in vivo by modulating toll-like receptor 4 dimerization and NF-kB/MAPKs signaling pathways[J]. Phytomedicine, 2020, 69: 153197. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153197 [5] 李刚, 余朝萍, 龚厚文, 等. 芒果苷减轻缺氧复氧所致人心肌细胞损伤[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2020, 36(4): 657-662. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4718.2020.04.011 [6] 王豕辰, 徐珺, 董恒, 等. 芒果苷抑制金黄色葡萄球菌诱导的细胞凋亡[J]. 北京农学院学报, 2020, 35(2): 39-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BNXB202002010.htm [7] 王明宇, 陈瑞家. 芒果苷通过下调热休克蛋白90表达抑制肝癌HepG2细胞增殖研究[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志, 2019, 35(23): 3052-3055. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLYZ201923030.htm [8] 陈星, 夏晓冬, 童德银, 等. 芒果苷改善肝损伤模型小鼠肝功能实验研究[J]. 中国药业, 2019, 28(10): 17-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4931.2019.10.006 [9] 郭伟, 张同强, 徐勇胜. 肺炎支原体肺炎患儿TNF-α、IFN-γ和IL-4细胞因子水平的变化[J]. 中国现代医学杂志, 2018, 28(23): 65-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8982.2018.23.014 [10] 韩小胜, 黄会, 魏小斌. 重症肺炎链球菌感染患儿血清TNF-α、IL-1β、IL-6的表达水平及意义[J]. 国际检验医学杂志, 2018, 39(9): 1068-1070, 1073. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4130.2018.09.013 [11] 刘钢, 李然然, 李萍萍, 等. 炎症因子在大叶性肺炎患儿支气管肺泡灌洗液及血清中的表达及临床意义[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2017, 17(20): 3917-3920. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWCX201720028.htm [12] 李帅, 方磊, 王炯, 等. 金黄色葡萄球菌通过TLR2/PI3K信号诱导巨噬细胞的炎症反应和自噬[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2017, 33(9): 1160-1164. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBFM201709002.htm [13] VANHECKE C, GIRERD R, DUJARDIN M, et al. Retrospective study of pneumonia due to Panton-Valentine leukocidin-producing Staphylococcus aureus in Reunion[J]. Med Mal Infect, 2019, 49(7): 534-539. doi: 10.1016/j.medmal.2019.01.010 [14] 胡正权, 孙欣娜, 杨青. microRNA 20a通过核因子-κB信号通路影响肺炎模型幼鼠炎症水平的机制研究[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志, 2020, 19(8): 815-819. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2020.08.009 [15] ESPIN I M, AGUILERA-ALONSO D, GARCIA-PEREA A, et al. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus community-acquired pneumonia in infants[J]. Enferm Infec Micrcl Clin, 2019, 37(8): 551-552. doi: 10.1016/j.eimc.2018.11.005 -





 下载:
下载: