Application of serum albumin, globulin and creatinine in predicting the severity of Guillain-Barré syndrome
-
摘要:
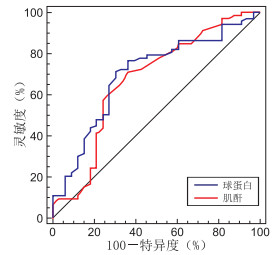
目的 探讨应用血清白蛋白、球蛋白及肌酐水平预测吉兰-巴雷综合征(Guillain-Barré syndrome,GBS)的严重程度。 方法 选取2016年6月—2020年5月蚌埠医学院第一附属医院神经内科收治的吉兰-巴雷综合征患者106例,采用Hughes功能评分,同时选取健康受试者150名,比较2组间白蛋白、球蛋白、肌酐的差异。采用Spearman相关性分析对白蛋白、球蛋白及肌酐水平与GBS患者疾病严重程度的相关性进行分析。选取与疾病严重程度相关的球蛋白与肌酐,并利用ROC曲线进行分析。 结果 GBS患者血清白蛋白(40.12±4.43)g/L和肌酐(63.47±11.64)μmol/L水平低于健康对照组[(47.42±4.14)g/L;(83.96±31.00)μmol/L,均P < 0.05];而球蛋白(29.94±5.68)g/L水平高于健康对照组[(24.58±6.17)g/L,P < 0.05];GBS患者球蛋白和肌酐水平与疾病严重程度有一定相关性(r=0.353,P < 0.001;r=-0.323,P=0.001)。受试者工作曲线(ROC)显示球蛋白预测GBS重症组的曲线下面积为0.699(95% CI:0.602~0.784)。肌酐预测GBS重症组的曲线下面积为0.671(95% CI:0.573~0.760)。 结论 GBS患者球蛋白水平与疾病严重程度呈正相关,肌酐水平与疾病严重程度呈负相关。球蛋白和肌酐对评估GBS严重程度有一定的价值。 Abstract:Objective To explore the application of serum albumin, globulin and creatinine to predict the severity of Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS). Methods A total of 106 patients with GBS treated in the Department of Neurology, the first affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College from June 2016 to May 2020 were selected. Hughes functional score was used to compare the differences of albumin, globulin and creatinine between the two groups. Spearman correlation analysis was used to analyze the correlation between the levels of albumin, globulin, creatinine and the severity of disease in patients with GBS. The globulin and creatinine related to the severity of the disease were selected and analyzed by ROC curve. Results The levels of serum albumin (40.12±4.43) g/L and creatinine (63.47±11.64) μmol/L in GBS patients were lower than those in healthy controls [(47.42±4.14) g/L, (83.96±31.00) μmol/L, all P < 0.05], while the levels of globulin (29.94±5.68) g/L were higher than those in healthy controls (24.58±6.17) g/L, P < 0.05. The levels of globulin and creatinine in patients with GBS were correlated with the severity of the disease (r=0.353, P < 0.001; r=0.323, P < 0.001). The ROC curve showed that the area under the curve of globulin predicting GBS severe group was 0.699 (95% CI: 0.602-0.784). The area under the curve predicted by creatinine in GBS severe group was 0.671 (95% CI: 0.573-0.760). Conclusion The level of globulin in patients with GBS is positively correlated with the severity of the disease, while the level of creatinine is negatively correlated with the severity of the disease. Globulin and creatinine have certain value in evaluating the severity of GBS. -
Key words:
- Albumin /
- Globulin /
- Creatinine /
- Guillain-Barré syndrome
-
表 1 GBS患者和健康对照组基线资料比较(x ±s)
组别 例数 年龄(岁) 性别(男/女,例) 白蛋白(g/L) 球蛋白(g/L) 肌酐(μmol/L) 尿素氮[M(P25,P75),mmol/L] 总胆红素(μmol/L) ALT(U/L) AST [M(P25,P75),U/L] GBS组 106 53.84±19.39 72/34 40.12±4.43 29.94±5.68 63.47±11.64 5.32(4.30,6.80) 12.78±5.44 35.80±39.51 24.00(20.00, 34.00) 对照组 150 53.59±19.29 97/53 47.42±4.14 24.58±6.17 83.96±31.00 5.33(4.27,6.65) 12.47±3.30 33.67±14.62 31.70(17.09, 40.69) 统计量 -0.171a 2.000b 13.501a 7.080a -6.490a -0.624c -0.563a -0.606a -1.119c P值 0.872 0.157 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 0.533 0.574 0.545 0.263 注:a为t值,b为χ2值,c为Z值。 表 2 GBS患者实验室指标与疾病严重程度的相关性分析
项目 r值 P值 白蛋白 -0.178 0.068 球蛋白 0.353 < 0.001 肌酐 -0.323 0.001 尿素氮 0.016 0.874 总胆红素 0.029 0.771 ALT 0.028 0.773 AST -0.012 0.904 表 3 GBS患者Hughes功能评分与临床特征间的多元线性回归分析结果
变量 B SE β t值 P值 常量 3.893 2.047 1.902 0.600 性别 0.001 0.288 <0.001 0.002 0.998 年龄 0.003 0.007 0.038 0.372 0.711 白蛋白 -0.027 0.032 -0.088 -0.839 0.403 球蛋白 0.075 0.023 0.315 3.313 0.001 肌酐 -0.035 0.011 -0.300 -3.099 0.003 尿素氮 -0.033 0.024 -0.122 -1.342 0.183 总胆红素 0.018 0.024 0.072 0.739 0.462 ALT -0.007 0.006 -0.208 -1.289 0.201 AST 0.009 0.008 0.185 1.137 0.258 注:性别按照男为0,女为1赋值,其他以实际数据赋值,因变量以Hughes评分赋值。 -
[1] ZHANG X, ZHANG H, LIU Z, et al. Inferring immune-associated signatures based on a co-expression network in Guillain-Barré Syndrome[J]. Cell Prolif, 2019, 52(4): e12634. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12634 [2] 中华医学会神经病学分会, 中华医学会神经病学分会周围神经病协作组, 中华医学会神经病学分会肌电图及临床神经电生理学组, 等. 中国吉兰-巴雷综合征诊治指南2019[J]. 中华神经科杂志, 2019, 52(11): 877-882. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1006-7876.2019.11.002 [3] TUNC A. Early predictors of functional disability in Guillain-Barré Syndrome[J]. Acta Neurol Belg, 2019, 119(4): 555-559. doi: 10.1007/s13760-019-01133-3 [4] 李瑞香, 张伟娜, 沈霞, 等. 基于单中心的重症吉兰-巴雷综合征预测因素分析[J]. 中国临床医学, 2019, 26(2): 252-255. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCYX201902021.htm [5] JASTI AK, SELMI C, SARMIENTO-MONROY J C, et al. Guillain-Barré Syndrome: causes, immunopathogenic mechanisms and treatment[J]. Expert Rev Clin Immunol, 2016, 12(11): 1175-1189. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2016.1193006 [6] ANTIER J L, DURETZ V, DEVOS V, et al. Comparison of antioxidant properties of different therapeutic albumin preparations[J]. Biologicals, 2016, 44(4): 226-233. doi: 10.1016/j.biologicals.2016.04.002 [7] 姚绍莉, 陈虹西, 张勤, 等. 吉兰-巴雷综合征患者血清尿酸和白蛋白及β羟基丁酸水平与疾病严重程度的关系[J]. 中国神经免疫学和神经病学杂志, 2019, 26(1): 12-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2963.2019.01.003 [8] SU Z, CHEN Z, XIANG Y, et al. Low serum levels of uric acid and albumin in patients with Guillain-Barre Syndrome[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2017, 96(15): e6618. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006618 [9] LEVINE S M. Albumin and multiple sclerosis[J]. BMC Neurol, 2016, 16: 47. doi: 10.1186/s12883-016-0564-9 [10] FUJIHARA R, CHIBA Y, NAKAGAWA T, et al. Albumin microvascular leakage in brains with diabetes mellitus[J]. Microsc Res Tech, 2016, 79(9): 833-837. doi: 10.1002/jemt.22708 [11] ZHOU Q, CAO H, XU Z, et al. Baseline serum globulin as a predictor of the recurrence of lone atrial fibrillation after radiofrequency catheter ablation[J]. Anatol J Cardiol, 2017, 17(5): 381-385. [12] LIU J, LIAN Z, CHEN H, et al. Associations between tumor necrosis factor-α gene polymorphisms and the risk of Guillain-Barré Syndrome and its subtypes: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Neuroimmunol, 2017, 313: 25-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2017.10.003 [13] LI K, FU W, BO Y, et al. Effect of albumin-globulin score and albumin to globulin ratio on survival in patients with heart failure: a retrospective cohort study in China[J]. BMJ Open, 2018, 8(7): e022960. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-022960 [14] YOSHINO Y, TAGUCHI A, SIMIZUGUCHI T, et al. A low albumin to globulin ratio with a high serum globulin level is a prognostic marker for poor survival in cervical cancer patients treated with radiation based therapy[J]. Int J Gynecol Cancer, 2019, 29(1): 17-22. doi: 10.1136/ijgc-2018-000025 [15] WALLIMANN T, RIEK U, MUDDEL M. Intradialytic creatine supplementation: A scientific rationale for improving the health and quality of life of dialysis patients[J]. Med Hypotheses, 2017, 99: 1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2016.12.002 [16] RIESBERG L A, MCDONALD T L, WANG Y, et al. Creatinine downregulates TNF-αin macrophage and T cell lines[J]. Cytokine, 2018, 110: 29-38. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2018.04.021 [17] TAN X, ZHU H, TAO Q, et al. FGF10 protects against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating autophagy and inflammatory signaling[J]. Front Genet, 2018, 9: 556. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00556 [18] SESTILI P, AMBROGINI P, BARBIER E, et al. New insights into the trophic and cytoprotective effects of creatine in in vitro and in vivo models of cell maturation[J]. Amino Acids, 2016, 48(8): 1897-911. doi: 10.1007/s00726-015-2161-4 [19] MUMTAZ A, ZAHOOR F, ZAIB S, et al. Synthesis, characterization and biological activities of creatinine amides and creatinine schiff bases[J]. Med Chem, 2017, 13(2): 196-203. doi: 10.2174/1573406412666160805100313 [20] MARTINEZ Y, LI X, LIU G, et al. The role of methionine on metabolism, oxidative stress, and diseases[J]. Amino Acids, 2017, 49(12): 2091-2098. doi: 10.1007/s00726-017-2494-2 -





 下载:
下载: