Expression of B cell activating factor and interleukin-21 in the plasma of patients with Hashimoto's thyroiditis
-
摘要:
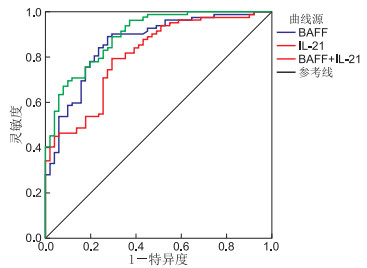
目的 检测桥本甲状腺炎(hashimoto thyroiditis,HT)患者和健康体检者血浆中B细胞活化因子(B-cell activating factor, BAFF)和白介素21(IL-21)表达水平,探讨二者在HT发病机制中的作用。 方法 选取2019年12月—2020年6月蚌埠医学院第一附属医院内分泌门诊就诊HT患者82例作为观察组(HT组), 并根据甲状腺功能将HT组分成NHT组(甲状腺功能正常,39例)和SHT组(甲状腺功能减退或亚临床甲减,43例),选取同期健康体检者51例作为对照组(NC组)。收集受试者外周静脉血血浆,酶联免疫吸附实验(ELISA)检测研究对象血浆BAFF、IL-21,化学发光免疫法检测甲状腺功能及相关抗体等指标。使用SPSS 24.0统计学软件对数据进行详细分析。 结果 HT组患者血浆中BAFF、IL-21表达水平较NC组明显上调(均P < 0.05)。HT患者血浆中BAFF与甲状腺球蛋白抗体(TgAb)、甲状腺微粒体抗体(TMAb)水平呈正相关(r=0.444、0.401,均P < 0.05),IL-21与TgAb、TMAb水平呈正相关(r=0.451、0.451,均P < 0.05),BAFF与IL-21呈正相关(r=0.324,P < 0.05),BAFF与总甲状腺素(TT4)呈负相关(r=-0.214,P < 0.05)。BAFF和IL-21(AUC=0.896)联合诊断HT较BAFF(AUC=0.862)、IL-21(AUC=0.809)单独诊断价值更高。 结论 BAFF与IL-21水平与HT病变有关,与TgAb、TMAb水平密切相关,可能参与HT的发生发展过程。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the expression of human B cell activating factor (BAFF) and interleukin-21 (IL-21) in the plasma of patients with Hashimoto's thyroiditis (HT) and explore their roles in the pathogenesis of HT. Methods Patients with HT in the Endocrinology Clinic of The First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College from December 2019 to June 2020 were selected as the observation group (HT group, n= 82). According to thyroid functions, the HT group was further divided into an NHT group (normal thyroid function, n= 39) and an SHT group (hypothyroidism or subclinical hypothyroidism, n=43). A total of 51 patients (NC group) who visited the hospital for consultation during the same period were designated as the control group. Peripheral venous blood plasma was collected. BAFF and IL-21 were tested via enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay(ELISA). Thyroid function, thyroid microsomal antibody (TMAB) and thyroglobulin antibody (TGAB) were detected via chemiluminescence immunoassay. Data were analysed using SPSS 24.0. Results The levels of BAFF and IL-21 in the plasma of the HT group were significantly higher than those of the NC group (all P < 0.05). The levels of BAFF in the SHT group was significantly higher than that in the NHT group (P < 0.05). The plasma levels of BAFF in the patients with HT were positively correlated with TGAB and TMAB (r=0.444 and 0.401, respectively; all P < 0.05). Similarly, IL-21 was positively correlated with TGAB and TMAB (r=0.451 and 0.451, respectively; all P < 0.05). A positive correlation was observed between BAFF and IL-21 (r=0.324, P < 0.05). By contrast, a negative correlation was found between BAFF and total T4(TT4, r=-0.214, P < 0.05). The combined diagnosis of HT with BAFF and IL-21 (AUC=0.896) was more valuable than that of BAFF (AUC=0.862) and IL-21 (AUC=0.809) alone. Conclusion BAFF combined with IL-21 has a certain value in the diagnosis of HT. BAFF and IL-21 play an important role in the occurrence and development of HT. Moreover, they participate in the maturation, proliferation and differentiation of B cells. Finally, they participate jointly in the production of TGAB and TMAR. -
表 1 各组研究对象一般情况比较(x ±s)
组别 例数 年龄(岁) 性别(男/女,例) BMI NHT亚组 39 39.15±11.41 2/37 21.86±1.81 SHT亚组 43 41.65±9.56 4/39 22.59±2.28 NC组 51 42.08±6.10 2/49 22.54±1.62 统计量 1.279a 1.216b 1.892a P值 0.282 0.544 0.155 注: a为F值,b为χ2值。 表 2 各组研究对象甲状腺功能及抗体比较(x ±s)
组别 例数 TT3(nmol/L) TT4(nmol/L) TSH(mIU/L) TgAb(%) TMAb(%) NC组 51 1.40±0.23 87.39±16.71 2.06±1.01 5.92±4.12 5.53±3.15 NHT亚组 39 1.49±0.57 85.65±20.96 2.21±1.14 48.52±12.89a 32.66±9.58a SHT亚组 43 1.30±0.40 62.22±25.97ab 22.61±31.78ab 50.14±11.85a 33.36±7.65a F值 2.195 19.194 18.671 259.770 239.993 P值 0.115 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 注:与NC组比较,aP < 0.05;与NHT组比较,bP < 0.05。 表 3 各组研究对象BAFF、IL-21水平比较(x ±s, pg/mL)
组别 例数 BAFF IL-21 NC组 51 82.55±14.13 762.93±441.12 NHT亚组 39 118.64±31.84a 1 497.70±960.02a SHT亚组 43 105.07±19.56ab 1 741.97±767.47a F值 30.364 23.040 P值 < 0.001 < 0.001 注:与NC组比较,aP < 0.05;与NHT组比较,bP < 0.05。 表 4 血浆中BAFF、IL21、TgAb、TMAb之间的相关分析
项目 BAFF IL-21 r值 P值 r值 P值 BAFF 0.324 < 0.001 IL-21 0.324 <0.001 TgAb 0.444 <0.001 0.451 <0.001 TMAb 0.401 <0.001 0.451 <0.001 TT3 0.013 0.884 0.001 0.988 TT4 -0.214 0.014 -0.124 0.154 TSH 0.090 0.301 0.065 0.458 表 5 BAFF和IL-21诊断效能评价
项目 AUC 标准误 P值 95% CI 敏感度(%) 特异度(%) 约登指数 BAFF 0.862 0.033 < 0.001 0.798~0.962 0.890 0.725 0.616 IL-21 0.809 0.038 < 0.001 0.735~0.883 0.793 0.706 0.499 BAFF+IL-21联合 0.896 0.027 < 0.001 0.844~0.948 0.695 0.902 0.597 -
[1] 方露, 朱武飞, 廖翔宇, 等. 桥本氏甲状腺炎患者年龄、性别分布及自身免疫抗体水平分析[J]. 微循环学杂志, 2020, 30(1): 69-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-1740.2020.01.015 [2] 王薇, 卢桂芝, 高燕明, 等. 甲状腺针吸细胞学检查的不同年龄段患者临床特点分析[J]. 中华全科医学, 2019, 17(5): 738-741. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYQY201905010.htm [3] LUTY J, RUCKEMANN-DZIURDZINSKA K, WITKOWSKI J M, et al. Immunological aspects of autoimmune thyroid disease-Complex interplay between cells and cytokines[J]. Cytokine, 2019, 116: 128-133. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2019.01.003 [4] 詹玲, 陈创, 孙圣荣. 免疫微环境在桥本甲状腺炎与甲状腺癌中作用研究进展[J]. 中华实用诊断与治疗杂志, 2020, 34(6): 640-642. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNZD202006027.htm [5] ROBINSON M J, PITT C, BRODIE E J, et al. BAFF, IL-4 and IL-21 separably program germinal center-like phenotype acquisition, BCL6 expression, proliferation and survival of CD40L-activated B cells in vitro[J]. Immunol Cell Biol, 2019, 97(9): 826-839. doi: 10.1111/imcb.12283 [6] ZHAO R Q, ZHANG H H, ZHANG Y, et al. In vivo screen identifies Zdhhc2 as a critical regulator of germinal center B cell differentiation[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 1025. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01025 [7] NAKAYAMA Y, KOSEK J, CAPONE L, et al. Aiolos overexpression in systemic lupus erythematosus B Cell subtypes and BAFF-induced memory B cell differentiation are reduced by CC-220 modulation of cereblon activity[J]. J Immunol, 2017, 199(7): 2388-2407. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601725 [8] GHARIBI T, HOSSEINI A, MAROFI F, et al. IL-21 and IL-21-producing T cells are involved in multiple sclerosis severity and progression[J]. Immunol Lett, 2019, 216: 12-20. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2019.09.003 [9] DINESH P, RASOOL M. Multifaceted role of IL-21 in rheumatoid arthritis: Current understanding and future perspectives[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2018, 233(5): 3918-3928. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26158 [10] ZHOU H, HU B, ZHAOPENG Z, et al. Elevated circulating T cell subsets and cytokines expression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2019, 38(7): 1831-1839. doi: 10.1007/s10067-019-04465-w [11] GENSOUS N, SCHMITT N, RICHEZ C, et al. T follicular helper cells, interleukin-21 and systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Rheumatology(Oxford), 2017, 56(4): 516-523. [12] CHENG C W, TANG K T, FANG W F, et al. Synchronized expressions of serum osteopontin and B cell-activating factor in autoimmune thyroid disease[J]. Eur J Clin Invest, 2019, 49(7): e13122. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31034586 [13] CHENG C W, WU C Z, TANG K T, et al. Simultaneous measurement of twenty-nine circulating cytokines and growth factors in female patients with overt autoimmune thyroid diseases[J]. Autoimmunity, 2020, 53(5): 261-269. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2020.1755965 [14] FENG Y, QIU T, CHEN H, et al. Association of serum IL-21 and vitamin D concentrations in Chinese children with autoimmune thyroid disease[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2020, 507: 194-198. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2020.04.030 [15] RAMOS-LEVI A M, MARAZUELA M. Pathogenesis of thyroid autoimmune disease: the role of cellular mechanisms[J]. Endocrinol Nutr, 2016, 63(8): 421-429. doi: 10.1016/j.endonu.2016.04.003 [16] RYDZEWSKA M, JAROMIN M, PASIEROWSKA I E, et al. Role of the T and B lymphocytes in pathogenesis of autoimmune thyroid diseases[J]. Thyroid Res, 2018, 11: 2. doi: 10.1186/s13044-018-0046-9 [17] MAO J N, SHEN Y S, LUO X Y, et al. Expression of IL-21 in rats with inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Genet Mol Res, 2015, 14(4): 17322-17328. doi: 10.4238/2015.December.16.33 [18] CARRILLO-BALLESTEROS F J, PALAFOX-SANCHEZ C A, FRANCO-TOPETE R A, et al. Expression of BAFF and BAFF receptors in primary Sjogren's syndrome patients with ectopic germinal center-like structures[J]. Clin Exp Med, 2020, 20(4): 615-626. doi: 10.1007/s10238-020-00637-0 [19] VINCENT F B, KANDANE-RATHNAYAKE R, KOELMEYER R, et al. Associations of serum soluble Fas and Fas ligand (FasL) with outcomes in systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Lupus Sci Med, 2020, 7(1): e000375. doi: 10.1136/lupus-2019-000375 [20] CAMPI I, TOSI D, ROSSI S, et al. B Cell Activating Factor (BAFF) and BAFF receptor expression in autoimmune and nonautoimmune thyroid diseases[J]. Thyroid, 2015, 25(9): 1043-1049. doi: 10.1089/thy.2015.0029 [21] CHENG C W, WU C Z, TANG K T, et al. Simultaneous measurement of twenty-nine circulating cytokines and growth factors in female patients with overt autoimmune thyroid diseases[J]. Autoimmunity, 2020, 53(5): 261-269. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2020.1755965 -





 下载:
下载: