Application value of heparin binding protein in the early diagnosis of sepsis in children
-
摘要:
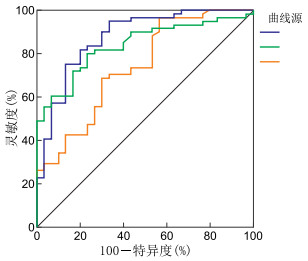
目的 研究肝素结合蛋白(heparin-binding protein, HBP)对早期诊断儿童脓毒症及病情评估的临床价值。 方法 选取2019年1月—2020年2月于蚌埠医学院第一附属医院住院治疗并诊断为脓毒症的患儿61例,根据患儿病情严重程度分为脓毒症组(35例)、严重脓毒症组(16例)以及脓毒性休克组(10例),同期因局部感染住院治疗的患儿(30例)设为局部感染组。比较各组患儿血清HBP、降钙素原(procalcitonin,PCT)、C反应蛋白(C-reactive protein,CRP)水平,对比分析各指标诊断脓毒症的诊断效能。 结果 4组患儿HBP、PCT、CRP组间总体比较差异均具有统计学意义(F=162.024、78.944、10.982,均P < 0.05);HBP水平分别为(19.74±15.20)μg/L、(34.79±14.08)μg/L、(57.42±14.63)μg/L、(191.20±53.28)μg/L,PCT水平分别为(1.33±1.07)ng/mL、(3.38±2.63)ng/mL、(9.93±6.65)ng/mL、(18.13±1.45)ng/mL,随病情加重而升高,差异均具有统计学意义(均P < 0.05);脓毒性休克组CRP[(79.47±18.94)mg/L]与严重脓毒症组[(73.60±26.22)mg/L]比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),其余各组CRP水平组间两两比较差异均具有统计学意义(均P < 0.05)。ROC曲线分析显示,3项指标联合检测诊断脓毒症时具有最大的曲线下面积(AUC=0.922),敏感度为72.13%,特异度为96.67%。 结论 血清HBP在儿童脓毒症诊断方面具有良好价值,3项指标联合检测诊断效能优于单一检测。 Abstract:Objective To examine the clinical value of heparin-binding protein (HBP) in the early diagnosis and evaluation of childhood sepsis. Methods Total 61 children with sepsis who were hospitalized in the First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College from January 2019 to February 2020 were selected and divided into sepsis group (35 cases), severe sepsis group (16 cases) and septic shock group (10 cases) according to the severity of the disease. Meanwhile, 30 children who were hospitalized due to local infection were set as local infection group. The levels of HBP, procalcitonin (PCT), and C-reactive protein (CRP) were compared per group, and the efficacy of each indicator in diagnosing sepsis was compared and analysed. Results The overall differences amongst the four groups were statistically significant (F=162.024, 78.944, 10.982, all P < 0.05). The levels of HBP were (19.74±15.2) μg/L, (34.79±14.08) μg/L, (57.42±14.63) μg/L, (191.20±53.28) μg/L; the levels of PCT were (1.33±1.07) ng/mL, (3.38±2.63) ng/mL, (9.93±6.65) ng/mL, (18.13±1.45) ng/mL, respectively, and increased with the aggravation of the disease (all P < 0.05). No statistically significant difference in CRP level existed between the septic shock group [(79.47±18.94) mg/L] and the severe sepsis group [(73.60±26.22) mg/L, P>0.05], and pausal differences between the other groups were statistically significant (all P < 0.05). ROC curve analysis showed that the maximum area under the curve (AUC) was 0.922, sensitivity was 72.13%, and specificity was 96.67% when the three indicators were combined to diagnose sepsis. Conclusion Serum HBP has good value in diagnosing childhood sepsis, and the combined detection of the three indices is better than single detection. -
Key words:
- Sepsis /
- Heparin-binding protein /
- Procalcitonin /
- Diagnosis /
- Children
-
表 1 各组患儿血清HBP、PCT、CRP水平比较(x±s)
组别 例数 HBP(μg/L) PCT(ng/mL) CRP(mg/L) 局部感染组 30 19.74±15.20 1.33±1.07 47.53±16.00 脓毒症组 35 34.79±14.08a 3.38±2.63a 57.59±16.85a 严重脓毒症组 16 57.42±14.63ab 9.93±6.65ab 73.60±26.22ab 脓毒性休克组 10 191.20±53.28abc 18.13±1.45abc 79.47±18.94ab F值 162.024 78.944 10.982 P值 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 注:与局部感染组比较,aP < 0.05;与脓毒症组比较,bP < 0.05;与严重脓毒症组比较,cP < 0.05。 表 2 HBP、PCT、CRP诊断脓毒症ROC曲线的参数比较
项目 AUC (95%CI) 约登指数 截断值 敏感度(%) 特异度(%) P值 HBP 0.878(0.792~0.937) 0.621 28.050 75.41 86.67 < 0.001 CRP 0.740(0.638~0.827) 0.401 39.610 96.70 43.30 < 0.001 PCT 0.841(0.749~0.909) 0.570 1.530 80.33 76.67 < 0.001 HBP+PCT 0.909(0.831~0.959) 0.701 0.455 93.44 76.67 < 0.001 HBP+CRP 0.898(0.817~0.951) 0.654 0.671 75.41 90.00 < 0.001 PCT+CRP 0.841(0.749~0.909) 0.570 0.502 80.33 76.77 < 0.001 HBP+PCT+CRP 0.922(0.846~0.968) 0.688 0.756 72.13 96.67 < 0.001 -
[1] WEISS S L, PETERS M J, ALHAZZANI W, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign international guidelines for the management of septic shock and sepsis-associated organ dysfunction in children[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2020, 46(12): 10-67. http://journals.lww.com/pccmjournal/Fulltext/2020/02000/Surviving_Sepsis_Campaign_International_Guidelines.20.aspx [2] DOWNES K J, FITZGERALD J C, WEISS S L. Utility of procalcitonin as a biomarker for sepsis in children[J]. J Clin Microbiol, 2020, 58(7): e01851. [3] FISHER J, LINDER A. Heparin-binding protein: a key player in the pathophysiology of organ dysfunction in sepsis[J]. J Intern Med, 2017, 281(6): 562-574. doi: 10.1111/joim.12604 [4] 王莹, 陆国平, 张育才. 儿童脓毒性休克(感染性休克)诊治专家共识(2015版)[J]. 中华儿科杂志, 2015, 53(8): 576-580. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1310.2015.08.007 [5] 余燕, 陈树强, 吴宝勤, 等. 血清降钙素原在门诊儿童感染性疾病诊断中的评价[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2018, 28(17): 2683-2685. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHYY201817036.htm [6] 许丽娇, 古旭东, 黄东平. 肝素结合蛋白与降钙素原在儿科重症感染中的诊断价值[J]. 齐齐哈尔医学院学报, 2017, 38(11): 1281-1282. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1256.2017.11.018 [7] HOLUB M, DŽUPOVÁO, RŪŽKOVÁ M, et al. Selected biomarkers correlate with the origin and severity of sepsis[J]. Mediators Inflammation, 2018: 1-11. DOI: 10.1155/2018/7028267. [8] 陆文峰, 张洁, 何兵, 等. 几种感染指标在儿童细菌性脓毒症的诊断价值[J]. 国际检验医学杂志, 2020, 41(1): 61-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4130.2020.01.016 [9] BROWN J, MEADER N, CLEMINSON J, et al. C-reactive protein for diagnosing late-onset infection in newborn infants[J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2019, 1(1): CD012126. [10] 洪开听, 王晔恺, 于倩, 等. 炎性因子在小儿脓毒症早期的临床对比初探[J]. 中华检验医学杂志, 2017, 40(4): 289-293. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-9158.2017.04.015 [11] 黄晓雯, 马力忠, 莫庆仪, 等. 降钙素原和C反应蛋白在小儿脓毒症早期诊断及判断病情严重程度中的价值[J]. 西部医学, 2017, 29(5): 627-631. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3511.2017.05.008 [12] NELSON J, HANSEN C, SCUPP T, et al. Implications of procalcitonin testing in critically ill patients with sepsis[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2019, 199(2): 232-234. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201712-2544RR [13] 中华医学会儿科学分会医院感染管理与控制专业委员会. 血清降钙素原检测在儿童感染性疾病中的临床应用专家共识[J]. 中华儿科杂志, 2019, 57(1): 9-15. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1310.2019.01.005 [14] 张瑾, 曲东, 任晓旭, 等. 降钙素原对新生儿败血症病情及预后的评估[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2018, 98(16): 1267-1272. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2018.16.016 [15] 杨亚南, 邵换璋, 史源, 等. 肝素结合蛋白联合SOFA评分对脓毒性休克的预测价值[J]. 中华危重病急救医学, 2019, 31(3): 336-340. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2019.03.015 [16] HONORE P M, DE BELS D, BARRETO G L, et al. Heparin-binding protein in sepsis: player! predictor! positioning?[J]. Ann Intensive Care, 2019, 9(1): 71. doi: 10.1186/s13613-019-0546-3 [17] 刘成, 许雅倩, 邹琪. 脓毒症患者外周血淋巴细胞自噬相关基因Beclin-1和LC3的变化研究[J]. 中华全科医学, 2020, 18(6): 913-916. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYQY202006009.htm [18] 任玮, 吴淼, 魏捷, 等. 肝素结合蛋白、降钙素原和白细胞计数在脓毒症早期的临床对比初探[J]. 国际检验医学杂志, 2018, 39(15): 1853-1856. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4130.2018.15.017 [19] KAHN F, TVERRING J, MELLHAMMAR L, et al. Heparin-binding protein as a prognostic biomarker of sepsis and disease severity at the emergency department[J]. Shock, 2019, 52(6): e135-e145. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000001332 [20] 钱定良, 闫绍荣, 潘晓荷. 肝素结合蛋白和降钙素原及C反应蛋白在脓毒症早期诊断中的价值比较[J]. 中华检验医学杂志, 2017, 40(6): 451-455. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-9158.2017.06.010 -





 下载:
下载: