Effect of ultrasound-guided transverse abdominal plane block on postoperative analgesia and early attention network in elderly patients with abdominal radical hysterectomy
-
摘要:
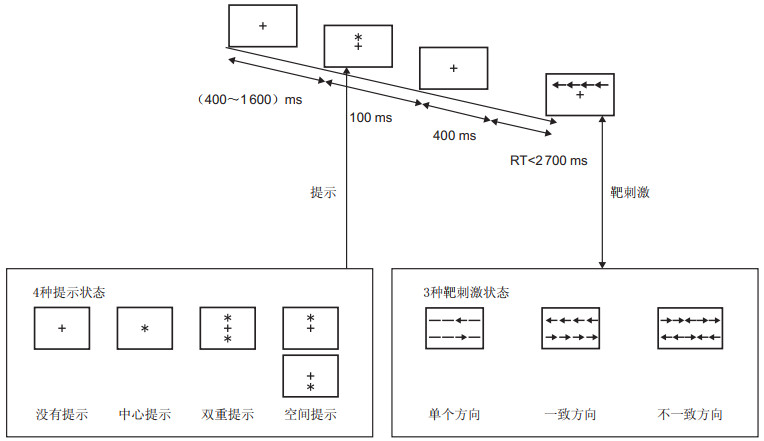
目的 探讨超声引导下腹横肌平面阻滞(transverse abdominal plane block,TAP)对经腹宫颈癌根治术老年患者术后镇痛、早期注意网络的影响。 方法 选择2018年10月—2019年12月蚌埠医学院第一附属医院行经腹宫颈癌根治术的老年患者60例,按麻醉方式分为2组,全麻诱导后,观察组(T组)切皮前在超声引导下行双侧TAP阻滞和全身麻醉,对照组(C组)单纯全麻,2组均用注意网络测试(attention network test,ANT)测定。观察麻醉诱导前、切皮即刻、拔管前5 min和拔管后30 min的MAP和HR及SpO2指标;术中阿片类药物用量;术后24、48和72 h的VSA评分;术前、术后1 d和术后5 d的注意网络效率;术后恶心呕吐和头晕嗜睡等不良反应发生率;患者的满意度。 结果 C组在各时间点的MAP和HR较T组均增加(均P<0.05);T组阿片类药物用量少于C组(均P<0.05);T组各时间点的VAS评分均低于C组(均P<0.05);2组术后1 d警觉、定向和执行控制、平均反应时间和准确率均较术前受损(均P<0.001);术后5 d,T组注意网络效率恢复(P>0.05), C组定向(P=0.323)和平均反应时间(P=0.256)恢复, 警觉(P<0.001)、执行控制(P<0.001)和准确率(P=0.014)未恢复;T组不良反应更少,患者满意度更高。 结论 超声引导下腹横肌平面阻滞可减轻经腹宫颈癌根治术的老年患者的术后疼痛,并可减轻早期注意网络损害。 Abstract:Objective This study aimed to investigate the effects of ultrasound-guided transverse abdominal plane block (TAP) on postoperative analgesia and early attention network in elderly patients undergoing radical abdominal cervical cancer. Methods A total of 60 elderly patients with cervical cancer undergoing radical laparotomy in the First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College from October 2018 to December 2019 were selected and divided into two groups using the anaesthesia method. After induction of general anaesthesia, the observation group (group T) was treated with bilateral TAP block and general anaesthesia under ultrasonic guidance before skin resection, whereas the control group (group C) was treated with simple general anaesthesia. Both groups were measured by the Attention Network Test and observed before anaesthesia induction. The skin was cut instantly, and 5 min before extubation and 30 min after extubation, MAP, HR and SpO2 indices were calculated. Intraoperative opioid dosage; postoperative 24, 48 and 72 h visual analogue scale method score; preoperative and postoperative 1 day and 5 day attention network efficiency; postoperative nausea, vomiting, dizziness sleepiness and incidence of adverse reactions; and patient's satisfaction were compared. Results MAP and HR of group C were higher than those of group T at each time point (all P < 0.05). The amount of opioids in group T was less than that in group C (P < 0.05); VAS score of group T was lower than that of group C at each time point (P < 0.05). Alertness, orientation, executive control, mean reaction time and accuracy were all impaired 1 day after operation (all P < 0.001). On the fifth day after operation, attention network efficiency of T group was restored (P < 0.05), and orientation (P=0.323) and mean reaction time (P=0.256) of the C group were restored, but alertness (P < 0.001), executive control (P < 0.001) and accuracy (P=0.014) were not restored. The T group had fewer adverse reactions and higher patient satisfaction that the C group. Conclusion Ultrasound-guided transverse abdominal plane block can alleviate postoperative pain and early attention network damage in elderly patients undergoing radical abdominal cervical cancer. -
表 1 2组开腹宫颈癌根治术患者一般情况及术中情况的比较(x ±s)
组别 例数 年龄(岁) 身高(cm) 体重(kg) ASA(Ⅰ/Ⅱ/Ⅲ,例) MMSE评分(分) 手术时间(min) 术中出血量(mL) T组 30 68.80±5.02 159.77±4.90 59.83±5.55 12/11/7 27.60±1.30 217.37±8.07 433.00±65.03 C组 30 69.17±5.18 158.07±5.91 61.80±6.77 13/9/8 28.00±1.36 214.93±7.64 427.33±63.73 统计量 -0.278a 1.213a -1.230a 0.040b -1.161a 1.199a 0.341a P值 0.782 0.230 0.224 0.969 0.250 0.235 0.734 注:a为t值,b为Z值。 表 2 2组开腹宫颈癌根治术患者不同时间点的MAP、HR和SPO2比较(x ±s)
组别 例数 MAP(mm Hg) HR(次/min) SpO2(%) T0 T1 T2 T3 T0 T1 T2 T3 T0 T1 T2 T3 T组 30 94.30±10.76 72.20±8.66a 63.96±5.42a 76.43±6.66a 78.33±11.32 72.56±6.60a 69.96±6.31a 73.53±9.46a 96.0±1.1 98.7±0.8 99.4±0.6 98.9±0.6 C组 30 91.43±10.46 80.70±9.32a 75.10±9.20ab 92.66±9.14abc 80.86±9.68 77.76±8.62a 73.9±6.81ab 79.40±9.11abc 95.8±1.0 99.4±0.6 99.1±0.8 98.9±0.8 t值 2.104 15.431 73.087 54.569 0.739 5.163 4.493 5.419 0.216 0.021 1.420 0.022 P值 0.158 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 0.397 0.031 0.043 0.027 0.645 0.887 0.243 0.882 注:与T0相比,aP<0.05;与T1比较,bP<0.05;与T2比较,cP<0.05。 表 3 2组开腹宫颈癌根治术患者术中瑞芬太尼和丙泊酚用量的比较(x ±s)
组别 例数 瑞芬太尼(μg) 丙泊酚(mg) T组 30 2 549.00±150.89 1 495.30±95.51 C组 30 2 779.30±134.03 1 699.90±106.92 t值 -6.251 -7.814 P值 < 0.001 < 0.001 表 4 2组开腹宫颈癌根治术患者不同时间点的动态和静态的VAS评分比较(x ±s,分)
组别 例数 动态 静态 术后24 h 术后48 h 术后72 h 术后24 h 术后48 h 术后72 h T组 30 4.2±1.6 4.3±1.4 2.4±1.2a 2.8±1.0 2.9±1.1 2.3±0.6a C组 30 6.6±1.4 5.8±1.4 3.2±1.2a 3.8±1.1 3.5±0.8 2.8±1.0a t值 52.639 16.567 6.415 18.227 4.552 7.097 P值 < 0.001 < 0.001 0.017 < 0.001 0.041 0.012 注:与术后24 h比较,aP<0.05。 表 5 2组开腹宫颈癌根治术患者不同时间点的注意网络比较(x ±s)
组别 例数 警觉 定向 执行控制 术前 术后1 d 术后5 d 术前 术后1 d 术后5 d 术前 术后1 d 术后5 d T组 30 45.70±3.39 39.1±2.57a 44.40±2.90 50.77±3.14 44.80±3.13a 50.33±3.51 131.90±10.14 140.97±14.55a 129.63±14.25 C组 30 44.17±3.42 31.73±4.62a 40.53±2.99b 51.27±4.14 38.83±3.32a 51.30±5.06 133.60±10.73 172.40±15.16a 141.93±10.71b F值 3.682 72.127 17.930 0.550 236.495 1.012 0.624 74.172 25.320 P值 0.065 < 0.001 < 0.001 0.464 < 0.001 0.323 0.436 < 0.001 < 0.001 组别 例数 平均反应时间 准确率 术前 术后1 d 术后5 d 术前 术后1 d 术后5 d T组 30 956.93±39.85 994.73±18.40 949.83±171.41 97.05±1.15 95.16±1.12a 96.92±1.06 C组 30 969.93±30.90 1 044.30±27.47a 983.97±35.32 97.04±0.96 93.01±1.03a 96.17±0.90b F值 1.843 54.908 1.344 0.004 143.415 6.850 P值 0.185 < 0.001 0.256 0.950 < 0.001 0.014 注:与术前相比,aP<0.001,bP<0.05。 表 6 2组术后不良反应及满意度比较[例(%)]
组别 例数 头晕 恶心呕吐 嗜睡 满意 不满意 T组 30 1(3.33) 0(0.00) 2(6.67) 26(86.67) 4(13.33) C组 30 3(10.00) 9(30.00) 0(0.00) 18(60.00) 12(40.00) 注:2组不良反应整体比较,χ2=7.200,P=0.007;2组满意度比较,χ2=5.455,P=0.019。 -
[1] MD C P W, MPH Z R, PHD D B P, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015[J]. CA Cancer J Clin 2016, 66(2): 115-132. doi: 10.3322/caac.21338 [2] 中华医学会妇科肿瘤学分会. 宫颈癌微创手术的中国专家共识[J]. 现代妇产科进展, 2019, 28(11): 801-803. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDFC201911001.htm [3] ANDROSOVA G, KRAUSE R, WINTERER G, et al. Biomarkers of postoperative delirium and cognitive dysfunction[J]. Front Aging Neurosci, 2015, 7: 112. http://edoc.mdc-berlin.de/14878/1/14878oa.pdf [4] POSNER M I, PETERSEN S E. The attention system of the human brain[J]. Annu Rev Neurosci, 1990, 13: 25-42. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.13.030190.000325 [5] FAN J, MCCANDLISSN B D, SOMMER T, et al. Testing the efficiency and independence of attentional networks[J]. J Cogn Neurosic, 2002, 14(3): 340-347. doi: 10.1162/089892902317361886 [6] MORIYA J. Attentional networks and visuospatial working memory capacity in social anxiety[J]. Cogn Emot, 2018, 32(1): 158-166. doi: 10.1080/02699931.2016.1263601 [7] LANNOY S, HEEREN A, MOYAERTS N, et al. Differential impairments across attentional networks in binge drinking[J]. Psychopharmacology(Berl), 2017, 234(7): 1059-1068. doi: 10.1007/s00213-017-4538-4 [8] FILARDI M, PIZZA F, TONETTI L, et al. Attention impairments and ADHD symptoms in adult narcoleptic patients with and without hypocretin deficiency[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(8): e0182085. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0182085 [9] SCHAEFER S T, KOENIGSPERGER S, OLOTU C, et al. Biomarkers and postoperative cognitive function: could it be that easy?[J]. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol, 2019, 32(1): 92-100. doi: 10.1097/ACO.0000000000000676 [10] 刘峰, 何宋兵, 郭兴坡, 等. 腹腔镜手术与传统开腹手术对老年结肠癌患者术后生理应激及凝血、认知功能和炎症因子的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2018, 38(2): 342-344. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2018.02.036 [11] DE COSMO G, SESSA F, FIORINI F, et al. Effect of remifentanil and fentanyl on postoperative cognitive function and cytokines level in elderly patients undergoing major abdominal surgery[J]. J Clin Anesth, 2016, 35: 40-46. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2016.07.016 [12] KOTEKAR N, SHENKAR A, NAGARAJ R. Postoperative cognitive dysfunction-current preventive strategies[J]. Clin Interv Aging, 2018, 13: 2267-2273. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S133896 [13] PAPPA M, THEODOSIADIS N, TSOUNIS A, et al. Pathogenesis and treatment of post-operative cognitive dysfunction[J]. Electron Physician, 2017, 9(2): 3768-3775. doi: 10.19082/3768 [14] 夏俊伟, 吴茜, 张霜, 等. 全髋关节置换术患者延迟出院的危险因素分析[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志, 2020, 36(4): 354-358. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCMZ202004011.htm [15] 李向南, 蔚冬冬, 李建立, 等. 腹横肌平面阻滞联合全身麻醉用于腹腔镜手术老年患者的改良效果[J]. 中华麻醉学杂志, 2018, 38(2): 177-180. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-1416.2018.02.012 [16] PATEL D, LUNN A D, SMITH A D, et al. Cognitive decline in the elderly after surgery and anaesthesia: results from the Oxford Project to Investigate Memory and Ageing (OPTIMA) cohort[J]. Anaesthesia, 2016, 71(10): 1144-1152. doi: 10.1111/anae.13571 [17] ELSHAMAA H A. Stress response in shoulder surgery under interscalene block, randomized controlled study comparing ultrasound guidance to nerve stimulation[J]. Saudi J Anaesth, 2015, 9(4): 359-364. doi: 10.4103/1658-354X.159454 [18] KRISTEK G, RADOSŠI, KRISTEK D, et al. Influence of postoperative analgesia on systemic inflammatory response and postoperative cognitive dysfunction after femoral fractures surgery: a randomized controlled trial[J]. Reg Anesth Pain Med, 2019, 44(1): 59-68. doi: 10.1136/rapm-2018-000023 -





 下载:
下载: