A five-year analysis of disease spectrum and clinical features of rheumatic inpatients in a new general hospital
-
摘要:
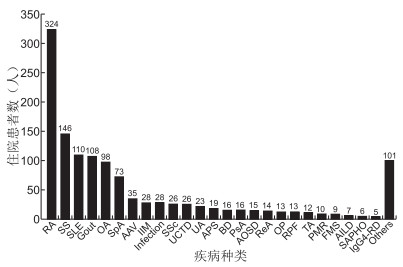
目的 通过对新成立的三级医院风湿科住院患者病种和临床特征分析,了解我国当前风湿免疫科住院患者的疾病谱分布和患者的一般特征。 方法 收集北京大学国际医院2015年1月—2019年12月风湿免疫科住院患者的性别、年龄、诊断、住院时长等临床资料,进行统计描述和分析。 结果 床位共22张,累计出院2 229人次,非重复住院患者共计1 236例。年龄(51.14±16.74)岁,其中≤65岁患者947例(76.62%),女∶男=1.81 ∶ 1。主要病种构成:类风湿关节炎占25.29%,干燥综合征占11.30%,系统性红斑狼疮占8.59%,痛风占8.43%,骨关节炎占7.65%,脊柱关节炎占5.70%,其他如炎性肌病、系统性硬化症等病种占比均 < 3%。年住院人次持续增长(56、282、542、595、752),但重复住院患者占比随之增加,于建科第3年新收治住院患者数增速减缓并呈现相对下滑。住院时长以炎性肌病最长[(19.79±11.86)d],系统性硬化症次之[(16.54±8.48)d]。因病情需要重复住院的患者比例类风湿关节炎为8.64%,炎性肌病和系统性硬化症分别为32.14%和34.60%,均显著高于前者(均P < 0.001)。 结论 风湿免疫科住院患者年龄多 < 65岁,女性居多,关节炎性疾病仍是主要住院病种,住院天数偏长和因病情需要重复住院的是炎性肌病和系统性硬化症。 Abstract:Objective To understand the disease spectrum distribution and general characteristics of inpatients in the Department of Rheumatology and immunology in China. Methods The clinical data of inpatients in the Department of Rheumatology and Immunology of Peking University International Hospital from January 2015 to December 2019, including gender, age, diagnosis and length of stay, were collected for statistical description and analysis. Results There were 22 beds, 229 patients discharged in total, and 1 236 non-repeat inpatients. The mean age was (51.14±16.74) years. Of all the patients, 947 patients were no more than 65 years (76.62%). The ratio of female to male was 1.81 ∶ 1. The most frequent rheumatic diseases inpatient was following, RA 25.29%, SS 11.30%, SLE 8.59%, Gout 8.43%, OA 7.65%, SpA 5.70%, and each of the other rheumatic diseases was less than 3%. The number of discharged patients increased year by year, with 56, 282, 542, 595 and 752 cases in each year, respectively. However, the number of repetitive inpatients increased. Different rheumatic diseases showed different hospital days, and patients with IIM need the longest hospital days [(19.79±11.86) d], and the average length of hospital stay of SSc was (16.54±8.48) days. The proportion of RA patients who were admitted to hospital repeatedly was 8.64%, but this proportion of IIM patients and SSc patients was 32.14% and 34.60%, respectively (all P < 0.001). Conclusion Most of the rheumatic inpatients were female and less than 65 years. Arthritis disease was still the main type of hospitalization in rheumatic disease. Patients with IIM or SSc need longer hospital stay and show a higher proportion of repeated hospitalization than patients with other rheumatic diseases. -
Key words:
- Rheumatic disease /
- Inpatients /
- Disease spectrum /
- Proportion
-
表 1 需反复住院诊治的风湿性疾病的重复住院情况分析
疾病种类 总重复住院率(%) χ2值 P值 因病情所需的重复住院率(%) χ2值 P值 RA 13.89(45/324) 8.64(28/324) SS 15.07(22/146) 0.115a 0.735 10.27(16/146) 0.637a 0.425 SLE 19.09(21/110) 1.732a 0.189 12.70(14/110) 1.568a 0.211 AAV 34.29(12/35) 9.839a 0.002 11.43(4/35) 0.056a 0.812 IIM 46.43(13/28) 19.829a < 0.001 32.14(9/28) 12.737a < 0.001 SSc 34.60(9/26) 6.415a 0.011 34.60(9/26) 14.538a < 0.001 TA 41.67(5/12) 5.027a 0.025 25.00(3/12) 2.002a 0.157 注:a为与RA比较。 -
[1] 张奉春. 第二次全国风湿免疫专科医师调查报告[J]. 中华临床免疫和变态反应杂志, 2014, 8(3): 165-169. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-OZHL201403001.htm [2] 王涛, 李志军. 类风湿关节炎的诊断与治疗[J]. 中华全科医学, 2020, 18(2): 170-171. [3] MATHEW A J, DANDA D, CONAGHAN P G. MRI and ultrasound in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Curr Opin Rheumatol, 2016, 28(3): 323-329. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000039412750810_73ae.html [4] YE H, SU Y, LI R, et al. Comparison of three classification criteria of rheumatoid arthritis in an inception early arthritis cohort[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2016, 35(10): 2397-2401. doi: 10.1007/s10067-016-3281-2 [5] ZHANG S, WANG Y, PENG L, et al. Comparison of clinical features in HLA-b27 positive and negative patients with axial spondyloarthritis: Results from a cohort of 4, 131 patients[J]. Front Med(Lausanne), 2020, 7: 609562. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/347900110_Comparison_of_Clinical_Features_in_HLA-B27_Positive_and_Negative_Patients_With_Axial_Spondyloarthritis_Results_From_a_Cohort_of_4131_Patients [6] FANOURIAKIS A, KOSTOPOULOU M, CHEEMA K, et al. 2019 Update of the joint european league against rheumatism and european renal association-european dialysis and transplant association(EULAR/ERA-EDTA) recommendations for the management of lupus nephritis[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2020, 79(6): 713-723. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-216924 [7] ARINGER M, COSTENBADER K, DAIKH D, et al. 2019 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2019, 78(9): 1151-1159. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-214819 [8] MARIAMPILLAI K, GRANGER B, AMELIN D, et al. Development of a new classification system for idiopathic inflammatory myopathies based on clinical manifestations and myositis-specific autoantibodies[J]. JAMA Neurol, 2018, 75(12): 1528-1537. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.2598 [9] SEROR R, BOWMAN S J, BRITO-ZERON P, et al. EULAR Sjogren's syndrome disease activity index(ESSDAI): A user guide[J]. RMD Open, 2015, 1(1): e000022. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2014-000022 [10] 谢长好, 李志军. 系统性红斑狼疮的诊断与治疗[J]. 中华全科医学, 2020, 18(4): 527-528. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYQY202004002.htm [11] SHIBOSKI C H, SHIBOSKI S C, SEROR R, et al. 2016 American College of Rheumatology/European league against rheumatism classification criteria for primary Sjogren's syndrome: A consensus and data-driven methodology involving three international patient cohorts[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2017, 69(1): 35-45. http://smartsearch.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=a16c81cd33d2923e59416a82d4798256 [12] LI Y, JIA X, SUN X, et al. Risk factors for cancer-associated myositis: A large-scale multicenter cohort study[J]. Int J Rheum Dis, 2021, 24(2): 268-273. [13] VOLKMANN E R, VARGA J. Emerging targets of disease-modifying therapy for systemic sclerosis[J]. Nat Rev Rheumatol, 2019, 15(4): 208-224. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000041601885999_c7d9.html [14] VACCHI C, SEBASTIANI M, CASSONE G, et al. Therapeutic options for the treatment of interstitial lung disease related to connective tissue diseases. a narrative review[J]. J Clin Med, 2020, 9(2): 407. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/339074498_Therapeutic_Options_for_the_Treatment_of_Interstitial_Lung_Disease_Related_to_Connective_Tissue_Diseases_A_Narrative_Review [15] MANFREDI A, SEBASTIANI M, CERRI S, et al. Prevalence and characterization of non-sicca onset primary Sjogren syndrome with interstitial lung involvement[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2017, 36(6): 1261-1268. http://smartsearch.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=5fb1bcb1076f285369dec2bcb3e994d1 [16] ROCA F, DOMINIQUE S, SCHMIDT J, et al. Interstitial lung disease in primary Sjogren's syndrome[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2017, 16(1): 48-54. http://smartsearch.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=8872cf04e04716f62c310183c0689a86 -





 下载:
下载: