A comparison of diagnosis of benign and malignant breast diseases between digital breast tomosynthesis and MRI
-
摘要:
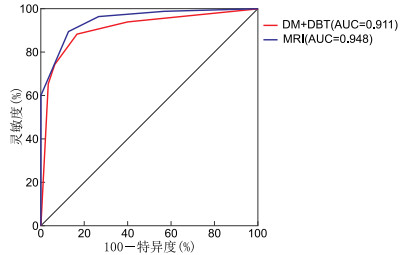
目的 探讨数字化乳腺摄影(digital mammography,DM)、数字乳腺断层摄影(digital breast tomosynthesis,DBT)和MRI在乳腺良恶性疾病诊断中的比较。 方法 回顾性分析2019年1月—2020年10月就诊蚌埠医学院第一附属医院,临床触诊怀疑存在乳腺病灶且同时行DM、DBT、MRI三种检查的116例乳腺疾病患者的资料。对所有图像中病灶参照乳腺影像报告和数据系统(BI-RADS)标准分类,以病理结果为“金标准”,评价DM+DBT和MRI对乳腺良恶性疾病的诊断效能、显示恶性病灶大小和相关恶性征象的能力、DM与DBT的辐射剂量差异。 结果 116例病灶中恶性86例,良性30例。DM+DBT、MRI诊断乳腺良恶性疾病的敏感度为88.4%、96.5%,特异度为86.7%、73.3%,准确度为87.9%、90.5%;两者的ROC曲线下面积(AUC)分别为0.911和0.948,差异无统计学意义(Z=1.084,P=0.278);DM+DBT与MRI均稍高估恶性肿瘤大小,但两者与病理大小均存在较好的一致性(均P>0.05);DM+DBT在显示微钙化方面优于MRI(χ2=22.114,P<0.05),在显示胸大肌浸润和腋窝淋巴结方面低于MRI(χ2=4.900、21.333,均P<0.05)。DM的平均辐射剂量为(1.574±0.422)mGy,DBT的平均辐射剂量为(2.534±0.521)mGy,DBT的辐射剂量高于DM的辐射剂量,差异具有统计学意义(t=-29.213,P<0.001)。 结论 DM+DBT可以较准确的诊断乳腺良恶性疾病,与MRI相似。而且简单易行,无须注射对比剂,建议有致密型乳腺内病变的患者常规行DM+DBT检查。 Abstract:Objective To explore the diagnostic of benign and malignant breast diseases between digital mammography (DM), digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) and MRI. Methods During the period from January 2019 to October 2020, 116 patients with suspected lesions by palpation underwent further imaging exam in the First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College. The DM, DBT and MRI were performed on all the patients. All breast lesions were analyzed according to BI-RADS. The pathological results were "gold standard" to evaluate the diagnostic efficacy of the DM+DBT and MRI in benign and malignant breast diseases. The ability of the DM+DBT and MRI to evaluate the actual lesion size and malignant signs. The difference of average glandular dose between DM and DBT. Results Among the 116 lesions, 86 were malignant and 30 were benign. The sensitivity of DM+DBT was 88.4%, specificity 86.7%, and accuracy 87.9%. The sensitivity of MRI was 96.5%, specificity 73.3%, and accuracy 90.5%. The ROC area under the curve of DM+DBT and MRI for diagnosis of breast diseases were 0.911 and 0.948. There was no significant difference in AUC value between DM+DBT and MRI (Z=1.084, P=0.278). The DM+DBT and MRI were slightly overestimated the size of malignant tumor, but both of them were positively correlated with the pathological measurements (all P>0.05). The calcification was significantly higher for DM+DBT detection than for MRI (χ2=22.114, P < 0.05). The infiltration of pectoralis major and axillary lymph nodes were significantly higher for MRI than that for DM+DBT detection (χ2=4.900, 21.333, all P < 0.05). The average glandular dose (AGD) of DM and DBT was (1.574±0.422) mGy and (2.534±0.521) mGy, respectively. The AGD of DBT was significantly higher than DM (t=-29.213, P < 0.001). Conclusion DM+DBT can effectively diagnose benign and malignant breast lesions, providing a comparable efficiency to MRI. It is easy for patients and does not need contrast injections. DM+DBT is recommend for patients with dense gland type breast. -
Key words:
- Digital breast tomosynthesis /
- Magnetic resonance imaging /
- Breast diseases /
- Tumor size /
- Calcification
-
表 1 2种检查方法显示乳腺癌恶性征象比较(例)
检查方法 例数 不规则肿块 星芒征 钙化 肿大淋巴结 胸大肌浸润 DM+DBT 86 68 45 28 11 6 MRI 86 71 47 4 36 14 χ2值 0.364 0.083 22.114 21.333 4.900 P值 0.549 0.774 <0.001 <0.001 0.021 -
[1] BRAY F, FERLAY J, SOERJOMATARAM I, et al. Erratum: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2020, 70(4): 313. [2] RAY K M, JOE B N, FREIMANIS R I, et al. Screening mammography in women 40-49 years old: Current evidence[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2018, 210(2): 264-270. doi: 10.2214/AJR.17.18707 [3] 代晓倩, 张伟. 数字乳腺断层摄影与超声对致密型乳腺内病变的诊断效能对比研究[J]. 中国医药, 2019, 14(5): 738-741. doi: 10.3760/j.issn.1673-4777.2019.05.024 [4] ALZAGHAL A A, DIPIRO P J. Applications of advanced breast imaging modalities[J]. Curr Oncol Rep, 2018, 20(7): 57. doi: 10.1007/s11912-018-0700-3 [5] 徐海燕, 赵红, 邹立巍, 等. 利用3.0T MR血管成像探讨乳腺癌周围血供特点及相关因素[J]. 中华全科医学, 2016, 14(1): 108-110, 130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYQY201601039.htm [6] 中国抗癌协会乳腺癌专业委员会. 中国抗癌协会乳腺癌诊治指南与规范(2019年版)[J]. 中国癌症杂志, 2019, 29(8): 609-680. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGAZ201709004.htm [7] NG K H, LAU S. Vision 20/20: Mammographic breast density and its clinical applications[J]. Med Phys, 2015, 42(12): 7059-7077. doi: 10.1118/1.4935141 [8] DESTOUET J M, BASSETT L W, YAFFE M J, et al. The acr's mammography accreditation program: Ten years of experience since mqsa[J]. J Am Coll Radiol, 2005, 2(7): 585-594. doi: 10.1016/j.jacr.2004.12.005 [9] MOSHINA N, AASE H S, DANIELSEN A S, et al. Comparing screening outcomes for digital breast tomosynthesis and digital mammography by automated breast density in a randomized controlled trial: Results from the to-betrial[J]. Radiology, 2020, 297 (3): 522-531. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2020201150 [10] BASHA M A A, SAFWAT H K, ALAA ELDIN A M, et al. The added value of digital breast tomosynthesis in improving diagnostic performance of BI-RADS categorization of mammographically indeterminate breast lesions[J]. Insights Imaging, 2020, 11(1): 26. doi: 10.1186/s13244-020-0835-2 [11] 黄新玲, 胡汉金. 数字乳腺断层合成摄影和MRI检查对乳腺癌诊断效能的比较[J]. 临床放射学杂志, 2020, 39(6): 1085-1089. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCFS202006013.htm [12] HA T, KANG D K, KIM T H. Percentage volume of delayed kinetics in computer-aided diagnosis of MRI of the breast to reduce false-positive results and unnecessary biopsies[J]. Clin Radiol, 2020, 75(12): 962e1-962e8. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2020.08.005 [13] 汤伟, 杨孟, 高毅, 等. 数字乳腺断层融合X线摄影术前评估乳腺癌肿块大小的效能对比研究[J]. 中国癌症杂志, 2018, 28(11): 813-818. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGAZ201811004.htm [14] CHAND J T, SHARMA M M, DHARMARAJAN J P, et al. Digital breast tomosynthesis as a tool in confirming negative surgical margins in non-palpable breast lesions[J]. Indian J Surg Oncol, 2019, 10(4): 624-628. doi: 10.1007/s13193-019-00956-z [15] MARINOVICH M L, BERNARDI D, MACASKILL P, et al. Agreement between digital breast tomosynthesis and pathologic tumour size for staging breast cancer, and comparison with standard mammography[J]. Breast, 2019, 43: 59-66. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2018.11.001 [16] GIROMETTI R, MARCONI V, LINDA A, et al. Preoperative assessment of breast cancer: Multireader comparison of contrast-enhanced mri versus the combination of unenhanced MRI and digital breast tomosynthesis[J]. Breast, 2020, 49: 174-182. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2019.11.013 [17] O'GRADY S, MORGAN M P. Microcalcifications in breast cancer: From pathophysiology to diagnosis and prognosis[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer, 2018, 1869(2): 310-320. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2018.04.006 [18] SPANGLER M L, ZULEY M L, SUMKIN J H, et al. Detection and classification of calcifications on digital breast tomosynthesis and 2d digital mammography: A comparison[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2011, 196(2): 320-324. doi: 10.2214/AJR.10.4656 [19] LI J T, ZHANG H W, JIANG H, et al. Diagnostic performance of digital breast tomosynthesis for breast suspicious calcifications from various populations: A comparison with full-field digital mammography[J]. Comput Struct Biotechnol J, 2019, 17: 82-89. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2018.12.004 [20] 谢四梅, 张安秦, 朱彩霞, 等. 触诊及影像学检查对乳腺癌腋淋巴结转移状况预测价值探讨[J]. 中华肿瘤防治杂志, 2014, 21(15): 1179-1183. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QLZL201415011.htm [21] 郭相华, 宋黎涛, 黄松, 等. 乳腺钼靶联合磁共振成像检查在老年乳腺癌患者诊断中的价值[J]. 中国肿瘤临床与康复, 2019, 26(3): 297-299. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZK201903017.htm -





 下载:
下载: