Relationship between serum B-cell activating factor expression and carotid atherosclerosis and its related factors in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
-
摘要:
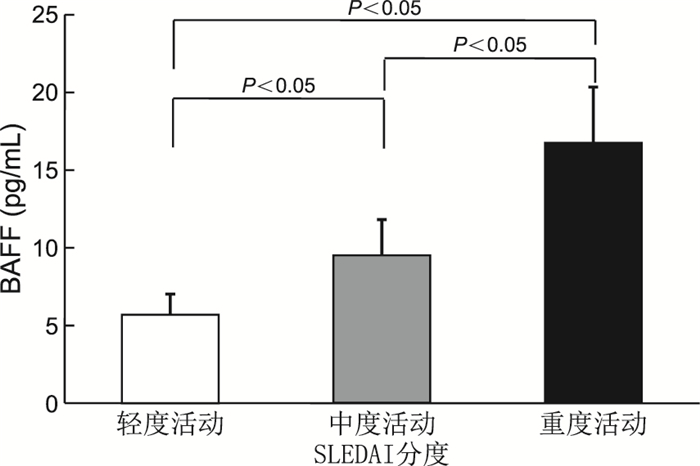
目的 探索血清B细胞活化因子(BAFF)的表达水平与系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)患者颈动脉粥样硬化及其相关因素的关系。 方法 选择2020年10月—2021年6月入住蚌埠医学院第一附属医院风湿免疫科的符合入组标准的SLE患者103例。根据颈动脉彩色多普勒影像学检查结果将103例SLE患者分为合并动脉斑块形成组(A组,32例)、内膜增厚组(B组,31例)及动脉无器质性病变组(C组,40例);同时选取健康人(D组,40例)的血清标本作为有关指标测定的对照组。采用酶联免疫吸附法(ELISA)检测4组血清BAFF表达水平,并分析BAFF与临床及有关实验室指标的相关性。 结果 SLE患者血清中BAFF的表达水平显著高于健康对照组[5.73(2.02,7.89)ng/mL vs. 1.01(0.76,1.31)ng/mL,Z=-9.265,P<0.001];在SLE患者中A组BAFF表达高于B、C组[14.55(11.44,20.18)ng/mL vs. 6.33(5.81,7.45)ng/mL vs. 5.26(4.22,6.93)ng/mL,Z=55.767,P<0.001]。相关性分析发现BAFF的表达水平与病程、年龄、SLEDAI2000、红细胞沉降率、抗dsDNA定量、IgA呈正相关关系,与补体C3呈负相关关系(r=-0.309)。 结论 SLE患者血清BAFF表达水平与其颈动脉粥样硬化的发生有一定的关联性,可能是SLE患者动脉粥样硬化形成的重要促进性因素;SLE患者血清BAFF水平与SLEDAI等病情活动性指标显著相关,可作为判断病情活动性的参考指标。 Abstract:Objective To explore the relationship between serum B-cell activating factor (BAFF) expression level and carotid atherosclerosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and its related factors. Methods A total of 103 SLE patients who met the inclusion criteria and were admitted to our department from October 2020 to June 2021 were selected. According to the results of carotid colour Doppler imaging, 103 SLE patients were divided into three groups: group A with arterial plaque formation (32 cases), group B with intima thickening (31 cases) and group C with no arterial disease (40 cases). At the same time, serum samples of healthy people (group D, 40 cases) were selected as the control group. The expression levels of serum BAFF in four groups were detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The correlation between BAFF and clinical and laboratory indicators was analysed. Results The expression level of BAFF in SLE patients was significantly higher than that in healthy controls [5.73(2.02, 7.89) ng/mL vs. 1.01(0.76, 1.31) ng/mL, Z=-9.265, P < 0.001]. The expression of BAFF in SLE patients in group A was higher than that in groups B and C [14.55(11.44, 20.18) ng/mL vs. 6.33(5.81, 7.45) ng/mL vs. 5.26(4.22, 6.93) ng/mL, Z=55.767, P < 0.001]. Correlation analysis showed that the expression level of BAFF was positively correlated with the course of disease, age, SLEDAI2000, ESR, anti-dsDNA quantisation and IgA and negatively correlated with complement C3 (r=-0.309). Conclusion The expression level of serum BAFF in SLE patients is correlated with the occurrence of carotid atherosclerosis, which may be an important factor promoting the formation of atherosclerosis in SLE patients. Serum BAFF level in SLE patients was significantly correlated with SLEDAI and other disease activity indicators, which could be used as a reference indicator to judge the disease activity. -
Key words:
- Systemic lupus erythematosus /
- Atherosclerosis /
- B cell activating factor
-
表 1 3组SLE患者一般临床资料比较
Table 1. Comparison of general clinical data of SLE patients in three groups
组别 例数 年龄
[M(P25, P75),岁]性别[例(%)] 病程
[M(P25, P75),月]高脂血症
[例(%)]IgG
(x±s,g/L)IgM
(x±s,g/L)IgA
(x±s,g/L)女性 男性 A组 32 51.50(46.00,57.00) 23(71.9) 9(28.1) 120.00(48.50,141.00) 23(71.9) 13.48±5.11 1.02±0.48 3.34±1.78 B组 31 43.00(36.00,47.00) 26(83.9) 5(16.1) 63.00(26.00,121.00) 17(54.8) 11.43±3.06 1.02±0.51 2.44±0.74 C组 40 40.00(31.25,45.75) 32(80.0) 8(20.0) 24.00(12.00,60.00) 34(85.0) 11.74±4.75 1.10±0.47 2.81±1.38 统计量 31.224a 1.421b 27.433a 7.854b 2.015c 0.272c 3.505c P值 <0.001 0.491 <0.001 0.020 0.139 0.762 0.034 组别 例数 C3
(x±s,g/L)C4
(x±s,g/L)SLEDAI 2000
(x±s)抗dsDNA定量
[M(P25, P75),g/L]ESR
[M(P25, P75),mm/h]CRP
[M(P25, P75),mg/L]BAFF
[M(P25, P75),ng/mL]A组 32 0.71±0.20 0.17±0.09 11.63±4.31 193(149,234) 34.00(27.25,42.50) 4.15(1.70,9.16) 14.55(11.44,20.18) B组 31 0.84±0.13 0.16±0.05 9.61±3.51 154(85,201) 24.00(12.00,37.00) 1.76(1.56,2.32) 6.33(5.81,7.45) C组 40 0.98±0.42 0.15±0.07 5.69±2.02 62(46,78) 17.00(9.00,26.75) 2.99(1.36,7.10) 5.26(4.22,6.93) 统计量 6.859c 0.946c 30.266c 36.119a 23.043a 5.231a 55.767a P值 0.002 0.392 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 0.103 <0.001 注:a为Z值,b为χ2值,c为F值。 表 2 BAFF与相关临床指标的相关性
Table 2. Correlation between BAFF and related clinical indicators
项目 r值 P值 年龄(岁) 0.432 <0.001 病程(月) 0.379 <0.001 CPR(mg/L) 0.019 0.851 SLEDAI2000 0.528 <0.001 ESR(mm/h) 0.409 <0.001 IgM(g/L) 0.002 0.983 IgA(g/L) 0.249 0.011 IgG(g/L) 0.200 0.043 抗dsDNA定量(g/L) 0.419 <0.001 补体C3(g/L) -0.309 0.001 补体C4(g/L) 0.062 0.534 -
[1] LI D, YOSHIDA K, FELDMAN C H, et al. Initial disease severity, cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality among patients with systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Rheumatology(Oxford), 2020, 59(3): 495-504. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kez288 [2] 谢长好, 李志军. 系统性红斑狼疮的诊断与治疗[J]. 中华全科医学, 2020, 18(4): 527-528. http://www.zhqkyx.net/article/id/240c4592-9f47-4c70-a324-2bf8221505c8XIE C H, LI Z J. Diagnosis and treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2020, 18(4): 527-528. http://www.zhqkyx.net/article/id/240c4592-9f47-4c70-a324-2bf8221505c8 [3] CINOKU I I, MAVRAGANI C P, MOUTSOPOULOS H M. Atherosclerosis: Beyond the lipid storage hypothesis. The role of autoimmunity[J]. Eur J Clin Invest, 2020, 50(2): e13195. [4] 穆怀玉, 郭晓辰, 陈馨浓, 等. 动脉粥样硬化中适应性免疫应答的研究进展[J]. 生物化学与生物物理进展, 2020, 47(5): 407-417. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHSW202005004.htmMU H Y, GUO X C, CHEN X N, et al. Advances of adaptive immune response in atherosclerosis[J]. Progress In Biochemistry and Biophysics, 2020, 47(5): 407-417. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHSW202005004.htm [5] MAGALLARES B, LOBO-PRAT D, CASTELLVÍ I, et al. Assessment of EULAR/ACR-2019, SLICC-2012 and ACR-1997 classification criteria in SLE with longstanding disease[J]. J Clin Med, 2021, 10(11): 2377. doi: 10.3390/jcm10112377 [6] 伍满燕, 梁文卿, 陈江天, 等. 颈动脉粥样硬化性疾病的诊治进展[J]. 中华老年心脑血管病杂志, 2019, 21(11): 1223-1226. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0126.2019.11.028WU M Y, LIANG W Q, CHEN J T, et al. Advances in diagnosis and treatment of carotid atherosclerotic diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Geriatric Heart Brain and Vessel Diseases, 2019, 21(11): 1223-1226. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0126.2019.11.028 [7] GIANNELOU M, MAVRAGANI C P. Cardiovascular disease in systemic lupus erythematosus: A comprehensive update[J]. J Autoimmun, 2017, 82: 1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2017.05.008 [8] GATTO M, ZEN M, IACCARINO L, et al. New therapeutic strategies in systemic lupus erythematosus management[J]. Nat Rev Rheumatol, 2019, 15(1): 30-48. doi: 10.1038/s41584-018-0133-2 [9] ZHU Y H, XIAN X M, WANG Z Z, et al. Research progress on the relationship between atherosclerosis and Inflammation[J]. Biomolecules, 2018, 8(3): 80. doi: 10.3390/biom8030080 [10] CHISTIAKOV D A, MELNICHENKO A A, GRECHKO A V, et al. Potential of anti-inflammatory agents for treatment of atherosclerosis[J]. Exp Mol Pathol, 2018, 104(2): 114-124. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2018.01.008 [11] 邹钰钿, 张艳林, 曹勇军. B细胞调控动脉粥样硬化性卒中研究进展[J]. 中国现代神经疾病杂志, 2020, 20(1): 15-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDJB202001009.htmZOU Y D, ZHANG Y L, CAO Y J. Progress in the regulation of B cells in atherosclerotic stroke[J]. Chinese Journal of Contemporary Neurology and Neurosurgery, 2020, 20(1): 15-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDJB202001009.htm [12] FRIEBUS-KARDASH J, BRANCO L, RIBI C, et al. Immune complexes containing serum B-cell activating factor and immunoglobulin G correlate with disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2018, 33(1): 54-64. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfx220 [13] THEODOROU E, NEZOS A, ANTYPA E, et al. B-cell activating factor and related genetic variants in lupus related atherosclerosis[J]. J Autoimmun, 2018, 92: 87-92. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0896841118301987 [14] MÖCKEL T, BASTA F, WEINMANN-MENKE J, et al. B cell activating factor (BAFF): Structure, functions, autoimmunity and clinical implications in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2021, 20(2): 102736. [15] GANJALI S, SHIRMOHAMMADI L, READ M I, et al. High-density lipoprotein functionality in systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Semin Arthritis Rheum, 2020, 50(4): 769-775. [16] ZAKI D, AYOUB N M, MOHAMMED Z A Z, et al. Study of B cell activating factor (BAFF) and BAFF-R in systemic lupus erythematosus patients[J]. Am J Med Sci, 2019, 9(6): 203-209. http://www.sapub.org/global/showpaperpdf.aspx?doi=10.5923/j.ajmms.20190906.06 [17] 郭芝璇, 艾雪忱, 唐增奇, 等. 外周血BAFF及Bregs水平与系统性红斑狼疮病情相关性研究[J]. 皮肤性病诊疗学杂志, 2020, 27(2): 65-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LPFZ202002002.htmGUO Z X, AI X C, TANG Z Q, et al. The levels of BAFF and regulatory B cells and their association with systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Journal of Diagnosis and Therapy on Dermato-venereology, 2020, 27(2): 65-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LPFZ202002002.htm [18] DHAMODHARAN U, TEENA R, KUMAR R V, et al. Circulatory levels of B-cell activating factor of the TNF family in patients with diabetic foot ulcer: Association with disease progression[J]. Wound Repair Regen, 2019, 27(5): 442-449. -





 下载:
下载: