Clinical verification and application of the modified Waterlow scale
-
摘要:
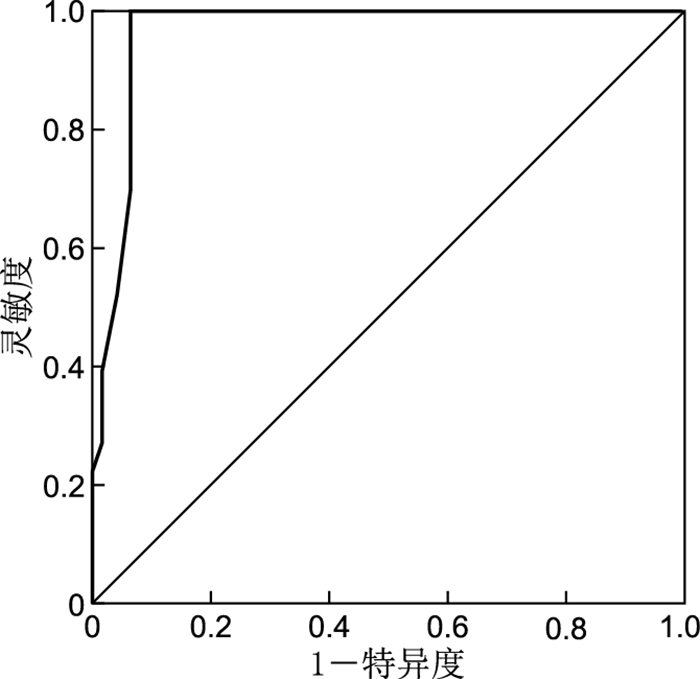
目的 精简国际通用的Waterlow量表后获得改良版Waterlow量表,并对其进行临床验证。 方法 运用属性约简方法回顾性分析204例病例样本,获得改良版Waterlow量表。然后选取2019年6—11月上海交通大学附属第一人民医院收治的249例住院患者进行前瞻性研究,计算受试者工作特征曲线(receiver operating characteristic curve,ROC)下面积(area under the curve,AUC)比较2种量表的预测效果。 结果 改良版Waterlow量表的最佳临界值为9.5分时,有较好的灵敏度(0.893)和特异度(0.963),且尤登指数(灵敏度+特异度-1)取最大值为0.856。改良版Waterlow量表与传统Waterlow量表ROC曲线下面积分别为0.879和0.931(均>0.7),且改良版Waterlow量表的阳性病例检出率是60.24%,传统的Waterlow量表为76.31%。Kappa检验值为0.737(>0.7),McNemar检验比较差异无统计学意义,两种量表的检验结果一致性成立(χ2=0.042,P=0.838),检出效果差异无统计学意义。 结论 改良版Waterlow表科学性较高。其检出效率与传统Waterlow量表一致、预测准确性较高,且评估条目少、使用简便,可有效提高护理工作效率。 Abstract:Objective After simplifying the commonly used Waterlow scale, the modified version was obtained and clinically verified. Methods A total of 204 cases were analysed retrospectively by attribute reduction method, and the improved Waterlow scale was obtained. Afterward, from June to November 2019, 249 inpatients from Shanghai General Hospital were selected for a prospective study, Paired chi square test and area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) were used to compare the prediction effect of these two scales. Results When the optimal critical value of the modified Waterlow scale was 9.5 marks, it had good sensitivity (0.893) and specificity (0.963), and the maximum value of Youden index (sensitivity + specificity-1) was 0.856. Moreover, the area under the ROC curve of the modified Waterlow scale and the traditional Waterlow scale were 0.879 and 0.931, respectively (both >0.7). The rate of positive case detection was 60.24% for the modified Waterlow scale and 76.31% for the traditional Waterlow scale. The kappa test value was 0.737 (> 0.7), and the result of McNemar test was no statistical difference, which indicated that the consistency of these two scales is established (χ2=0.042, P=0.838). Moreover, no statistical difference was observed between these two scales. Conclusion The modified Waterlow scale has highly scientific. The detection efficiency is consistent with the traditional Waterlow scale, the prediction accuracy is high, and there are few evaluation items and easy to use, which can effectively improve the efficiency of nursing work. -
Key words:
- Pressure injury /
- Risk profile /
- Assessment scale
-
表 1 249例住院患者压力性损伤分析结果[例(%)]
Table 1. Results of 249 inpatients with pressure ulcer [cases (%)]
评估指标 发生压力性损伤 未发生压力性损伤 统计量 P值 BMI 2.486a < 0.005 中等 78(38.24) 37(18.14) 超过中等 26(12.75) 11(5.39) 肥胖 12(5.88) 1(0.49) 低于中等 34(16.67) 5(2.45) 皮肤类型 5.913a < 0.001 正常 56(27.45) 47(23.04) 薄 38(18.63) 2(0.98) 干燥 8(3.92) 1(0.49) 水肿 18(8.82) 4(1.96) 潮湿 5(2.45) 0 颜色差 12(5.88) 0 裂开/红斑 13(6.37) 0 是否进食很差或缺乏食欲 2.431b 0.015 是 58(28.43) 11(5.39) 否 92(45.10) 43(21.08) 失禁情况 4.303a < 0.001 完全控制 70(34.31) 42(20.59) 偶失禁 11(5.39) 2(0.98) 尿/大便失禁 34(16.67) 10(4.90) 大小便失禁 35(17.16) 0 活动能力 4.303a < 0.001 完全 23(11.27) 33(16.18) 烦躁不安 4(1.96) 1(0.49) 冷漠的 9(4.41) 0 限制的 70(34.31) 16(7.84) 迟钝 38(18.63) 4(1.96) 固定 6(2.94) 0 糖尿病/多发性硬化/心血管疾病 3.740a < 0.001 无 79(38.73) 43(21.08) 轻度 49(24.02) 11(5.39) 中度 17(8.33) 0 重度 5(2.45) 0 感觉受限 6.214a < 0.001 无 56(27.45) 48(23.53) 轻度 57(27.94) 4(1.96) 中度 26(12.75) 2(0.98) 重度 11(5.39) 0 注:a为Z值,b为χ2值。 表 2 采用信息增益方法约简指标
Table 2. Reduction index by information gain method
序号 评价指标 平均得分 平均排名 4 皮肤类型 0.18 1.40 12 感觉受限 0.17 1.90 9 运动能力 0.16 2.70 8 失禁情况 0.10 4.00 11 糖尿病/多发性硬化/心血管疾病 0.07 5.00 3 BMI 0.04 8.60 表 3 采用χ2检验方法约简指标
Table 3. Reduction index by chi-square method
序号 评价指标 平均得分 平均排名 9 运动能力 40.56 1.60 4 皮肤类型 37.69 2.20 12 感觉受限 38.32 2.20 8 失禁情况 18.80 4.00 11 糖尿病/多发性硬化/心血管疾病 13.43 5.20 3 BMI 7.71 8.00 表 4 改良版Waterlow量表(部分)
Table 4. The modified Waterlow scale (part)
项目 类别 评分 项目 类别 评分 活动能力 ①完全 0分 失禁情况 ①完全控制 0分 ②烦躁不安 1分 ②偶失禁 1分 ③冷漠的 2分 ③尿/大便失禁 2分 ④限制的 3分 ④大小便失禁 3分 ⑤迟钝 4分 糖尿病/多发性硬化/心血疾病 ①无 0分 ⑥固定 5分 ②轻度 4分 皮肤类型 ①正常 0分 ③中度 5分 ②薄 1分 ④重度 6分 ③干燥 1分 BMI ①中等20~24.9 0分 ④水肿 1分 ②超过中等25~29.9分 1分 ⑤潮湿 1分 ③肥胖 > 30分 2分 ⑥颜色差 2分 ④低于中等 < 20分 3分 ⑦裂开/红斑 3分 感觉受限 ①无 0分 ②轻度 4分 ③中度 5分 ④重度 6分 表 5 改良版Waterlow量表评估总分的灵敏度和特异度
Table 5. The sensitivity and specificity for the score of the modified Waterlow scale
评估总分 灵敏度 特异度 评估总分 灵敏度 特异度 2.0 1.000 0 11.5 0.533 0.981 3.5 0.987 0.222 12.5 0.400 0.981 4.5 0.960 0.370 13.5 0.333 0.981 5.5 0.940 0.611 14.5 0.220 0.981 6.5 0.927 0.796 15.5 0.153 1.000 7.5 0.913 0.852 16.5 0.113 1.000 8.5 0.907 0.926 17.5 0.100 1.000 9.5 0.893 0.963 18.5 0.073 1.000 10.5 0.740 0.963 20.0 0.053 1.000 表 6 2种量表预测结果(例)
Table 6. Prediction results of 2 scales (cases)
改良版Waterlow量表 Waterlow量表 合计 0 1 0 48 13 61 1 11 177 188 合计 59 190 249 -
[1] 童琍琍, 赵梅. 国内压疮评估量表的应用进展[J]. 护理管理杂志, 2019, 19(4): 275-279. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-315x.2019.04.012TONG L L, ZHAO M. Application progress of pressure ulcer evaluation scale in China[J]. J Nurs Manage, 2019, 019 (4): 275-279. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-315x.2019.04.012 [2] CHARALAMBOUS C, KOULORI A, VASILOPOULOS A, et al. Evaluation of the validity and reliability of the Waterlow pressure ulcer risk assessment scale[J]. Med Arch, 2018, 72(2): 141-144. doi: 10.5455/medarh.2018.72.141-144 [3] BRIENZA D, KRISHNAN S, KARG P, et al. Predictors of pressure ulcer incidence following traumatic spinal cord injury: A secondary analysis of a prospective longitudinal study[J]. Spinal cord, 2018, 56(1): 28-34. doi: 10.1038/sc.2017.96 [4] MERVIS J S, PHILLIPS T J. Pressure ulcers: Pathophysiology, epidemiology, risk factors, and presentation[J]. J Am Acad Dermatol, 2019, 81(4): 881-890. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2018.12.069 [5] 孙留梅, 陶琳, 易银萍, 等. 基于改良Waterlow压疮风险评估表的压力性损伤管理在重症患者ICU住院期间的应用效果观察[J]. 齐鲁护理杂志, 2021, 27(16): 21-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7256.2021.16.007SUN L M, TAO L, YI Y P, et al. Application effect of pressure ulcer management based on improved Waterlow scale in ICU patients[J]. Qilu J Nurs, 2021, 27 (16): 21-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7256.2021.16.007 [6] 龚艳, 蒋琪霞, 陈文芳, 等. 手术获得性压力性损伤风险评估量表对手术患者压力性损伤预测效果的研究[J]. 护理学报, 2021, 28(9): 66-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NFHL202109014.htmGong Y, Jiang Q X, Chen W F, et al. Study on the predictive effect of surgical acquired pressure ulcer scale on surgical patients[J]. J Nurs, 2021, 28 (9): 66-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NFHL202109014.htm [7] 庄丽娟, 梁桂仙, 徐瑜涓, 等. 基于治疗干预评分系统和护理工时测量的ICU护理人力资源配置模型研究[J]. 护理研究, 2018, 32(14): 2208-2211. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXHZ201814015.htmZhuang L J, Liang G X, Xu Y J, et al. Research on ICU nursing human resource allocation model based on treatment intervention scoring system and nursing work hour measurement[J]. Nurs Res, 2018, 610 (14): 54-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXHZ201814015.htm [8] COLEMAN S, SMITH I L, MCGINNIS E, et al. Clinical evaluation of a new pressure ulcer risk assessment instrument, the pressure ulcer risk primary or secondary evaluation tool (purpose t)[J]. J Adv Nurs, 2018, 74(2): 407-424. doi: 10.1111/jan.13444 [9] 周洋, 王繁可, 杨朵儿, 等. 南京市某三甲专科医院人力资源配置状况及投入产出效率分析[J]. 中华全科医学, 2021, 19(10): 1768-1771. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002163Zhou Y, Wang F K, Yang D E, et al. Analysis on human resource allocation and invest-produce efficiency of a class Ⅲ specialized hospital in Nanjing[J]. Chin J Gen Pract, 2021, 19 (10): 1768-1771. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002163 [10] 姚捷, 孙志明, 施雯慧, 等. 老龄化背景下江苏省护理人力资源配置公平性研究[J]. 中国临床研究, 2021, 34(8): 1148-1152. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGCK202108035.htmYao J, Sun Z M, Shi W H, et al. Study on the fairness of nursing human resources allocation in Jiangsu Province under the background of aging[J]. Chin Clin Res, 2021, 34 (8): 1148-1152. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGCK202108035.htm [11] 陈慧玲, 王淑东. Waterlow压力性损伤量表与Braden压力性量表在预测ICU病人压疮预防中的价值[J]. 蚌埠医学院学报, 2020, 45(8): 1107-1109, 1113.Chen H L, Wang S D. Value of Waterlow scale and Braden scale in predicting pressure ulcer prevention in ICU patients[J]. J Bengbu Med Coll, 2020, 45(8): 1107-1109, 1113. [12] WATERLOW J. Pressure sores: A risk assessment card[J]. Nurs Times, 1985, 81(48): 49-55. [13] 姜安丽. 新编护理学基础[M]. 2版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2012: 371.Jiang A L. Newly compiled fundamentals of nursing[M]. 2th ed. Beijing: People ' s Medical Publishing House, 2012: 371. [14] 赵上萍, 陈红. 中文版类风湿关节炎自我效能量表信度与效度检验[J]. 护理研究, 2019, 33(10): 1681-1685. doi: 10.12102/j.issn.1009-6493.2019.10.009Zhao S P, Chen H. Reliability and validity test of Chinese rheumatoid arthritis self-efficacy scale[J]. Nurs Res, 2019, 33(10): 1681-1685. doi: 10.12102/j.issn.1009-6493.2019.10.009 [15] 李春朋. 两种量表在预测ICU患者压力性损伤风险的对比研究[D]. 晋中: 山西中医药大学, 2019.Li C P. Comparative study of two scales in predicting the risk of pressure ulcer in ICU patients[D]. Jinzhong: Shanxi University of traditional Chinese medicine, 2019. [16] 曹艳, 徐春艳, 杨丽红, 等. 两种评估量表对肿瘤病人压疮评价的比较研究[J]. 护理研究, 2017, 31(4): 479-482. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6493.2017.04.027Cao Y, Xu C Y, Yang L H, et al. Comparative study of two scales in the evaluation of pressure ulcer for tumor patients[J]. Nurs Res, 2017, 31 (4): 479-482. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6493.2017.04.027 [17] 郭蕊, 丁选胜, 张晋萍, 等. 三种量表对老年晚期癌症患者抑郁状态评估一致性比较[J]. 实用预防医学, 2019, 26(6): 762-765. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3110.2019.06.037Guo R, Ding X S, Zhang J P, et al. Comparison of the consistency of three scales in the evaluation of depression in elderly patients with advanced cancer[J]. Pract Prev Med, 2019, 26(6): 762-765. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3110.2019.06.037 [18] 叶彤, 何月, 董丽. ICU患者专用压力性损伤风险评估表的研究进展[J]. 中国护理管理, 2017, 17(12): 1699-1703. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1756.2017.12.027Ye T, He Y, Dong L. Research progress of special pressure ulcer scale for ICU patients[J]. Chin Nurs Manag, 2017, 17(12): 1699-1703. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1756.2017.12.027 -





 下载:
下载: