Analysis of risk factors for the prognosis of IgA nephropathy
-
摘要:
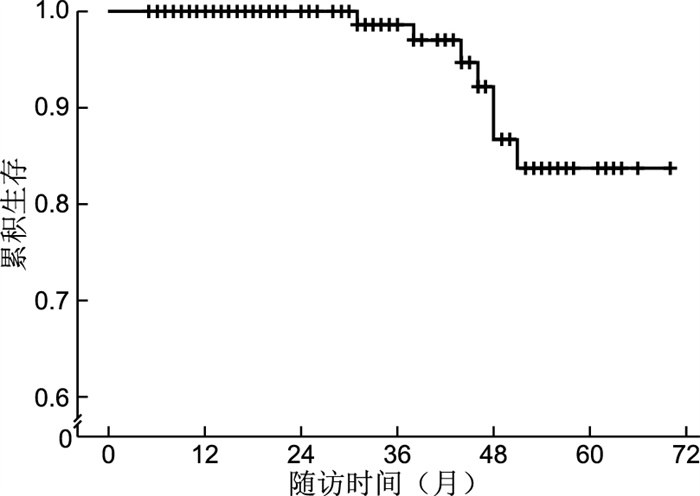
目的 通过分析IgA肾病患者临床及病理资料,探讨影响IgA肾病患者预后的危险因素,为临床提供参考,重视早期诊断及长期随访。 方法 分析2012年12月—2015年12月于上海交通大学医学院附属仁济医院行肾活检确诊为IgA肾病患者的临床及病理资料,每3个月记录患者血肌酐、24小时蛋白尿等指标,血清肌酐水平比基础值升高50%及以上或进入终末期肾病为终点事件,采用Kaplan-Meier生存分析法分析IgA肾病患者肾脏生存率;用Cox回归分析IgA肾病预后的危险因素。 结果 共有163例IgA肾病患者在仁济医院长期随访, 中位随访时间为29个月,活检中位年龄为33岁,男性82例(50.3%),7例(4.3%)患者进入随访终点,4年肾存活率为86.8%。Cox比例风险模型多因素分析结果显示基线收缩压(HR=1.073,95%CI:1.018~1.132,P=0.009)、时间平均蛋白尿(HR=2.123,95%CI:1.367~3.329,P=0.001)是IgA肾病预后的独立影响因素。 结论 多种因素和预后相关,而基线收缩压、时间平均蛋白尿是IgA肾病预后的独立影响因素。 Abstract:Objective To explore the risk factors affecting the prognosis of patients with IgA nephropathy by analyzing the clinical and pathological data of patients with IgA nephropathy, so as to provide clinical reference, and pay attention to early diagnosis and long-term follow-up. Methods The clinical and pathological data of patients with IgA nephropathy who underwent renal biopsy in Renji Hospital from December 2012 to December 2015 were analyzed. Serum creatinine (SCr) and 24-hour urinary protein were recorded every 3 months. The end points were set as SCr increased over 50% or reached end stage renal disease (ESRD) while following up. Kaplan Meier survival analysis was used to analyze the renal survival rate of patients with IgA nephropathy. Cox regression was used to analyze the prognostic risk factors of IgA nephropathy. Results Total 163 IgA nephropathy patients who had long term follow up (median follow up period 29 months) were included. The median age was 33 years old, 82(50.3%) were male, 7 patients (4.3%) reached the end points and 4-year kidney survival rate was 86.8%. The results of multivariate analysis of Cox proportional risk model showed that baseline systolic blood pressure (HR= 1.073, 95% CI: 1.018 - 1.132, P=0.009) and time averaged urinary protein excretion (TA-UPE, HR=2.123, 95% CI: 1.367-3.329, P=0.001) were the independent risk factors for prognosis of IgA nephropathy. Conclusion Various factors are correlated to the prognosis of IgA nephropathy whereas baseline systolic blood pressure and TA-UPE are the independent risk factors. -
Key words:
- IgA nephropathy /
- Prognosis /
- Risk factors
-
表 1 163例IgA肾病患者肾活检时总体人口学及临床指标
Table 1. Demographic and clinical data of 163 patients with IgA nephropathy at renal biopsy
项目 数据 年龄[M(P25, P75),岁] 33.00(28.00, 49.00) 性别(男/女,例) 82/81 BMI[M(P25, P75)] 23.22(20.75, 24.92) 镜检尿红细胞[M(P25, P75), /HP] 23.50(7.90, 60.00) 镜检尿白细胞[M(P25, P75), /HP] 2.90(1.00, 1.50) UPE[M(P25, P75), g/d] 1.27(0.60, 2.46) SBP[M(P25, P75), mm Hg] 123.00(118.00, 133.00) DBP[M(P25, P75), mm Hg] 80.00(71.00, 86.50) Hb(x±s, g/L) 130.41±19.75 SCr[M(P25, P75)μmol/L] 87.00(69.00, 113.00) BUN[M(P25, P75), mmol/L] 5.70(4.50, 6.70) UA(x±s, μmol/L) 356.94±100.04 eGFR[M(P25, P75), mL/(min·1.73 m2)] 85.50(61.75, 109.00) ALB[M(P25, P75), g/L] 39.00(35.00, 42.00) AG[M(P25, P75), mmol/L] 1.36(1.02, 1.80) AC[M(P25, P75), mmol/L] 4.83(4.30, 5.75) IgA(x±s, g/L) 3.26±0.95 IgG(x±s, g/L) 10.79±3.07 IgM[M(P25, P75), g/L] 1.05(0.74, 1.48) 肾小球硬化比例[M(P25, P75), %] 31.00(13.00, 52.00) M1[例(%)] 127(77.9) E1[例(%)] 49(30.1) S1[例(%)] 123(75.5) T1+T2[例(%)] 89(54.9) C1+C2[例(%)] 72(44.2) Lee分级4级以上[例(%)] 100(61.3) 炎症细胞浸润[例(%)] 26(16.0) 注:1 mm Hg=0.133 kPa。 表 2 变量赋值方法
Table 2. Variable assignment method
变量 赋值 性别 男性=1, 女性=2 是否Lee分级≥4级 否=1, 是=2 结局事件 否=1, 是=2 连续变量 以实际值纳入 表 3 IgAN进展影响因素的Cox单因素分析结果
Table 3. Cox univariate analysis of the influencing factors of IgAN progression
项目 B SE Wald χ2 P值 HR值 95%CI 年龄(岁) 0.009 0.032 0.080 0.777 1.009 0.947~1.075 性别 0.453 0.765 0.351 0.554 1.573 0.351~7.045 SBP(mm Hg) 0.075 0.023 10.647 0.001 1.078 1.031~1.128 DBP(mm Hg) 0.023 0.035 0.439 0.508 1.024 0.955~1.097 Hb(g/L) -0.041 0.022 3.442 0.064 0.960 0.910~1.002 BMI 0.018 0.118 0.024 0.877 1.018 0.809~1.282 UPE(g/d) 0.325 0.123 7.008 0.008 1.384 1.088~1.760 TA-UPE(g/d) 0.640 0.204 9.795 0.002 1.896 1.270~2.830 BUN(mmol/L) 0.360 0.103 12.102 0.001 1.433 1.170~1.755 SCr(μmol/L) 0.014 0.004 10.225 0.001 1.014 1.005~1.022 UA(μmol/L) 0.006 0.004 2.012 0.156 1.006 0.998~1.014 TA-UA(μmol/L) 0.012 0.003 12.134 <0.001 1.012 1.005~1.019 eGFR[mL/(min·1.73 m2)] -0.081 0.023 12.242 0.007 0.942 0.902~0.983 ALB(g/L) -0.106 0.053 3.978 0.046 0.900 0.811~0.998 TA-ALB(g/L) -0.308 0.089 11.868 0.001 0.735 0.617~0.876 Lee分级4级以上 0.912 1.081 0.712 0.399 2.490 0.299~20.697 肾小球硬化率(%) 4.350 1.641 7.030 0.008 77.474 3.109~1 930.506 新月体比例(%) 0.006 0.143 0.002 0.966 1.112 0.760~1.333 镜检尿红细胞(/HP) 0.000 0.003 0.014 0.907 1.000 0.995~1.006 镜检尿白细胞(/HP) -0.001 0.017 0.005 0.946 0.999 0.966~1.032 表 4 IgAN进展影响因素的Cox多因素分析结果
Table 4. Cox multivariate analysis of the influencing factors of IgAN progression
项目 B SE Wald χ2 P值 HR值 95%CI SBP(mm Hg) 0.071 0.027 6.774 0.009 1.073 1.018~1.132 TA-UPE(g/d) 0.757 0.227 11.121 0.001 2.123 1.367~3.329 -
[1] HAO Y, ZHAO Y L, HUANG R S, et al. Analysis of the relationship between Oxford classification, IgM deposition and multiple indexes and the adverse prognosis of patients with primary IgA nephropathy and related risk factors[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2019, 17(2): 1234-1239. [2] 范晶, 王玲, 陈雅, 等. IgA肾病在终末期肾病中构成比横断面调查[J]. 上海医学, 2019, 42(2): 70-75.FAN J, WANG L, CHEN Y, et al. Cross-section study of the constituent ratio of IgA nephropathy in End-stage renal disease[J]. Shanghai Med J, 2019, 42(2): 70-75. [3] SUZUKI H. Biomarkers for IgA nephropathy on the basis of multi-hit pathogenesis[J]. Clin Exp Nephrol, 2019, 23(1): 26-31. [4] KIDNEY F N. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: Evaluation, classification, and stratification[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 2002, 39: 1-266. [5] LEVEY A S, STEVENS L A, SCHMID C H, et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate[J]. Ann Intern Med, 2009, 150(9): 604-612. [6] LAA S M K, RAO V M, FRANKLIN W A, et al. IgA nephropathy: Morphologic predictors of progressive renal disease[J]. Hum Pathol, 1982, 13(4): 314-322. [7] TRIMARCHI H, BARRATT J, CATTRAN D C, et al. Oxford Classification of IgA nephropathy 2016: An update from the IgA nephropathy classification working group[J]. Kidney Int, 2017, 91(5): 1014-1021. [8] NI Z H, YUAN Y H, WANG Q, et al. Time-averaged albumin predicts the long-term prognosis of IgA nephropathy patients who achieved remission[J]. J Transl Med, 2014, 12(1): 194. [9] LI M, WANG L, SHI D C, et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis identifies three novel susceptibility loci and reveals ethnic heterogeneity of genetic susceptibility for IgA nephropathy[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2020, 31(12): 2949-2963. [10] MAIXNEROVA D, REILY C, BIAN Q, et al. Markers for the progression of IgA nephropathy[J]. J Nephrol, 2016, 29(4): 535-541. [11] SEVILLANO A M, DIAZ M, CARAVACA-FONTAN F, et al. IgA nephropathy in elderly patients[J]. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol, 2019, 14(8): 1183-1192. [12] NAGARAJU S P, RANGASWAMY D, MAREDDY A S, et al. Impact of body mass index on progression of primary immunoglobulin a nephropathy[J]. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl, 2018, 29(2): 318-325. [13] MORENO J A, YUSTE C, GUTIERREZ E, et al. Haematuria as a risk factor for chronic kidney disease progression in glomerular diseases: A review[J]. Pediatr Nephrol, 2016, 31(4): 523-533. [14] SHU D H, XU F F, SU Z, et al. Risk factors of progressive IgA nephropathy which progress to end stage renal disease within ten years: A case-control study[J]. BMC Nephrol, 2017, 18(1): 11. [15] NAM K H, KIE J H, LEE M J, et al. Optimal proteinuria target for renoprotection in patients with IgA nephropathy[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(7): e101935. [16] 汪晶华, 杨洁, 刘宇, 等. 伴有高血压的IgA肾病临床表现、病理特点及高血压发生的影响因素分析[J]. 解放军医药杂志, 2016, 28(10): 73-76. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBGF201610020.htmWANG J H, YANG J, LIU Y, et, al. A study on clinical and pathological characteristics of iga nephropathy patients associated with hypertension and influential factors of hypertension pathogenesy[J]. Med & Pharm J Chin PL, 2016, 28(10): 73-76. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBGF201610020.htm [17] SHI S F, WANG S X, JIANG L, et al. Pathologic predictors of renal outcome and therapeutic efficacy in IgA nephropathy: Validation of the oxford classification[J]. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol, 2011, 6(9): 2175-2184. [18] HAO Y, ZHAO Y L, HUANG R S, et al. Analysis of the relationship between Oxford classification, IgM deposition and multiple indexes and the adverse prognosis of patients with primary IgA nephropathy and related risk factors[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2019, 17(2): 1234-1239. [19] LV J C, YANG Y H, ZHANG H, et al. Prediction of outcomes in crescentic IgA nephropathy in a multicenter cohort study[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2013, 24: 2118-2125. [20] ZHANG W, ZHOU Q, HONG L Y, et al. Clinical outcomes of IgA nephropathy patients with different proportions of crescents[J]. Medicine, 2017, 96(11): e6190. [21] 王蔚, 李贵森, 邹玉蓉, 等. IgA肾病呈单纯性血尿和/或轻度蛋白尿的病理特点及预后分析[J]. 实用医院临床杂志, 2017, 14(6): 94-97. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYLC201706024.htmWANG W, LI G S, ZOU Y R, et al. Pathological features and outcomes of IgA nephropathy with hematuria and / or minimal pro-teinuria[J]. Practical Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2017, 14(6): 94-97. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYLC201706024.htm [22] 陈蕊, 刘昌华, 高波. 无症状尿检异常患者的临床病理和预后分析[J]. 中华全科医学, 2012, 10(12): 1845-1846. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYQY201212009.htmCHEN R, LIU C H, GAO B, et al. Clinicopathological and prognostic analysis of patients presented with asymptomatic urinary abnormalities[J]. Chinese general practice, 2012, 10(12): 1845-1846. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYQY201212009.htm -





 下载:
下载: