Application of MIMICS software three-dimensional reconstruction in complex segmental resection of lung adenocarcinoma
-
摘要:
目的 评价交互式医学图像控制系统(MIMICS)软件行三维重建联合胸腔镜在肺腺癌复杂肺段切除术中的应用价值。 方法 以2016年1月—2017年6月在河北医科大学第四医院进行单纯胸腔镜肺段切除术的42例患者为对照组,以2017年7月—2018年7月期间行MIMICS软件三维重建联合胸腔镜肺段切除术的48例患者为观察组。比较2组围手术期临床指标、手术并发症;比较术前和拔除胸腔引流管后2组肺功能指标,包括1 s用力呼气容积(FEV1)、用力肺活量(FVC)、每分钟最大通气量(MVV)。 结果 2组患者病灶数量、结节性质差异无统计学意义(均P>0.05),观察组并发症发生率(10.42%,5/48)显著低于对照组(28.57%,12/42,P<0.05)。观察组手术时间、术中出血量、术后胸管留置时间、术后住院时间显著短于对照组(均P<0.05)。2组术前FEV1、FVC、MVV差异无统计学意义(均P>0.05);拔除胸腔引流管后,2组患者肺功能均显著低于术前,但观察组FEV1、FVC、MVV显著高于对照组[(1.67±0.52) L vs. (1.38±0.69) L, (1.73±0.64) L vs. (1.48±0.51) L, (54.27±7.14) L/min vs. (50.36±6.08) L/min, 均P < 0.05]。 结论 对于行复杂肺段切除术的肺腺癌患者,采用MIMICS软件在术前进行三维重建有利于在术中分辨肺部解剖结构,确定结节位置,有利于提高手术准确性,缩短手术时间,减少并发症,减轻手术对肺功能的损伤,利于术后康复。 Abstract:Objective To evaluate the clinical value of Materialise's interactive medical image control system (MIMICS) software 3D reconstruction combined with thoracoscopy in complex segmental resection of lung adenocarcinoma. Methods The control group comprised 42 patients who underwent thoracoscopic segmentectomy in our hospital from January 2016 to June 2017. The observation group was composed of 48 patients who underwent MIMICS software 3D reconstruction combined with thoracoscopic segmentectomy in the Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University from July 2017 to July 2018. The perioperative clinical parameters and operative complications were compared between the two groups. The pulmonary function indexes before operation and after removal of thoracic drainage tube were compared, including forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1), forced vital capacity (FVC) and maximum voluntary ventilation (MVV) per minute. Results No significant difference was found in the number of lesions and the nature of nodules between the two groups (P>0.05). The incidence of complications in the observation group (10.42%, 5/48) was significantly lower than that in the control group (28.57%, 12/42, P < 0.05). The average operation time, average intraoperative bleeding volume, average post-operative thoracic tube indwelling time and average post-operative hospital stay in the observation group were significantly shorter than those in the control group (all P < 0.05). There was no significant difference in FEV1, FVC and MVV between the two groups before the operation (all P>0.05). After removal of the thoracic drainage tube, the pulmonary function indexes of the two groups were significantly lower than those before the operation. The FEV1, FVC and MVV of the observation group were significantly higher than those of the control group [(1.67±0.52) L vs. (1.38±0.69) L, (1.73±0.64) L vs. (1.48±0.51) L, (54.27±7.14) L/min vs. (50.36±6.08) L/min, all P < 0.05)]. Conclusion For patients with pulmonary adenocarcinoma undergoing complex segmental resection, using MIMICS software 3D reconstruction before operation can help distinguish the anatomical structure of the lungs, determine the location of the nodules, improve the accuracy of the operation, shorten the operation time, reduce complications, reduce the damage of the lung function caused by the operation and facilitate rehabilitation after the operation. -
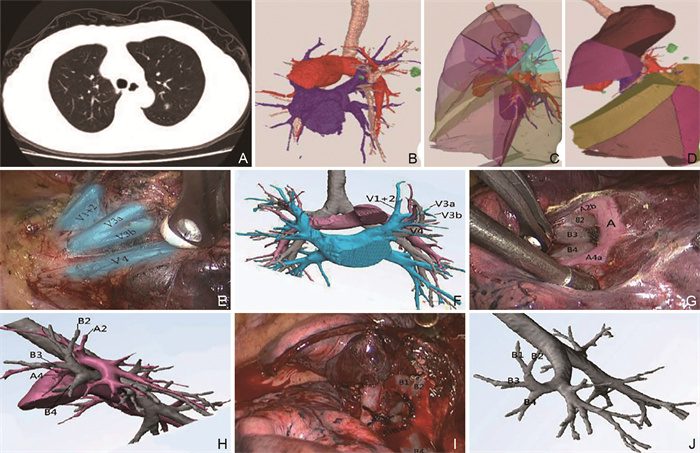
图 1 术前三维重建与术中解剖对照
注:患者男性,65岁,肺腺癌早期。A为CT平扫水平面图像,可见结节位于左上肺后段;B为MIMICS三维重建显示肺动静脉、支气管与肺结节图像;C为MIMICS三维重建20%透明度下肺段/亚段划分(不同颜色标记不同肺段);D为规划手术路径,模拟切除肺段/亚段;E、F为三维重建下胸腔镜肺段切除显示3支上肺静脉;G、H分离显露A2b、A4a及B4、B3分叉;I、J为离断后显露B1、B2、B4。
Figure 1. Comparison of preoperative three-dimensional reconstruction and intraoperative anatomy
表 1 2组行肺段切除术患者围手术期临床指标比较(x±s)
Table 1. Comparison of perioperative clinical indicators between two groups of patients undergoing segmentectomy(x±s)
组别 例数 手术时间(min) 术中出血量(mL) 术后胸管留置时间(d) 住院时间(d) 对照组 42 128.36±11.29 96.25±14.17 7.96±1.61 8.65±1.43 观察组 48 115.36±8.79 88.64±10.92 7.11±1.45 7.34±1.11 t值 6.133 2.872 2.635 4.885 P值 < 0.001 0.005 0.010 < 0.001 表 2 2组行肺段切除术患者切除肺段分布(例)
Table 2. Distribution of resected lung segments in two groups of patients undergoing segmentectomy (cases)
切除肺段 对照组(42例) 观察组(48例) 右上肺分段 S1 0 3 S2 2 3 S3 4 5 S1+S2 5 4 右基底分段 S7+S8 3 3 S9+S10 5(1例术中转S8+S9+S10) 6 S6+S9+S10 1 2 左上肺固有段分段 S1+2(a)(亚段) 2(1例术中转S1+S2) 6 S1+2(c)(亚段) 0 3 S3 7 1 S1+S2 5(2例术中转S1+S2+S3) 1 S1+S2+S3 4 3 左侧基底分段 S8 1 6 S9+S10 3(1例术中转S7+S8+S9+S10) 2 表 3 2组行肺段切除术患者肺功能指标对比(x±s)
Table 3. Comparison of pulmonary function indexes between two groups of patients undergoing segmentectomy(x±s)
组别 例数 FEV1(L) FVC(L) MVV(L/min) 术前 拔除胸腹引流管后 术前 拔除胸腹引流管后 术前 拔除胸腹引流管后 对照组 42 2.78±0.92 1.38±0.69a 3.06±0.72 1.48±0.51a 81.29±4.75 50.36±6.08a 观察组 48 2.85±0.97 1.67±0.52a 2.94±0.66 1.73±0.64a 79.76±5.22 54.27±7.14a t值 0.350 2.268 0.825 2.029 1.446 2.776 P值 0.727 0.026 0.412 0.045 0.152 0.007 注:与同组术前比较,aP<0.05。 -
[1] AOKAGE K, SAJI H, SUZUKI K, et al. A non-randomized confirmatory trial of segmentectomy for clinical T1N0 lung cancer with dominant ground glass opacity based on thin-section computed tomography (JCOG1211)[J]. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2017, 65(5): 267-272. doi: 10.1007/s11748-016-0741-1 [2] 颜威, 奚小冰, 蒋涛, 等. 基于Mimics软件构建桡骨远端骨折三维模型[J]. 中国数字医学, 2020, 15(7): 95-97, 108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YISZ202007031.htmYAN W, XI X B, JIANG T, et al. Construction of the 3D model of distal radius fracture based on mimics software[J]. China Digital Medicine, 2020, 15(7): 95-97, 108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YISZ202007031.htm [3] 陆舜, 虞永峰, 纪文翔. 2015年肺癌诊疗指南: 共识和争议[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2016, 41(1): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JFJY201601002.htmLU S, YU Y F, JI W X. Guidelines for lung cancer in 2015: Consensus and controversy[J]. Medical Journal of Chinese People's Liberation Army, 2016, 41(1): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JFJY201601002.htm [4] 佘晓伟, 顾云斌, 徐春, 等. 3D-CTBA及3D-VATS单操作孔行解剖性肺段切除治疗非小细胞肺癌[J]. 中国肺癌杂志, 2017, 20(9): 598-602. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FAIZ201709002.htmSE X W, GU Y B, XU C, et al. Combining 3D-CTBA and 3D-VATS single-operation-hole to anatomical segmentectomy in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Chinese Journal of Lung Cancer, 2017, 20(9): 598-602. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FAIZ201709002.htm [5] DZIEDZIC R, ZUREK W, MARJANSKI T, et al. Stage I non-small-cell lung cancer: Long-term results of lobectomy versus sublobar resection from the Polish National Lung Cancer Registry[J]. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg, 2017, 52(2): 363-369. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezx092 [6] 王丽. 中国原发性肺癌诊疗规范(2015年版)解读[J]. 世界临床药物, 2016, 37(7): 433-436. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWHH201607001.htmWANG L. Interpretation of Chinese lung cancer treatment guidelines(2015 edition)[J]. World Clinical Drugs, 2016, 37(7): 433-436. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWHH201607001.htm [7] 陈亮, 吴卫兵. 胸腔镜解剖性肺段切除术技术要点[J]. 中国肺癌杂志, 2016, 19(6): 377-381. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FAIZ201606018.htmCHEN L, WU W B. The main technical points of thoracoscopic anatomical lung segment resection[J]. Chinese Journal of Lung Cancer, 2016, 19(6): 377-381. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FAIZ201606018.htm [8] 段亮, 朱余明, 胡学飞, 等. 52例单孔胸腔镜解剖性肺段切除术临床分析和技术探讨[J]. 中华胸心血管外科杂志, 2017, 33(4): 208-211. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-4497.2017.04.004DUAN L, ZHU Y M, HU X F, et al. Uniportal video-assisted thoraeoscopic anatomic segmentectomy for lung diseases: 52 cases report[J]. Chinese Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, 2017, 33(4): 208-211. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-4497.2017.04.004 [9] 崔子涵. 三维重建软件Exoview在解剖性肺段切除术中的应用与研究[D]. 苏州: 苏州大学, 2020.CUI Z H. Application and study of 3D reconstruction software Exoview in anatomical segmentectomy[D]. Suzhou: Soochow University, 2020. [10] 王德国, 李洋, 尹红灵, 等. 椎体成形术填充剂最优化分布模式三维有限元分析[J]. 中国骨伤, 2021, 34(1): 26-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGU202101006.htmWANG D G, LI Y, YIN H L, et al. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of optimal distribution model of fillers in vertebroplasty[J]. China Journal of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, 2021, 34(1): 26-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGU202101006.htm [11] CHEN D, CHEN C H, TANG L, et al. Three-dimensional reconstructions in spine and screw trajectory simulation on 3D digital images: A step by step approach by using Mimics software[J]. J Spine Surg, 2017, 3(4): 650-656. [12] 马立敏, 周烨, 周霞, 等. 3D打印技术辅助个性化定制钢板在膝关节周围骨肿瘤中的应用[J]. 中国数字医学, 2019, 14(2): 5-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YISZ201902003.htmMA L M, ZHOU Y, ZHOU X, et al. Application of 3D print personalized titanium plates in the treatment of bone tumor around the knee[J]. China Digital Medicine, 2019, 14(2): 5-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YISZ201902003.htm [13] HOU N Z, LI M Z, HE L, et al. Predicting 30-days mortality for MIMIC-Ⅲ patients with sepsis-3: A machine learning approach using XGboost[J]. J Transl Med, 2020, 18(1): 462. [14] AATLAY H A, CANAT H L, VLKEY V, et al. Impact of personalized three-dimensional 3D printed pelvicalyceal system models on patient information in percutaneous nephrolithotripsy surgery: A pilot study[J]. Int Braz J Urol, 2017, 43(3): 470-475. [15] 张书新, 刘阳. 个人电脑上肺癌64排CT数据的三维重建及虚拟手术[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2016, 36(4): 562-566. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DYJD201604022.htmZHANG S X, LIU Y. Computer-based three-dimensional reconstruction of lung cancer using 64-slice CT scanning data and virtual surgery[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2016, 36(4): 562-566. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DYJD201604022.htm [16] 王黎彬, 戚维波. 三维重建及虚拟手术规划在胸腔镜解剖性肺段切除术中的应用进展[J]. 浙江医学, 2019, 41(5): 86-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJYE201905032.htmWANG L S, QI W B. Application progress of three-dimensional reconstruction and virtual surgical planning in thoracoscopic anatomic segmentectomy[J]. Zhejiang Medical Journal, 2019, 41(5): 86-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJYE201905032.htm [17] 李小军, 朱潇, 杏福宝, 等. 三维重建及3D打印在微创肺外科中的应用[J]. 中华全科医学, 2020, 18(7): 1190-1194. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.001462LI X J, ZHU X, XING F B, et al. Application of three-dimensional reconstruction and 3D printing in minimally invasive lung surgery[J]. Chinese general practice, 2020, 18(7): 1190-1194. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.001462 -





 下载:
下载: