Expression of miRNA-107 in peripheral blood of children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
-
摘要:
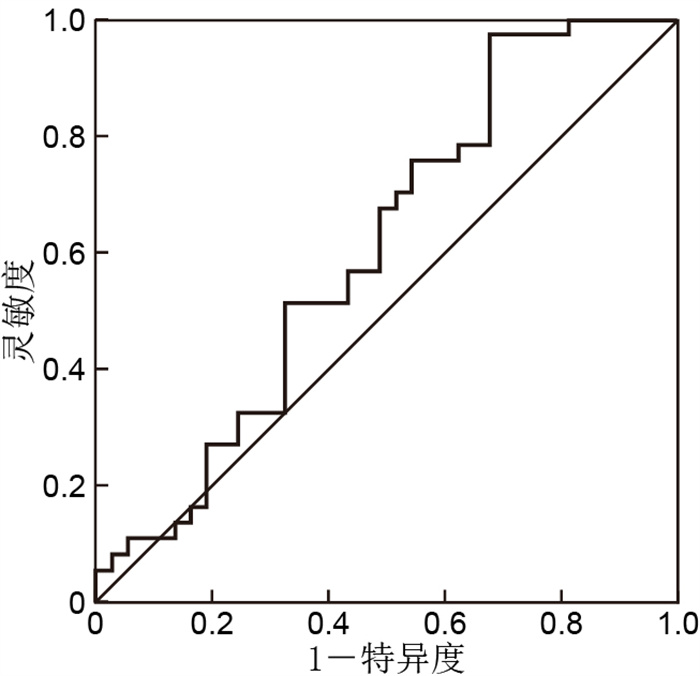
目的 探讨miRNA-107、miR-34c-3p在注意缺陷多动障碍(ADHD)儿童中的表达意义。 方法 选取2018年1月—2019年9月就诊于杭州市儿童医院儿童保健发育行为专科门诊的ADHD儿童共37名,设为ADHD组,74例杭州市儿童医院同期健康体检儿童设为健康对照组。用定量逆转录-聚合酶链反应(RT-PCR)方法检测外周循环血中miRNA-107、miR-34c-3p相对表达量;根据ROC曲线分析miRNA-107在诊断ADHD中的灵敏度及特异度;分析miRNA-107表达量与ADHD核心症状之间的相关性。 结果 ADHD儿童外周循环中miRNA-107的相对表达量降低,与健康对照组比较差异有统计学意义(4.06±1.57 vs. 4.62±1.30,t=1.994,P=0.049),miR-34c-3p相对表达量与健康对照组比较差异无统计学意义;miRNA-107的AUC为0.609,灵敏度为97.3%,特异度为67.6%;相关性分析显示,ADHD女童的miRNA-107表达水平与注意缺陷程度呈负相关关系(r=-0.861, P < 0.05)。 结论 MiRNA-107可能是潜在的诊断儿童ADHD的生物标记,具有一定的诊断意义。 Abstract:Objective To measure the expression levels of miRNA-107 and miR-34c-3p in children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Methods From January 2018 to September 2019, 37 children were admitted to the Developmental Behaviour Clinic of Children's Health Care in Hangzhou Children's Hospital and were set as the ADHD group. Seventy-four healthy children in our hospital were set as the healthy control group. The relative expression levels of miRNA-107 and miR-34c-3p in peripheral blood were detected by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. The sensitivity and specificity of miRNA-107 in diagnosing ADHD were analysed according to the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. The correlation between miRNA-107 expression and ADHD core symptoms was analysed. Results The relative expression of miRNA-107 in peripheral circulation was significantly lower in the ADHD group than in the control group (4.06±1.57 vs. 4.62±1.30, t=1.994, P=0.049), whereas miR-34c-3p showed no significant difference. The AUC of miRNA-107 was 0.609, the sensitivity was 97.3% and the specificity was 67.6%. Correlation analysis showed that the expression level of miRNA-107 in ADHD girls was negatively correlated with the degree of attention deficit (r=-0.861, P < 0.05). Conclusion MiRNA-107 may be a potential biomarker of ADHD and has a certain diagnostic significance. -
Key words:
- Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder /
- MicroRNA-107 /
- Diagnoses /
- Biomarker
-
表 1 2组儿童危险因素、身高、体重、年龄情况比较
Table 1. Comparison of risk factors, height, weight and age between the two groups
组别 例数 是否早产[例(%)] 是否顺产[例(%)] 胎龄(x±s, 周) 多胞胎状况[例(%)] 是 否 是 否 是 否 ADHD组 37 2(5.41) 35(94.59) 30(81.08) 7(18.92) 41.50±2.24 4(10.81) 33(89.19) 对照组 74 6(8.11) 68(91.89) 60(81.08) 14(18.92) 41.60±2.03 8(10.81) 66(89.19) 统计量 0.017a 0.001a 0.236b 0.105a P值 0.604 0.995 0.814 0.991 组别 例数 出生情况[例(%)] 身高(x±s, cm) 体重(x±s, kg) 年龄(x±s, 岁) 正常 疾病 ADHD组 37 36(97.30) 1(2.70) 123.60±25.40 31.30±5.70 8.13±3.56 对照组 74 72(97.30) 2(2.70) 122.90±20.30 31.60±5.10 8.45±3.77 统计量 0.385a 0.157b 0.281b 0.429b P值 0.924 0.875 0.779 0.669 注:a为χ2值,b为t值。 表 2 PCR引物序列
Table 2. PCR primer sequence
引物名称 引物序列 miR-15b 5'-TACTGTAGCAGCACATCAT-3' miR-15bRT 5'-GTCGTATCCAGTGChGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGAT ACGACTGTAAA-3' hsa-miR-34c-3p 5'-GGTGGAATCACTAACCACACG-3' hsa-miR-34c-3p-RT 5'-GTGCAGGGTCCGAGGT-3' miRNA-107 5'-GCCGCAGCAGCATTGTACAGGG-3' hsa-miRNA-107-RT 5'-GTCGTATGCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGCAT ACGACTGATAG-3' RNU6RT 5'-AAAATATGGAACGCT-3' RNU6a 5'-AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT-3' RNU6s 5'-CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA-3' 表 3 ADHD组及健康对照组儿童miRNA-107、miR-34c-3p表达水平比较(x±s)
Table 3. The expression levels of miRNA-107 and miR- 34C -3p in children with ADHD and healthy controls(x±s)
组别 例数 has-miRNA-107 hsa-miR-34c-3p ADHD组 37 4.06±1.57 1.76±0.03 健康对照组 74 4.62±1.30 1.77±0.03 t值 1.994 1.656 P值 0.049 0.101 表 4 不同性别ADHD儿童miRNA-107表达量与SNAP-Ⅳ量表得分的相关性(r值)
Table 4. Correlation between the expression of miRNA-107 and the score of SNAP- Ⅳ in ADHD children of different genders (r value)
项目 注意缺陷 多动冲动 男童miRNA-107表达量 0.245 0.244 女童miRNA-107表达量 -0.861a 0.505 注:aP < 0.05。 -
[1] BAKER A S, FREEMAN M P. Management of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder during pregnancy[J]. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am, 2018, 45(3): 495-509. doi: 10.1016/j.ogc.2018.04.010 [2] 李世明, 冯为, 方芳, 等. 中国儿童注意缺陷多动障碍患病率meta分析[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2018, 39(7): 993-998. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2018.07.024LI S M, FENG W, FANG F, et al. Prevalence of attention deficit and hyperactivity disorder in children in China: a systematic review and Meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Epidemiology, 2018, 39(7): 993-998. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2018.07.024 [3] ADLER L A, FARAONE S V, SPENCER T J, et al. The structure of adult ADHD[J]. Int J Methods Psychiatr Res, 2017, 26(1): e1555. doi: 10.1002/mpr.1555 [4] CAO T, ZHEN X C. Dysregulation of miRNA and its potential therapeutic application in schizophrenia[J]. CNS Neurosci Ther, 2018, 24(7): 586-597. doi: 10.1111/cns.12840 [5] 赵旭凡, 杨红菊. 微核糖核酸在非酒精性脂肪性肝病中的研究进展[J]. 中国基层医药, 2019, 26(7): 893-896.ZHAO X F, YANG H J. Research progress of miRNA in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Primary Medicine and Pharmacy, 2019, 26(7): 893-896. [6] BATTLE D E. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders(DSM)[J]. Codas, 2013, 25(2): 191-192. [7] AL-KAFAJI G, SAID H M, ALMA M A, et al. Blood-based microRNAs as diagnostic biomarkers to discriminate localized prostate cancer from benign prostatic hyperplasia and allow cancer-risk stratification[J]. Oncol Lett, 2018, 16(1): 1357-1365. [8] PAUL S, REYES P R, GARRZA B S, et al. MicroRNAs and child neuropsychiatric disorders: A brief review[J]. Neurochem Res, 2020, 45(2): 232-240. doi: 10.1007/s11064-019-02917-y [9] ZADEHBAGHERI F, HOSSEINI E, BAGHERI-HOSSEINABADI Z, et al. Profiling of miRNAs in serum of children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder shows significant alterations[J]. J Psychiatr Res, 2019, 109(10): 185-192. [10] VASU M M, SUMITHA P S, RAHNA P, et al. MicroRNAs in autism spectrum disorders[J]. Curr Pharm Des, 2019, 25(41): 4368-4378. [11] HU Y, EHLI E A, BOOMSMA D I. MicroRNAs as biomarkers for psychiatric disorders with a focus on autism spectrum disorder: Current progress in genetic association studies, expression profiling, and translational research[J]. Autism Res, 2017, 10(7): 1184-1203. doi: 10.1002/aur.1789 [12] MAES M, ANDERSON G, BETANCORT MEDINA S R, et al. Integrating autism spectrum disorder pathophysiology: Mitochondria, vitamin A, CD38, oxytocin, serotonin and melatonergic alterations in the placenta and gut[J]. Curr Pharm Des, 2019, 25(41): 4405-4420. [13] WOHLFARTH C, SCHMITTECKERT S, HARTLE J D, et al. Mir-16 and Mir-103 impact 5-HT4 receptor signalling and correlate with symptom profile in irritable bowel syndrome[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 14680. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-13982-0 [14] OSES M, MARGARETO SANCHEZ J, et al. Circulating miRNAs as biomarkers of obesity and obesity-associated comorbidities in children and adolescents: A systematic review[J]. Nutrients, 2019, 11(12): 2890. doi: 10.3390/nu11122890 [15] KANDEMIR H, ERDAL M E, SELEK S, et al. Evaluation of several micro RNA (miRNA) levels in children and adolescents with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder[J]. Neuroscience Letters, 2014, 580: 158-162. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2014.07.060 [16] WU L H, CHENG W, YU M, et al. Nr3C1-Bhlhb2 Axis dysregulation is involved in the development of attention deficit hyperactivity[J]. Mol Neurobiol, 2017, 54(2): 1196-1212. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9679-z [17] DICKSON D A, PAULUS J K, MENSAH V, et al. Reduced levels of miRNAs 449 and 34 in sperm of mice and men exposed to early life stress[J]. Transl Psychiatry, 2018, 8(1): 101. doi: 10.1038/s41398-018-0146-2 [18] 王海明, 王建华. 微小RNA与胆管癌关系的研究进展[J]. 癌症进展, 2020, 18(10): 989-992, 1018. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AZJZ202010005.htmWANG H M, WANG J H. Research progress on the relationship between microrNA and cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Oncology Progress, 2020, 18(10): 989-992, 1018. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AZJZ202010005.htm [19] LAMBEZ B, HARWOOD-GROSS A, GOLUMBIC E Z, et al. Non-pharmacological interventions for cognitive difficulties in ADHD: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Psychiatr Res, 2020, 12(10): 40-55. [20] WANG T, SHI F, JIN Y, et al. Abnormal changes of brain cortical anatomy and the association with plasma microRNA107 level in amnestic mild cognitive impairment[J]. Front Aging Neurosci, 2016, 18(8): 112. [21] WANG T, SHI F, JIN Y, et al. Abnormal changes of brain cortical anatomy and the association with plasma microRNA107 level in amnestic mild cognitive impairment[J]. Front Aging Neurosci, 2016, 8: 112. DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2016.00112. -





 下载:
下载: