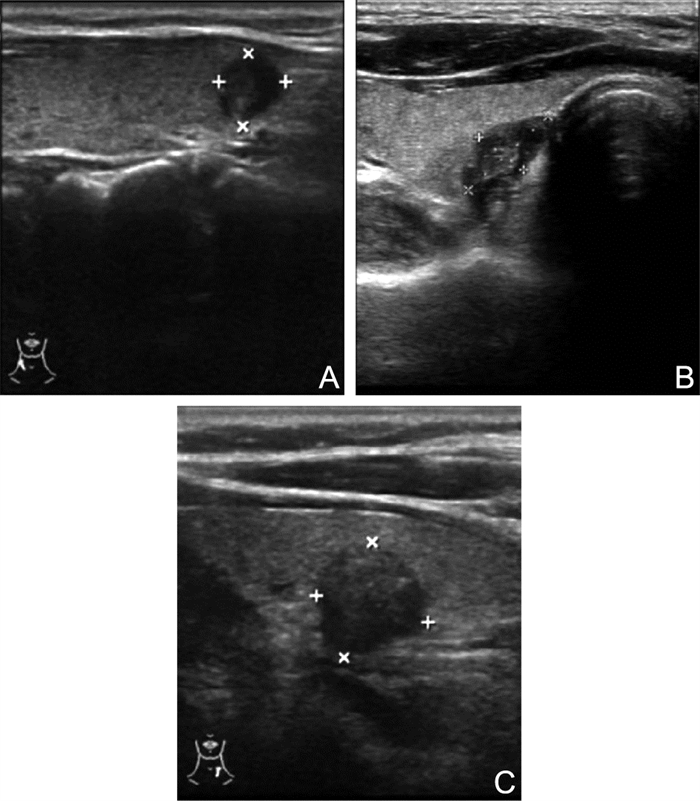
Diagnostic value of preoperative ultrasound combined with BRAF gene in lymph node staging in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
-
摘要:
目的 探讨超声联合BRAF基因突变检测在甲状腺乳头状癌(PTC)术前诊断率方面的差异, 为临床是否选择手术治疗及其手术方式的选择提供科学、可靠的影像学及分子学依据。 方法 回顾性分析2020年1-10月河南大学第一附属医院收治的120例PTC患者, 根据美国癌症联合委员会(AJCC)甲状腺癌分期系统标准, 将PTC患者分为N0、N1a与N1b期。120例患者术前均进行超声检查, 进行甲状腺切除手术治疗, 以病理组织学诊断结果为金标准。分析PTC超声声像图、患者性别、年龄、BRAF基因检测结果及N0与N1组, N1b与非N1b间的差异; 采用单因素和多因素logistic回归分析对可能影响PTC N分期的相关因素进行分析。 结果 120例PTC患者中, 63例患者病理诊断为N0期, 38例为N1a期, 19例为N1b期, N1期共57例; 超声诊断结果显示, 57例为N0期, 45例为N1a期, 18例为N1b期, N1期共63例。术前超声评估N分期与病理诊断结果, N分期具有一致性, 差异有统计学意义(Kappa=0.725, P < 0.05)。N0期和N1期患者的年龄、肿瘤直径、BRAF基因突变差异有统计学意义(均P < 0.05)。非N1b期和N1b期患者的肿瘤直径、多发病灶、包膜外侵犯比较差异有统计学意义(均P < 0.05)。多因素logistic回归分析结果显示, 年龄、肿瘤直径、BRAF基因突变是N0期和N1期的影响因素(均P < 0.05);肿瘤直径>1 cm、多发病灶、包膜外侵犯是影响N1b期的独立危险因素(均P < 0.05)。 结论 结合超声检查和年龄、肿瘤直径、BRAF基因、多发病灶、包膜外侵犯临床相关影响指标与PTC的N分期有关。术前超声检查可用于PTC N分期评估, 有助于辅助临床诊断与治疗。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the difference in the preoperative diagnostic rate of papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) by using ultrasound combined with BRAF gene mutation detection, and to provide scientific and reliable imaging and molecular basis for the selection of surgical treatment and surgical method. Methods A total of 120 patients with PTC admitted to our hospital from January to October 2020 were retrospectively analysed.According to the American Joint Committee on Cancer thyroid cancer staging system standard, patients with PTC were divided into three groups: N0, N1a and N1b.All 120 patients underwent preoperative ultrasound examination and thyroidectomy, and the pathological diagnosis was the gold standard.PTC ultrasonography, gender, age, BRAF gene test results and Hashimoto's thyroiditis background were analysed between N0 and N1 groups and between N1b and non-N1b groups.Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis were used to compare the related factors that may affect PTC N staging. Results Amongst 120 PTC patients, 63 patients were pathologically diagnosed as N0 stage, 38 as N1a stage, 19 as N1b stage and 57 as N1 stage.Ultrasonic diagnosis showed that 57 cases were N0 stage, 45 cases were N1a stage, 18 cases were N1b stage, and 63 cases were N1 stage.Preoperative ultrasound assessment of N stage was consistent with pathological diagnosis, and the difference was statistically significant (Kappa=0.725, P < 0.05).There were significant differences in age, tumour diameter and BRAF gene mutation between N0 and N1 patients (all P < 0.05).There were significant differences between non-N1B stage and N1b stage patients in tumour diameter, multiple lesions and extracapsular invasion (all P < 0.05).Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that age, tumour diameter and BRAF gene mutation were independent influencing factors for N0 stage and N1 stage (all P < 0.05), while tumour diameter>1 cm, multiple lesions and extracapsular invasion were independent risk factors for N1b stage (all P < 0.05). Conclusion Combined with ultrasound examination, age, tumour diameter, BRAF gene, multiple lesions and extracapsular invasion, clinical-related influencing indicators are correlated with N stage of PTC.Preoperative ultrasonography can be used to evaluate PTC N staging, which is helpful to assist clinical diagnosis and treatment. -
Key words:
- Ultrasonography /
- Papillary thyroid carcinoma /
- N stages
-
表 1 术前超声诊断PTC分期与病理诊断结果比较(例)
Table 1. Comparison of preoperative ultrasound diagnosis of PTC staging and pathological results (cases)
超声N分期 病理N分期 合计 N0期 N1a期 N1b期 N0期 51 6 0 57 N1a期 10 28 7 45 N1b期 2 4 12 18 合计 63 38 19 120 注:2种方法比较,Kappa=0.725,P=0.008。 表 2 N0期和N1期PTC患者临床特征比较[例(%)]
Table 2. Comparison of clinical characteristics of patients with PTC in N0 and N1 stages [cases (%)]
项目 类别 N0期
(n=63)N1期
(n=57)χ2值 P值 性别 男性 14(22.22) 12(21.05) 0.024 0.877 女性 49(77.78) 45(78.95) 年龄(岁) <55 36(57.14) 51(89.47) 15.689 < 0.001 ≥55 27(42.86) 6(10.53) 肿瘤直径(cm) >1 26(41.27) 36(63.16) 5.741 0.017 ≤1 37(58.73) 21(36.84) 多发病灶 是 20(31.75) 18(31.58) < 0.001 0.984 否 43(68.25) 39(68.42) 包膜外侵犯 是 21(33.33) 20(35.09) 0.041 0.840 否 42(66.67) 37(64.91) 慢性桥本甲状腺炎 是 22(34.92) 20(35.09) < 0.001 0.985 否 41(65.08) 37(64.91) BRAF基因 阳性 25(39.68) 37(64.91) 9.224 0.010 阴性 14(22.22) 11(19.30) 不确定 24(38.10) 9(15.79) 表 3 非N1b期和N1b期患者的临床特征比较[例(%)]
Table 3. Comparison of clinical characteristics of patients with non-N1b stage and N1b stage [cases (%)]
项目 类别 非N1b期
(n=101)N1b期
(n=19)χ2值 P值 性别 男性 21(20.79) 5(26.32) 0.287 0.592 女性 80(79.21) 14(73.68) 年龄(岁) <55 86(85.15) 16(84.21) 0.011 0.916 ≥55 15(14.85) 3(15.79) 肿瘤直径(cm) >1 40(39.60) 15(78.95) 9.971 0.002 ≤1 61(60.40) 4(21.05) 多发病灶 是 28(27.72) 13(68.42) 11.776 0.001 否 73(72.28) 6(31.58) 包膜外侵犯 是 36(35.64) 15(78.95) 12.271 < 0.001 否 65(64.36) 4(21.05) 慢性桥本甲状腺炎 是 35(34.65) 7(36.84) 0.034 0.854 否 66(65.35) 12(63.16) BRAF基因 阳性 45(44.55) 8(42.11) 0.126 0.939 阴性 23(22.77) 4(21.05) 不确定 33(32.67) 7(36.84) 表 4 N0期和N1期的logistic回归分析结果
Table 4. Logistic regression analysis results of N0 and N1 stages
项目 B SE Wald χ2 P值 OR(95% CI) 年龄 1.854 0.528 12.334 < 0.001 6.386(2.269~17.973) 肿瘤直径 0.894 0.418 4.565 0.033 2.444(1.077~5.547) BRAF基因突变(阳性) 1.165 0.508 5.257 0.022 3.206(1.184~8.677) BRAF基因突变(阴性) 0.441 0.609 0.524 0.469 1.555(0.417~5.133) 注:因变量为是否N1期,否=0,是=1;自变量赋值如下,年龄 < 55岁=1,≥55岁=0;肿瘤直径>1 cm=1,≤1 cm=0;BRAF基因突变,不确定为(0,0),阳性为(1,0),阴性为(0,1)。 表 5 N1b与非N1b的logistic回归分析结果
Table 5. Logistic regression analysis results of N1b and non-N1b
项目 B SE Wald χ2 P值 OR(95% CI) 肿瘤直径>1 cm 1.296 0.641 4.090 0.043 3.653(1.041~12.824) 多发病灶 1.295 0.588 4.853 0.028 3.651(1.154~11.557) 包膜外侵犯 1.497 0.636 5.532 0.019 4.468(1.283~15.556) 注:因变量为是否N1b期,否=0,是=1;自变量赋值如下,肿瘤直径>1 cm=1,≤1 cm=0;多发病灶,是=1,否=0;包膜外侵犯,是=1,否=0。 -
[1] BASTÉ N, MORA M, GRAU J J. Emerging systemic antitarget treatment for differentiated thyroid carcinoma[J]. Curr Opin Oncol, 2021, 33(3): 184-195. doi: 10.1097/CCO.0000000000000727 [2] EDAFE O, BALASUBRAMANIAN S P. A systematic review of the incidence of thyroid carcinoma in patients undergoing thyroidectomy for thyrotoxicosis[J]. Clin Otolaryngol, 2020, 45(6): 452-453. [3] BURTT J J, RICKARD M, MCALLISTER A, et al. Projecting thyroid cancer risk to the general public from radiation exposure following hypothetical severe nuclear accidents in Canada[J]. J Radiol Prot, 2020, 40(4): 856-858. [4] WU J H, OU L, ZHANG C Y. Comparison of 68Ga-FAPI and 18F-FDG PET/CT in metastases of papillary thyroid carcinoma[J]. Endocrine, 2021, 73(3): 767-768. doi: 10.1007/s12020-021-02668-3 [5] ZOU Y, ZHANG H L, LI W F, et al. Prediction of ipsilateral lateral cervical lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma: A combined dual-energy CT and thyroid function indicators study[J]. BMC Cancer, 2021, 21(1): 221. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-07951-0 [6] LIU C H, ZHANG L, LIU Y W, et al. Ultrasonography for the prediction of high-volume lymph node metastases in papillary thyroid carcinoma: Should surgeons believe ultrasound results?[J]. World J Surg, 2020, 44(12): 4142-4148. doi: 10.1007/s00268-020-05755-0 [7] 孙威, 贺亮, 张浩. 美国癌症联合委员会甲状腺癌分期系统(第8版)更新解读[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2017, 37(3): 255-258.SUN W, HE L, ZHANG H. Interpretations on the updates of American Joint Committee on cancer staging system (8th edition) for thyroid cancer[J]. Chinese Journal of Practical Surgery, 2017, 37(3): 255-258. [8] 管晓蕾, 王萍, 于清, 等. BRAFV600E突变对甲状腺乳头状癌HMGB1表达的影响[J]. 中华全科医学, 2017, 15(8): 1313-1316, 1439. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.2017.08.011GUAN X L, WANG P, YU Q, et al. Effect of BRAFV600E mutations on the expression of HMGB1 in papillary thyroid cancer[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2017, 15(8): 1313-1316, 1439. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.2017.08.011 [9] DONG S, XUE S, SUN Y, et al. MicroRNA-363-3p downregulation in papillary thyroid cancer inhibits tumor progression by targeting NOB1[J]. J Investig Med, 2021, 69(1): 66-74. doi: 10.1136/jim-2020-001562 [10] TAO L L, ZHOU W, ZHAN W W, et al. Preoperative prediction of cervical lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma via conventional and contrast-enhanced ultrasound[J]. J Ultrasound Med, 2020, 39(10): 2071-2080. doi: 10.1002/jum.15315 [11] GAO L, WANG J, JIANG Y, et al. The number of central lymph nodes on preoperative ultrasound predicts central neck lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma: A prospective cohort study[J]. Int J Endocrinol, 2020, 20(11): 628-631. [12] KIM W W, LEE J, JUNG J H, et al. Usefulness of intraoperative determination of central lymph node metastasis by palpation in papillary thyroid cancer[J]. J Ultras Med, 2020, 41(22): 869-871. [13] JIAO W P, ZHANG L. Using ultrasonography to evaluate the relationship between capsular invasion or extracapsular extension and lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinomas[J]. Chin Med J(Engl), 2017, 130(11): 1309-1313. [14] 刘文, 闫雪晶, 程若川, 等. 术前临床及超声检查特征对甲状腺乳头状癌中央区淋巴结转移预测价值研究[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2020, 40(10): 1197-1201. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGCY201711002.htmLIU W, YAN X J, CHENG R C, et al. Predictive central lymph node metastasis on the basis of preoperative features of clinic and ultrasonography in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma[J]. Chinese Journal of Practical Surgery, 2020, 40(10): 1197-1201. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGCY201711002.htm [15] 王欣, 郑凯, 黄敏. 合并桥本甲状腺炎的甲状腺乳头状癌临床病理及超声特征[J]. 中国医学影像学杂志, 2018, 26(10): 747-751. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5185.2018.10.006WANG X, ZHENG K, HUANG M. Clinicopathological and ultrasonographic characteristics of papillary thyroid carcinoma combined with hashimoto ' s thyroiditis[J]. Chinese Journal of Medical Imaging, 2018, 26(10): 747-751. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5185.2018.10.006 [16] 姜波, 罗渝昆, 张艳, 等. 甲状腺乳头状癌的常规超声及超声造影特征与淋巴结转移的相关性[J]. 首都医科大学学报, 2019, 40(6): 818-823. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7795.2019.06.002JIANG B, LUO Y K, ZHANG Y, et al. Correlation between conventional ultrasound and contrast-enhanced ultrasound and lymph node metastasis of papillary thyroid carcinoma[J]. Journal of Capital Medical University, 2019, 40(6): 818-823. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7795.2019.06.002 [17] 张静雯, 詹维伟, 董屹婕, 等. 术前超声评估甲状腺乳头状癌N分期及不同N分期的影响因素[J]. 中华医学超声杂志(电子版), 2019, 16(2): 126-130. doi: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1672-6448.2019.02.009ZHANG J W, ZHAN W W, DONG Y J, et al. Value of preoperative ultrasound in evaluating of N stage of papillary thyroid carcinoma and predictive factors of lymph node metastasis[J]. Chinese Journal of Medical Ultrasound(Electronic Edition), 2019, 16(2): 126-130. doi: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1672-6448.2019.02.009 [18] 詹玲, 陈创, 孙圣荣. 甲状腺乳头状癌淋巴结转移数目与临床病理特征的相关性分析[J]. 中华实用诊断与治疗杂志, 2020, 34(12): 1206-1208.ZHAN L, CHEN C, SUN S R. Correlation between the number of metastaic lymph nodes and clinicopathological characteristics in papillary thyroid carcinoma[J]. Journal of Chinese Practical Diagnosis and Therapy, 2020, 34(12): 1206-1208. [19] 陈蕾, 陈路增, 刘晶华, 等. 超声造影及BRAF基因突变诊断甲状腺乳头状癌被膜外侵犯[J]. 中国医学影像技术, 2020, 36(1): 50-54.CHEN L, CHEN L Z, LIU J H, et al. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound and BRAF mutation in diagnosis of extracapsular extension of papillary thyroid carcinoma[J]. Chinese Journal of Medical Imaging Technology, 2020, 36(1): 50-54. [20] 薛坤, 齐铮琴, 史文宗, 等. 甲状腺微小乳头状癌超声特征与淋巴结转移的分析[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2020, 36(4): 306-309. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0101.2020.04.006XUE K, QI Z Q, SHI W Z, et al. Relevant factors between ultrasound imaging features of papillary thyroid micropapillary carcinoma and cervical lymph node metastases[J]. Chinese Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine, 2020, 36(4): 306-309. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0101.2020.04.006 [21] 赵堃, 崔秋丽, 严昆, 等. 常规超声及超声造影参数对甲状腺乳头状癌被膜侵犯的评估[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2020, 36(1): 4-7.ZHAO K, CUI Q L, YAN L, et al. The evaluation of conventional ultrasound and contrast enhanced ultrasound parameters in extrathyroidal extension of thyroid papillary carcinoma[J]. Chinese Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine, 2020, 36(1): 4-7. -





 下载:
下载: