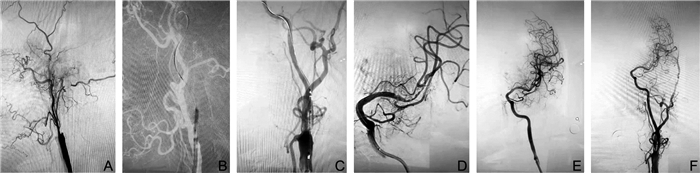
Analysis of safety and efficacy of emergent carotid artery stenting in patients with acute anterior circulation stroke with tandem lesion treated with mechanical thrombectomy
-
摘要:
目的 探讨急性前循环串联闭塞卒中患者行机械取栓治疗中颅外颈动脉病变的治疗方案,评估其有效性和安全性。 方法 回顾性分析2018年1月—2019年12月南阳市中心医院收治的18例行血管内治疗的颈内动脉颅外段伴同侧颅内动脉急性串联闭塞患者的临床资料。其中男性9例,女性9例,年龄为60~70岁。根据治疗方式的不同,将18例患者分为急诊支架组(11例)和急诊非支架组(7例)。术中即刻血管再通情况根据脑梗死溶栓(TICI)分级判断,将卒中发生90 d改良Rankin量表(mRS)评分0~2分定义为临床预后良好。 结果 2组患者年龄、性别、术前美国国立卫生研究院卒中量表(NIHSS)评分、术前Alberta卒中项目早期CT(ASPECT)评分、病因分型、治疗方式、病变类型、血管闭塞部位等临床基线资料比较,差异均无统计学意义(均P>0.05);急诊支架组和急诊非支架组的术后血管成功再通率(TICI分级为2b~3级)分别为72.7%和71.4%,组间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);2组术后症状性颅内出血率分别为9.1%和0,组间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);2组患者术后90 d改良mRS评分及90 d病死率比较差异无统计学意义(均P>0.05);2组患者术后残余狭窄率差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。 结论 在急性前循环串联闭塞的血管内治疗中,急诊颈动脉颅外段支架置入术可能是有效和安全的。 Abstract:Objective To explore the treatment options of mechanical thrombectomy for extracranial carotid artery lesions in patients with acute anterior circulation tandem occlusion stroke, and to evaluate its efficacy and safety. Methods From January 2018 to December 2019, 18 patients with acute tandem occlusion of the extracranial internal carotid artery and intracranial large artery were admitted to Department of Neurology, Nanyang City Central Hospital and treated by endovascular treatment. There were 9 males and 9 females, aged 60 to 70 years old. According to different treatment methods, 18 patients were divided into emergency stent group (11 cases) and emergency non-stent group (7 cases). The immediate intraoperative recanalization of blood vessels during the operation was judged according to the classification of cerebral infarction thrombolysis (mTICI), and the 90-day modified Rankin Scale (mRS) score of 0-2 was defined as a good clinical prognosis. Results There was no statistically significant difference in clinical baseline data such as age, gender distribution, preoperative National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score, preoperative Alberta stroke project early CT (ASPECT) score, etiology classification, treatment method, lesion type, blood vessel occlusion site in two groups (all P > 0.05). The rates of successful recanalization of blood vessels (mTICI class 2b-3) of the emergency stent group and emergency non-stent group was 72.7% and 71.4%, respectively; however, there was no statistically significant difference (P > 0.05). The rates of symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage were 9.1% and 0, respectively. Also, there was no statistically significant difference (P > 0.05). There was no statistically significant difference in the modified mRS score and 90-day mortality between the two groups of patients after 90 days (all P > 0.05). The difference in the residual stenosis rate between the two groups was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion In the endovascular treatment of acute anterior circulation tandem occlusion, emergency extracranial carotid artery stenting may be effective and safe. -
Key words:
- Emergent carotid artery stenting /
- Tandem occlusion /
- Mechanical thrombectomy /
- Prognosis
-
表 1 2组急性前循环串联闭塞卒中患者临床基线资料比较
Table 1. Comparison of clinical baseline data of acute ischemic stroke patients with acute anterior circulation tandem occlusion in two groups
项目 急诊支架组(n=11) 急诊非支架组(n=7) 统计量 P值 性别(男/女,例) 6/5 3/4 0.221a 0.638 年龄[M(P25, P75),岁] 64(60, 67) 66(61, 70) -0.917b 0.359 术前NIHSS(x±s,分) 16.7±7.8 18.9±7.1 -0.582c 0.569 术前ASPECT(x±s,分) 8.1±0.5 8.0±0.8 0.286c 0.778 术前静脉溶栓[例(%)] 3(27.3) 4(57.1) 1.517a 0.218 危险因素[例(%)] 高血压 7(63.6) 5(71.4) 0.110a 0.740 糖尿病 5(45.5) 2(28.6) 0.485a 0.486 血脂异常 6(54.5) 3(42.9) 0.221a 0.638 房颤 1(9.1) 1(14.3) 0.110a 0.740 吸烟史 6(54.5) 1(14.3) 2.755a 0.097 颈动脉病变类型[例(%)] 0.072a 0.789 闭塞 7(63.6) 4(57.1) 重度狭窄 4(36.4) 3(42.9) 时间 发病-入院(x±s,min) 147.5±27.6 125.4±12.0 1.977c 0.065 入院-穿刺(x±s,min) 76.0±32.0 90.0±31.0 -0.905c 0.379 穿刺-再通
[M(P25, P75),min]115.1(99.3, 130.9) 114.0(98.6, 129.4) -0.182b 0.860 发病-再通
[M(P25, P75),min]223.5(197.6, 249.3) 215.3(190.4, 240.2) -0.317b 0.791
颅内闭塞位置[例(%)]0.763a 0.382 C7 0 1(14.3) A1 1(9.1) 1(14.3) M1 9(81.8) 4(57.1) M2 1(9.1) 1(14.3) 颅内病变治疗方法[例(%)] 0.613a 0.434 支架取栓 10(90.9) 6(85.7) 抽吸 1(9.1) 0 动脉溶栓 0 1(14.3) 注:a为χ2值,b为Z值,c为t值。 表 2 2组急性前循环串联闭塞卒中患者预后和安全性指标比较[例(%)]
Table 2. Comparison of prognosis and safety indexes of acute ischemic stroke patients with acute anterior circulation tandem occlusion in groups[cases (%)]
组别 例数 mTICI分级 90 d mRS评分(分) 90 d死亡 颅内出血 术后残余颈动脉狭窄(≥70%) 0~2a级 2b~3级 0~2 3~6 症状性出血 非症状性出血 急诊支架组 11 3(27.3) 8(72.7) 7(63.6) 4(36.4) 2(18.2) 1(9.1) 0 1(9.1) 急诊非支架组 7 2(28.6) 5(71.4) 4(57.1) 3(42.9) 2(28.6) 0 0 4(57.1) P值 0.999a 0.999a 0.999a 0.999a 0.047a 注:a为使用Fisher精确检验。 -
[1] YANG D, SHI Z, LIN M, et al. Endovascular retrograde approach may be a better option for acute tandem occlusions stroke[J]. Interv Neuroradiol, 2019, 25(2): 194-201. doi: 10.1177/1591019918805140 [2] GOYAL M, DEMCHUK A M, MENON B K, et al. Randomized assessment of rapid endovascular treatment of ischemic stroke[J]. N Engl J Med, 2015, 372(11): 1019-1030. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1414905 [3] BERKHEMER O A, FRANSEN P S, BEUMER D, et al. A randomized trial of intraarterial treatment for acute ischemic stroke[J]. N Engl J Med, 2015, 372(1): 11-20. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1411587 [4] JOVIN T G, CHAMORRO A, COBO E, et al. Thrombectomy within 8 hours after symptom onset in ischemic stroke[J]. N Engl J Med, 2015, 372(24): 2296-2306. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1503780 [5] GOYAL M, MENON B K, ZWAM W H V, et al. Endovascular thrombectomy after large-vessel ischaemic stroke: A meta-analysis of individual patient data from five randomised trials[J]. Lancet, 2016, 387(10029): 1723-1731. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00163-X [6] POPPE A Y, JACQUIN G, ROY D, et al. Tandem carotid lesions in acute ischemic stroke: Mechanisms, therapeutic challenges, and future directions[J]. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol, 2020, 41(7): 1142-1148. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A6582 [7] WALLOCHA M, CHAPOT R, NORDMEYER H, et al. Treatment methods and early neurologic improvement after endovascular treatment of tandem occlusions in acute ischemic stroke[J]. Front Neurol, 2019, 10: 127. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00127 [8] BLASSIAU A, GAWLITZA M, MANCEAU P F, et al. Mechanical thrombectomy for tandem occlusions of the internal carotid artery-results of a conservative approach for the extracranial lesion[J]. Front Neurol, 2018, 9: 928. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00928 [9] 符晓艳, 王羚入, 江礼, 等. 颈动脉支架置入术并发高灌注综合征的研究[J]. 中华全科医学, 2020, 18(2): 163-165. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.001236FU X Y, WANG L J, JIANG L, et al. Study of carotid artery stenting with high perfusion syndrome[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2020, 18(2): 163-165. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.001236 [10] 白永杰, 张帅, 李顺, 等. 静脉溶栓联合颈动脉支架置入术在急性前循环大血管串联性闭塞卒中患者机械取栓治疗中的安全性和有效性分析[J]. 中国脑血管病杂志, 2019, 16(9): 449-455. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5921.2019.09.001BAI Y J, ZHANG S, LI S, et al. Analysis of safety and efficacy of intravenous thrombolysis combined with emergent carotid arterystenting in patients with acute anterior circulation stroke with tandem lesion treated with mechanical thrombectomy[J]. Chinese Journal of Cerebrovascular Diseases, 2019, 16(9): 449-455. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5921.2019.09.001 [11] PANAGIOTIS P, DIOGO C H, FRANCIS T, et al. Carotid stenting with antithrombotic agents and intracranial thrombectomy leads to the highest recanalization rate in patients with acute stroke with tandem lesions[J]. JACC Cardiovasc Interv, 2018, 11(13): 1290-1299. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2018.05.036 [12] ZHU F, LABREUCHE J, HAUSSEN D C, et al. Hemorrhagic transformation after thrombectomy for tandem occlusions[J]. Stroke, 2019, 50(2): 516-519. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.023689 [13] ZHU F, ANADANI M, LABREUCHE J, et al. Impact of antiplatelet therapy during endovascular therapy for tandem occlusions: A collaborative pooled analysis[J]. Stroke, 2020, 51(5): 1522-1529. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.028231 [14] WALLOCHA M, CHAPOT R, NORDMEYER H, et al. Treatment methods and early neurologic improvement after endovascular treatment of tandem occlusions in acute ischemic stroke[J]. Front Neurol, 2019, 10: 127. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00127 [15] POPPE A, JACQUIN G, STAPF C, et al. A randomized pilot study of patients with tandem carotid lesions undergoing thrombectomy[J]. J Neuroradiol, 2020, 47(6): 416-420. doi: 10.1016/j.neurad.2019.08.003 [16] MORVAY A B, MORDASINI P, SLEZAK A, et al. Does antiplatelet therapy during bridging thrombolysis increase rates of intracerebral hemorrhage in stroke patients?[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(1): e0170045. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170045. -





 下载:
下载: