Clinical value of serum VCAM-1 combined with Fazekas score in evaluating the prognosis of acute cerebral infarction with leukoaraiosis
-
摘要:
目的 探讨血管细胞黏附因子-1(VCAM-1)联合Fazekas评分对合并脑白质疏松的急性脑梗死(ACIL)患者发病后90 d转归的预测价值。 方法 选取2020年8月—2021年10月安徽医科大学附属宿州医院收治的首次发病NIHSS评分为8分的ACIL患者96例为研究对象。采用酶联免疫吸附法(ELISA)检测血清VCAM-1水平,并对ACIL患者进行Fazekas评分。根据改良的Rankin量表(mRS)评价患者发病后90 d的预后情况,mRS≤2分为预后良好(70例),mRS≥3分为预后不良(26例)。采用ROC曲线分析血清VCAM-1联合Fazekas评分对ACIL患者预后的评估价值。 结果 与预后良好组比较,预后不良组患者年龄[(71.23±3.66)岁vs.(64.57±5.24)岁]、血清VCAM-1[2.66(2.48,2.78)ng/mL vs. 2.10(1.40,2.23)ng/mL]、Fazekas评分[4(4,5)分vs. 3(2,3)分]显著升高(均P<0.05)。多因素logistic回归分析显示年龄大、VCAM-1升高及Fazekas评分升高是预后不良的独立危险因素。ROC曲线分析结果显示血清VCAM-1联合Fazekas评分评估预后不良的灵敏度为92.31%,特异度为94.29%。 结论 血清VCAM-1联合Fazekas评分对ACIL患者发病后90 d转归具有较高的预测价值。 -
关键词:
- 急性脑梗死 /
- 脑白质疏松 /
- 血管细胞黏附因子-1 /
- Fazekas评分 /
- 预后
Abstract:Objective To explore the predictive value of serum vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) level combined with Fazekas score in the clinical outcome of acute cerebral infarction with leukoaraiosis (ACIL) patients after 90 days. Methods A total of 96 acute cerebral infarction patients with an National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score of 8 who were admitted to the Suzhou Hospital Affiliated to Anhui Medical University from August 2020 to October 2021 were selected as the research objects. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to detect serum VCAM-1 levels, and Fazekas score was determined for all patients according to brain magnetic resonance. Based on the modified Rankin scale (mRS), the prognosis of patients at 90 days was evaluated. mRS≤2 was regarded as good prognosis (70 cases), and mRS≥3 was regarded as poor prognosis (26 cases). The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to analyse the value of serum VCAM-1 level combined with Fazekas score in evaluating the prognosis of ACIL patients. Results Compared with the good-prognosis group, the age [(71.23±3.66) years vs. (64.57±5.24) years], serum VCAM-1 level [2.66 (2.48, 2.78) ng/mL vs. 2.10 (1.40, 2.23) ng/mL], and Fazekas score [4 (4, 5) points vs. 3 (2, 3) points] of the poor-prognosis group were significantly higher than those in the good-prognosis group (all P < 0.05). Multivariate logistic-regression analysis showed that age, VCAM-1 level and Fazekas score were independent risk factors for poor prognosis. ROC curve analysis results revealed that the sensitivity and specificity of poor prognosis assessment were 92.31% and 94.29%, respectively. Conclusion Serum VCAM-1 combined with Fazekas score has a high predictive value for the 90-day outcome of acute cerebral infarction patients. -
表 1 ACIL组与对照组一般资料及VCAM-1水平比较
Table 1. Comparison of general data and VCAM-1 level between ACIL group and control group
组别 例数 性别[例(%)] 年龄(x±s,岁) Fazekas评分[M(P25, P75),分] VCAM-1[M(P25, P75),ng/mL] 男性 女性 ACIL组 96 55(57.3) 41(42.7) 66.38±5.69 3(2,4) 2.17(1.70,2.49) 对照组 50 29(58.0) 21(42.0) 64.86±4.40 1(1,1) 1.31(1.20,1.47) 统计量 0.007a 1.644b 8.925c 9.801c P值 0.935 0.102 <0.001 <0.001 注:a为χ2值,b为t值,c为Z值。 表 2 预后良好组与预后不良组患者临床资料及VCAM-1水平比较
Table 2. Comparison of clinical data and VCAM-1 levels between the good prognosis group and the poor prognosis group
项目 预后良好组(n=70) 预后不良组(n=26) 统计量 P值 性别[例(%)] 0.002a 0.961 男性 40(57.1) 15(57.7) 女性 30(42.9) 11(42.3) 年龄(x±s,岁) 64.57±5.24 71.23±3.66 5.953b <0.001 Fazekas评分[M(P25, P75),分] 3(2,3) 4(4,5) 2.779c 0.005 高血压[例(%)] 0.109a 0.741 无 14(20.0) 6(23.1) 有 56(80.0) 20(76.9) 糖尿病[例(%)] 0.087a 0.768 无 49(70.0) 19(73.1) 有 21(30.0) 7(26.9) 血糖[M(P25, P75),mmol/L] 5.62(5.26,7.77) 5.46(5.34,7.18) 0.552c 0.581 糖化血红蛋白[M(P25, P75),%] 6.2(5.8,6.6) 6.1(5.8,8.2) 1.030c 0.303 TC[M(P25, P75),mmol/L] 5.92(5.77,6.23) 5.89(5.73,5.99) 0.887c 0.375 LDL(x±s,mmol/L) 3.15±0.47 3.09±0.52 0.591b 0.556 Hcy[M(P25, P75), μmol/L] 11.3(8.1,13.6) 9.5(7.7,15.3) 0.870c 0.384 CRP[M(P25, P75),mg/L] 3.6(2.1,5.4) 2.6(2.4,3.9) 1.129c 0.259 VCAM-1[M(P25, P75),ng/mL] 2.10(1.40,2.23) 2.66(2.48,2.78) 4.440c <0.001 注:a为χ2值,b为t值,c为Z值。 表 3 影响预后的多因素logistic回归分析结果
Table 3. The results of multivariate logistic regression analysis affecting prognosis
变量 B SE Wald χ2 P值 OR(95% CI) 年龄 0.311 0.115 7.290 0.007 1.360(1.091~1.712) Fazekas评分 2.699 0.775 12.133 <0.001 14.861(3.260~67.861) VCAM-1 2.404 0.890 7.298 0.007 11.070(1.940~63.351) 表 4 年龄、Fazekas评分及血清VCAM-1水平对预后的评估
Table 4. Age, Fazekas score and serum VCAM-1 level for the evaluation of prognosis
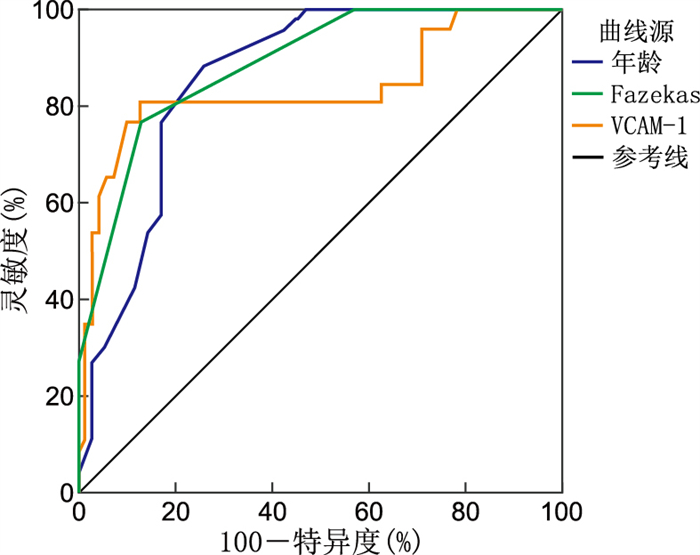
项目 AUC 95% CI 约登指数 灵敏度(%) 特异度(%) 截断值 P值 年龄 0.861 0.775~0.923 0.628 88.46 74.29 67.000 <0.001 Fazekas评分 0.887 0.806~0.943 0.641 76.92 87.14 3.000 <0.001 VCAM-1 0.834 0.745~0.902 0.679 80.77 87.11 2.379 <0.001 VCAM-1联合Fazekas评分 0.961 0.900~0.990 0.866 92.31 94.29 <0.001 -
[1] 袁俊亮, 王双坤, 顾华, 等. 脑小血管病的发病机制研究进展[J]. 中华老年心脑血管病杂志, 2018, 20(1): 102-104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LNXG201801031.htmYUAN J L, WANG S K, GU H, et al. Advances in the pathogenesis of small cerebral vascular disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Geriatric Heart Brain and Vessel Diseases, 2018, 20(1): 102-104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LNXG201801031.htm [2] KONG D H, KIM Y K, KIM M R, et al. Emerging roles of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) in immunological disorders and cancer[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2018, 19(4): 1057. doi: 10.3390/ijms19041057 [3] TRONCOSO M F, ORTIZ-QUINTERO J, GARRIDO-MORENO V, et al. VCAM-1 as a predictor biomarker in cardiovascular disease[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis, 2021, 1867(9): 166170. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2021.166170. [4] HAYEK A, PACCALET A, MECHTOUFF L, et al. Kinetics and prognostic value of soluble VCAM-1 in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction patients[J]. Immun Inflamm Dis, 2021, 9(2): 493-501. doi: 10.1002/iid3.409 [5] ZENG W Y, CHEN Y J, ZHU Z B, et al. Severity of white matter hyperintensities: Lesion patterns, cognition, and microstructural changes[J]. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab, 2020, 40(12): 2454-2463. doi: 10.1177/0271678X19893600 [6] LITAK J, MAZUREK M, KULESZA B, et al. Cerebral small vessel disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(24): 9729. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249729 [7] LIN C C, PAN C S, WANG C Y, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces VCAM-1-mediated inflammation via c-Src-dependent transactivation of EGF receptors in human cardiac fibroblasts[J]. J Biomed Sci, 2015, 22(1): 53. doi: 10.1186/s12929-015-0165-8 [8] 李占增, 任英巧, 伍淑玲, 等. 炎症因子水平与老年缺血性脑血管病患者介入治疗预后的关系研究[J]. 国际检验医学杂志, 2020, 41(18): 2228-2230, 2235. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWSQ202018012.htmLI Z Z, REN Y Q, WU S L, et al. Relationship between inflammatory factors levels and prognosis of elderly patients with ischemic cerebrovascular disease after interventional therapy[J]. International Journal of Laboratory Medicine, 2020, 41(18): 2228-2230, 2235. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWSQ202018012.htm [9] 吴从印, 陈娟, 冯光球, 等. 老年缺血性脑血管病患者血管内皮细胞功能指标与沉默信息调节因子1的相关性分析[J]. 中国医药, 2019, 14(4): 549-552. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYG201904019.htmWU C Y, CHEN J, FENG G Q, et al. Relation between vascular endothelial function indexes and silencing information regulator 1 in senile ischemic cerebrovascular disease[J]. China Medicine, 2019, 14(4): 549-552. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYG201904019.htm [10] EL HUSSEINI N, BUSHNELL C, BROWN C M, et al. Vascular cellular adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) and memory impairment in African-Americans after small vessel-type stroke[J]. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis, 2020, 29(4): 104646. DOI: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2020.104646. [11] 郭艳侠, 国娟. CD4+CD28-T细胞、TNF-α、VCAM-1在急性脑梗死中的意义及其与颈动脉斑块性质的相关性分析[J]. 中风与神经疾病杂志, 2020, 37(1): 22-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZFSJ202001005.htmGUO Y X, GUO J. The significance of CD4+CD28-T cells, TNF-α and VCAM-1 in acute cerebral infarction and its correlation with the properties of carotid plaque[J]. Journal of Apoplexy and Nervous Diseases, 2020, 37(1): 22-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZFSJ202001005.htm [12] 袁治玲, 苏洲, 袁燕, 等. 外周血ET-1、MMP-9、RDW-CV与急性脑梗死病情的关系及对预后的预测价值[J]. 分子诊断与治疗杂志, 2022, 14(1): 124-128. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXYQ202201030.htmYUAN Z L, SU Z, YUAN Y, et al. Relationship between ET-1, MMP-9, RDW-CV and acute cerebral infarction and their prognostic value[J]. Journal of Molecular Diagnostics and Therapy, 2022, 14(1): 124-128. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXYQ202201030.htm [13] KONGBUNKIAT K, WILSON D, KASEMSAP N, et al. Leukoaraiosis, intracerebral hemorrhage, and functional outcome after acute stroke thrombolysis[J]. Neurology, 2017, 88(7): 638-645. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003605 [14] GAO C S, JIA W Y, XU W D, et al. Downregulation of CD151 restricts VCAM-1 mediated leukocyte infiltration to reduce neurobiological injuries after experimental stroke[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2021, 18(1): 118. [15] 刘艳艳, 张敏, 恽文伟, 等. 中重度脑白质疏松对急性脑梗死静脉溶栓患者出血转化及预后的影响[J]. 中华神经科杂志, 2017, 50(12): 885-891. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XCYS201902044.htmLIU Y Y, ZHANG M, YUN W W, et al. Influence of moderate to severe leukoaraiosis on hemorrhagic transformation and prognosis of acute ischemic stroke patients after intravenous thrombolysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Neurology, 2017, 50(12): 885-891. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XCYS201902044.htm [16] 刘晓微, 胡文立. 脑白质疏松与老年急性脑梗死静脉溶栓患者症状性颅内出血及功能预后的关系研究[J]. 中国卒中杂志, 2020, 15(6): 650-654. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZUZH202006014.htmLIU X W, HU W L. Impact of leukoaraiosis on symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage and functional outcome after intravenous thrombolysis in elderly patients with acute cerebral infarction[J]. Chinese Journal of Stroke, 2020, 15(6): 650-654. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZUZH202006014.htm [17] 刘时华, 张超, 田志刚, 等. 缺血性脑白质病变患者血清S-100β蛋白水平表达及其临床意义[J]. 中华全科医学, 2021, 19(1): 38-41. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.001724LIU S H, ZHANG C, TIAN Z G, et al. Expression and clinical significance of serum S-100β protein in patients with white matter ischaemic lesions[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2021, 19(1): 38-41. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.001724 -





 下载:
下载: