A comparative study of clinical efficacy and safety between Lvis and Solitaire stent-assisted embolization for unruptured wide-necked ophthalmic segment aneurysms of internal carotid artery
-
摘要:
目的 探讨比较Lvis和Solitaire支架辅助弹簧圈治疗未破裂宽颈眼动脉段动脉瘤的临床疗效及安全性。 方法 回顾性分析2018年3月—2019年7月在浙江省台州医院应用Lvis或Solitaire支架辅助弹簧圈栓塞的53例未破裂宽颈颈内动脉眼动脉段动脉瘤患者的临床资料,其中Lvis组29例,Solitaire组24例。应用术毕即刻栓塞程度(Raymond分级)和术后6~12个月数字减影血管造影(DSA)随访结果比较2组的手术疗效,手术相关并发症发生情况比较2组的手术安全性。 结果 术后即刻造影结果显示,Lvis组术后即刻达RaymondⅠ级的有24例(82.8%),Ⅱ级5例(17.2%),Solitaire组Ⅰ级17例(70.8%),Ⅱ级6例(25.0%),另外有1例(4.2%)为Ⅲ级,2组比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。术后6~12个月DSA随访结果显示,Lvis组显著优于Solitaire组(P < 0.05)。Lvis组手术相关并发症发生率为13.8%(4/29),高于Solitaire组的4.2%(1/24)。 结论 Lvis和Solitaire两种支架在辅助弹簧圈栓塞治疗未破裂宽颈眼动脉段动脉瘤中各有优劣。Lvis支架可能更有利于减少远期复发,而Solitaire支架有更低的并发症发生率。 -
关键词:
- Lvis支架 /
- 未破裂 /
- 眼段 /
- 宽颈动脉瘤 /
- Solitaire支架
Abstract:Objective To compare the clinical efficacy and safety of Lvis and Solitaire stent-assisted embolization in the treatment of unruptured wide-necked ophthalmic segment aneurysms of internal carotid artery. Methods The clinical data of 53 patients with unruptured wide-necked ophthalmic segment aneurysms treated by Lvis or Solitaire stent-assisted embolization from March 2018 to July 2019 in Taizhou Hospital of Zhejiang Province were analysed retrospectively. A total of 29 patients were treated with Lvis stents, whereas 24 were treated with Solitaire stents. The surgical efficacy of the two groups was compared by Raymond classification based on immediate postoperative angiography, and follow-up results were based on digital subtraction angiography (DSA) at 6 - 12 months. The incidence of perioperative complications was used to compare the safety of the two groups. Results Statistical analysis showed no significant differences in patients after the procedure in the instant Raymond classification (P>0.05). DSA immediately after the embolization showed that 24 (82.8%) received Raymond grade Ⅰ and 5 (17.2%) were Raymond grade Ⅱ in the Lvis stent group, whereas 17 (70.8%) received Raymond grade Ⅰ, 6 (25.0%) received Raymond grade Ⅱ and 1 (4.2%) received Raymond grade Ⅲ. The follow-up results based on DSA at 6 - 12 months in the Lvis stent group were better than those in the Solitaire stent group, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). The incidence of surgery-related complications in the Lvis stent group was 13.8% (4/29), which was higher than 4.2% (1/24) in the Solitaire stent group. Conclusion Lvis stent and Solitaire stent-assisted coil embolization have their own advantages and disadvantages in the treatment of unruptured wide-necked ophthalmic segment aneurysms of the internal carotid artery. Lvis stent-assisted embolization for unruptured wide-necked ophthalmic segment aneurysm is beneficial to decrease recurrence rate, whereas Solitaire stent has a good safety level. -
Key words:
- Lvis stent /
- Unruptured /
- Ophthalmic segment /
- Wide-necked aneurysm /
- Solitaire stent
-
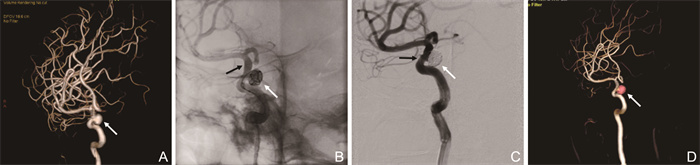
图 1 1例未破裂眼动脉段宽颈动脉瘤患者Lvis支架辅助弹簧圈栓塞术前、术中及术后影像
注:A为栓塞前三维图像,白色箭头示未破裂眼动脉段宽颈动脉瘤,大小约8.2 mm×6.4 mm,瘤颈约5.1 mm;B为栓塞术中工作角度,Lvis支架半释放状态下(黑色箭头所示)弹簧圈填塞动脉瘤(白色箭头所示);C为栓塞术后工作角度,动脉瘤致密栓塞(白色箭头所示),达Raymond Ⅰ级,载瘤动脉通畅(黑色箭头所示);D为术后7个月复查DSA三维图像,动脉瘤基本治愈(白色箭头所示)。
Figure 1. Preoperative, intraoperative and postoperative images of a patient with unruptured wide-necked ophthalmic artery segment aneurysm treated with Lvis stent-assisted coil embolization
表 1 2组未破裂宽颈颈内动脉眼动脉段动脉瘤患者临床资料比较
Table 1. Comparison of clinical data between two groups of patients with unruptured wide-necked internal carotid artery aneurysms
组别 例数 年龄(x±s, 岁) 性别(例) 瘤体大小(例) 男性 女性 小 中 大 巨大 Lvis组 29 58.1±11.0 10 19 19 9 1 0 Solitaire组 24 57.7±9.4 8 16 15 9 0 0 统计量 0.154a 0.008b 0.128c P值 0.878 0.930 0.898 注:a为t值,b为χ2值,c为Z值。 表 2 2组未破裂宽颈颈内动脉眼动脉段动脉瘤患者术后即刻造影Raymond分级比较(例)
Table 2. Comparison of Raymond grade of immediate postoperative angiography in two groups of patientswith unruptured wide-necked internal carotid artery aneurysms (cases)
组别 例数 Ⅰ级 Ⅱ级 Ⅲ级 Lvis组 29 24 5 0 Solitaire组 24 17 6 1 注:2组Raymond分级比较,Z=-1.082,P=0.279。 表 3 2组未破裂宽颈颈内动脉眼动脉段动脉瘤患者术后6~12个月DSA复查结果比较(例)
Table 3. Comparison of DSA review results between the two groups of patients with unruptured wide-necked internal carotid artery ophthalmic artery aneurysms 6 - 12 months after surgery (cases)
组别 例数 治愈 改善 稳定 复发 Lvis组 29 27 2 0 0 Solitaire组 24 17 1 4 2 注:2组DSA复查结果比较,Z=-2.282,P=0.022。 -
[1] 杨杰, 管生, 徐浩文, 等. 眼动脉段动脉瘤血管内栓塞治疗方法探讨[J]. 介入放射学杂志, 2016, 25(9): 750-754. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-794X.2016.09.002YANG J, GUAN S, XU H W, et al. Discussion on the endovascular embolization treatment of ophthalmic segment aneurysms[J]. Journal of Interventional Radiology, 2016, 25(9): 750-754. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-794X.2016.09.002 [2] GRIESSENAUER C J, PISKE R L, BACCIN C E, et al. Flow diverters for treatment of 160 ophthalmic segment aneurysms: Evaluation of safety and efficacy in a multicenter cohort[J]. Neurosurgery, 2017, 80(5): 726-732. doi: 10.1093/neuros/nyw110 [3] YU J W, SHIM Y S, LEE J W, et al. Vision outcomes of endovascular treatment for unruptured ophthalmic artery aneurysms[J]. World Neurosurg, 2018, 116: e1223-e1229. DOI: 10.1016/j.wneu.2018.05.238. [4] LAI L T, MORGAN M K. Outcomes for unruptured ophthalmic segment aneurysm surgery[J]. J Clin Neurosci, 2013, 20(8): 1127-1133. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2012.12.004 [5] LIU Y Q, WANG Q J, ZHENG T, et al. Single-centre comparison of procedural complications, clinical outcome, and angiographic follow-up between coiling and stent-assisted coiling for posterior communicating artery aneurysms[J]. J Clin Neurosci, 2014, 21(12): 2140-2144. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2014.03.033 [6] 牟磊, 秦军, 雷军荣, 等. LVIS Jr支架在治疗前交通宽颈动脉瘤中的疗效分析[J]. 中华显微外科杂志, 2019, 42(5): 504-506. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-2036.2019.05.023MOU L, QIN J, LEI J R, et al. Efficacy analysis of LVIS Jr stent in the treatment of anterior communicating wide-necked aneurysm[J]. Chinese Journal of Microsurgery, 2019, 42(5): 504-506. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-2036.2019.05.023 [7] MURAKAMI T, NISHIDA T, ASAI K, et al. Long-term results and follow-up examinations after endovascular embolization for unruptured cerebral aneurysms[J]. Am J Neuroradiol, 2019, 40(7): 1191-1196. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A6101 [8] KOYANAGI M, ISHⅡ A, IMAMURA H. Long-term outcomes of coil embolization of unruptured intracranial aneurysms[J]. J Neurosurg, 2018, 129(6): 1492-1498. doi: 10.3171/2017.6.JNS17174 [9] RAYMOND J, GUILBERT F, WEILL A, et al. Long-term angiographic recurrences after selective endovascular treatment of aneurysms with detachablecoils[J]. Stroke, 2003, 34(6): 1398-1403. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000073841.88563.E9 [10] 李修珍, 吴日乐, 纪文军, 等. 颈内动脉眼动脉段未破裂动脉瘤支架辅助栓塞治疗的随访分析[J]. 中国脑血管病杂志, 2016, 13(4): 187-190. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5921.2016.04.005LI X Z, WU R L, JI W J, et al. Follow-up study on stent-assited coiling of unruptured ophthalmic segment aneurysms of internal carotid[J]. Chinese Journal of Cerebrovascular Diseases, 2016, 13(4): 187-190. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5921.2016.04.005 [11] YANG P F, ZHAO K J, ZHOU Y, et al. Stent-assisted coil placement for the treatment of 211 acutely ruptured wide-necked intracranial aneurysms: A single-center 11-year experience[J]. Radiology, 2015, 276(2): 545-552. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2015140974 [12] KAMIDE T, TABANI H, SAFAEE M M, et al. Microsurgical clipping of ophthalmic artery aneurysms: Surgical results and visual outcomes with 208 aneurysms[J]. J Neurosurg, 2018, 129(6): 1511-1521. doi: 10.3171/2017.7.JNS17673 [13] LEE S J, CHO Y D, KANG H S, et al. Coil embolization using the self-expandable closed-cell stent for intracranial saccular aneurysm: A single-center experience of 289 consecutiveaneurysms[J]. Clin Radiol, 2013, 68(3): 256-263. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2012.07.017 [14] 马修尧, 任超, 刘彬, 等. 比较Lvis支架辅助弹簧圈和Solitaire支架辅助弹簧圈栓塞治疗颅内破裂宽颈动脉瘤的安全性和有效性[J]. 中华全科医学, 2018, 16(8): 1247-1249, 1348. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.000342MA X R, REN C, LIU B, et al. A comparative study of safety and efficiency between LVIS stent assistant spring ring and Solitaire stent spring ring for the ruptured wide-necked intracranial aneurysm[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2018, 16(8): 1247-1249, 1348. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.000342 [15] 王璐瑶, 冯欣, 张宝瑞, 等. LVIS及Enterprise两种支架辅助弹簧圈治疗椎动脉夹层动脉瘤的疗效分析[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2019, 99(9): 685-689. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2019.09.010WANG L Y, FENG X, ZHANG B R, et al. Efficacy analysis of LVIS and Enterprise stent assisted coil in the treatment of vertebral artery dissection aneurysm[J]. National Medical Journal of China, 2019, 99(9): 685-689. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2019.09.010 [16] 吕超, 谢非, 李侠, 等. LVIS支架辅助弹簧圈栓塞治疗后循环夹层动脉瘤的效果分析[J]. 中国脑血管病杂志, 2020, 17(10): 576-581. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5921.2020.10.002LYU C, XIE F, LI X, et al. Effect analysis of LVIS stent assisted coil embolization in the treatment of posterior circulation dissecting aneurysms[J]. Chinese Journal of Cerebrovascular Diseases, 2020, 17(10): 576-581. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5921.2020.10.002 [17] 闫亚洲, 曾张伟, 吴一娜, 等. LVIS支架治疗大脑中动脉分叉部未破裂动脉瘤的临床效果分析[J]. 中国脑血管病杂志, 2020, 17(4): 186-191, 221. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5921.2020.04.004YAN Y Z, ZENG Z W, WU Y N, et al. Clinical efficacy of endovascular treatment with the low profile visualized intraluminal support stent for unruptured aneurysm of middle cerebral artery bifurcation[J]. Chinese Journal of Cerebrovascular Diseases, 2020, 17(4): 186-191, 221. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5921.2020.04.004 [18] 李欢欢, 李俊, 盛柳青, 等. LVIS支架辅助栓塞颈内动脉床突上段破裂夹层动脉瘤[J]. 中国临床神经外科杂志, 2020, 25(7): 430-432. doi: 10.13798/j.issn.1009-153X.2020.07.005LI H H, LI J, SHENG L Q, et al. LVIS stent assisted coils embolization for ruptured dissecting aneurysms in the internal carotid artery supraclinoid segment[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Neurosurgery, 2020, 25(7): 430-432. doi: 10.13798/j.issn.1009-153X.2020.07.005 [19] LEE M, PARK I S, LEE K H, et al. Endovascular treatments for ruptured intracranial vertebral artery dissecting aneurysms: Experience in 16 patients[J]. J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg, 2017, 19(4): 268-275. doi: 10.7461/jcen.2017.19.4.268 [20] 程美雄, 张天, 刘泠. Lvis支架辅助弹簧圈栓塞颅内宽颈微小动脉瘤的疗效分析[J]. 中国脑血管病杂志, 2019, 16(11): 597-600, 617. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5921.2019.11.007CHENG M X, ZHANG T, LIU L. Effect analysis of Lvis stent-assisted coiling embolization of intracranial wide-necked microaneurysms[J]. Chinese Journal of Cerebrovascular Diseases, 2019, 16(11): 597-600, 617. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5921.2019.11.007 [21] 凌国源, 莫立根, 冯大勤, 等. Lvis支架与Enterprise支架辅助栓塞颅内宽颈动脉瘤的比较[J]. 中国微创外科杂志, 2020, 20(9): 769-774. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6604.2020.09.001LING G Y, MO L G, FENG D Q, et al. A comparative study of safety and efficiency between lvis stent and enterprise stent assisted coil embolization in wide-necked intracranial aneurysm[J]. Chinese Journal of Minimally Invasive Surgery, 2020, 20(9): 769-774. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6604.2020.09.001 [22] 李立, 李天晓, 薛绛宇, 等. LVIS支架辅助栓塞未破裂颅内宽颈动脉瘤[J]. 中华神经外科杂志, 2019, 35(8): 833-836. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-2346.2019.08.016LI L, LI T X, XUE J Y, et al. LVIS assisted coiling in endovascular emblization of unruptured wide-neck intracranial aneurysms[J]. Chinese Journal of Neurosurgery, 2019, 35(8): 833-836. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-2346.2019.08.016 [23] ZHANG X G, ZHONG J J, GAO H, et al. Endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms with the LVIS device: A systematic review[J]. J Neurointerv Surg, 2016, 9(6): 553-557. [24] 肖贾伟, 赵瑞, 李嘉楠, 等. LVIS支架在颈内动脉海绵窦段打开不良与血管弯曲的关系[J]. 中国脑血管病杂志, 2017, 14(3): 118-121. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NXGB201703002.htmXIAO J W, ZHAO R, LI J N, et al. Relationship between unsatisfactory release of LVIS stent and vascular tortuosity in the cavernous segment of internal carotid artery[J]. Chinese Journal of Cerebrovascular Diseases, 2017, 14(3): 118-121. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NXGB201703002.htm [25] 刘远来, 孙异春, 何永超, 等. Solitaire支架与lvis支架辅助弹簧圈栓塞对颅内宽颈动脉瘤的疗效对比[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(3): 423-426. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DYJD202003024.htmLIU Y L, SUN Y C, HE Y C, et al. Treatment efficacy of Solitaire stent-and LVIS stent-assisted coil embolization for intracranial wide-neck carotid aneurysm[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2020, 40(3): 423-426. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DYJD202003024.htm [26] 秦琨, 曾少建, 舒航, 等. Solitaire AB与Enterprise支架辅助栓塞颅内宽颈动脉瘤患者的疗效对比[J]. 中国脑血管病杂志, 2016, 13(10): 511-515. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NXGB201610002.htmQIN K, ZENG S J, SHU H, et al. Efficacy comparison of Solitaire AB and Enterprise stent-assisted embolization of intracranial wide-necked aneurysms[J]. Chinese Journal of Cerebrovascular Diseases, 2016, 13(10): 511-515. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NXGB201610002.htm [27] HOU S Y, KVHN A L, PURI A S, et al. Open-cell stent and use of cone-beam CT enables a safe and effective coil embolization of true ophthalmic artery and anterior choroidal artery aneurysms with preservation of parent vessel: Clinical and angiographic results[J]. Interv Neuroradiol, 2018, 24(2): 135-139. [28] BRITZ G W, SALEM L, NEWELL D W, et al. Impact of surgical clipping on survival in unruptured and ruptured cerebral aneurysms: A population-based study[J]. Stroke, 2004, 35(6): 1399-1403. [29] 黄鹞, 白鹏. 颈内动脉眼段未破裂动脉瘤的血管内治疗[J]. 昆明医科大学学报, 2019, 40(5): 80-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KMYX201905016.htmHUANG Y, BAI P. Endovascular treatment for unruptured wide-necked ophthalmic segment aneurysms of internal carotid artery[J]. Journal of Kunming Medical University, 2019, 40(5): 80-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KMYX201905016.htm -





 下载:
下载: