Under the background of "Mountain and Sea" promotion project, the investigation of county doctors'common ultrasound practice and the preliminary exploration of PBL ultrasonic training mode
-
摘要:
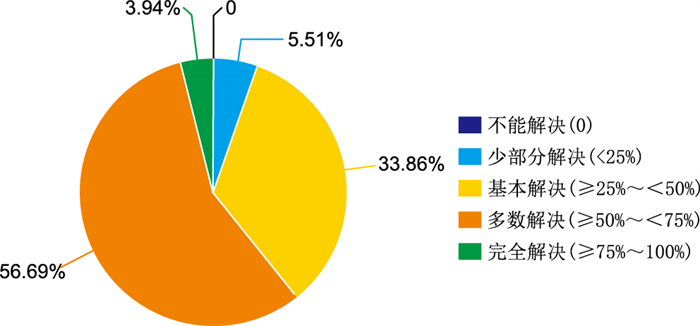
目的 通过“山海”提升工程省级医院与县级医院的合作帮扶模式,调查县域医共体的超声实践能力,探索超声基于问题式学习培训模式的成效。 方法 下沉专家于2021年4—10月在仙居县人民医院进行帮扶,针对127名超声医学专科医生采用基于问题式学习(PBL),以问题为基础,基层医院超声医生为主体,小组讨论为形式,下沉专家为导向的教学方法,将心脏超声作为重点培训内容,分析专家在仙居帮扶期间与专家结束后的相关数据,分别与2020、2021年同期心脏超声检查数据进行比较。 结果 基层临床医生对超声解决实际工作认可度较高,有94.49%(120/127)的临床医生认为超声可以基本解决临床问题; 不同学历的基层医生对科研的兴趣也不同; 在基于问题式学习的培训模式下,专家帮扶期间心脏超声检查例数、复杂心脏病的诊断例数较2020年同期增多,检查总例数增长率为7.40%,复杂阳性病例增长率为162.86%;专家帮扶结束后(2021年11月—2022年2月)心脏超声检查例数、复杂心脏病的诊断例数较2020—2021年同期增多,检查总例数增长率为10.63%,复杂阳性病例增长率为10.18%。 结论 医疗卫生“山海”提升工程是一项将帮扶工作落到实处的惠民工程,充分发挥省级医院优势学科,不断提高基层医生的医、教、研水平,也使基层百姓能获得省级医院“同质化”的医疗资源。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the ultrasound-practice ability of county doctors and explore the effectiveness of ultrasonic problem-based learning-training mode through the "Mountain and Sea" project, which improved the cooperative assistance mode between provincial hospitals and county-level hospitals. Methods Experts were assisted in Xianju County People's Hospital from April to October 2021. Problem-based learning (PBL) was adopted for ultrasound medical specialists. The teaching method was problem-based, with 127 ultrasound doctors in basic hospitals as the main body, in the form of group discussion and the expert as the guidance. Taking cardiac ultrasound as a key training content, the relevant data of experts during and after Xianju assistance were analysed and compared with the cardiac ultrasound data of the same period in 2020 and 2021. Results Grassroots clinicians had a high recognition of ultrasound to solve the practical work. About 94.49% (120/127) of clinicians believed that ultrasound can basically solve clinical problems. Doctors had different interests in scientific research to different degrees. In the training mode based on PBL, during the period of expert assistance, the number of cases of cardiac ultrasound examination and the diagnosis of complex heart disease increased compared with the same period in 2020. The growth rate of the total cases was 7.40%, and the growth rate of complex positive cases was 162.86%. After the end of expert assistance (November 2021 to February 2022), the number of cases of cardiac ultrasound examination and the diagnosis of complex heart disease increased compared with the same period of 2020-2021. The growth rate of the total number of cases examined was 10.63%, and that of complex positive cases was 10.18%. Conclusion The medical and health "Mountain and Sea" promotion project is a project to help the people and put the work into practice. It gives full play to the superior disciplines of provincial hospitals, thereby constantly improving the medical, teaching, and research level of grassroot doctors and also enabling grassroot people to avail of the "homogenised" medical resources of provincial hospitals. -
表 1 不同学科对超声亚专业的感兴趣情况(人)
Table 1. Interest in the ultrasound subspecialty in different disciplines
科室 心血管 腹部 浅表 肌骨 介入 其他 内科 28 13 10 4 16 5 外科 0 8 6 2 2 0 急重症 6 7 6 0 0 1 其他 5 5 3 2 3 0 注:不同学科比较,χ2=28.546,P=0.018。 表 2 学历、科研经验、科研兴趣相关性的分析(r值)
Table 2. Analysis of the correlation between educational background, research experience and research interest (r values)
项目 学历 科研经验 科研兴趣 学历 1 科研经验 -0.182a 1 科研兴趣 -0.158 0.308b 1 注:aP<0.05,bP<0.01。 表 3 A组与B组阳性检出例数的比较(例)
Table 3. Comparison of the number of positive cases between group A and group B (cases)
组别 复杂阳性例数 普通阳性例数 合计 A组 184 174 358 B组 70 247 317 注:2组比较,χ2=61.560, P<0.001。 表 4 A组与B组各类复杂心脏病检出例数比较(例)
Table 4. Comparison of the detected cases of complex heart disease between group A and group B (cases)
组别 先天性心脏病 心脏瓣膜病 心肌病 大血管疾病 合计 A组 67 62 37 18 184 B组 14 18 25 13 70 注:2组比较,χ2=13.578, P=0.004。 表 5 C组与D组阳性检出例数比较(例)
Table 5. Comparison of positive detection cases between group C and group D
组别 复杂阳性例数 普通阳性例数 合计 C组 184 66 250 D组 167 167 334 注:2组比较,χ2=33.209, P<0.001。 表 6 C组与D组各类复杂心脏病检出例数比较(例)
Table 6. Comparison of detected cases of complex heart disease between group C and group D (cases)
组别 先天性心脏病 心脏瓣膜病 心肌病 大血管疾病 合计 C组 30 85 33 36 184 D组 5 109 32 21 167 注:2组比较,χ2=24.022, P<0.001。 -
[1] 陈曦, 刘丽文, 宋宏萍, 等. 陕西省基层超声医师继续教育规范化培训模式的探索[J]. 中华医学教育杂志, 2021, 41(6): 550-553. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115259-20210207-00184CHAN X, LIU L W, SONG S P, et al. The innovative mode of continuous education and standardized training for primary ultrasound doctors in Shaanxi province[J]. Chinese Journal of Medical Education, 2021, 41(6): 550-553. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115259-20210207-00184 [2] 苏伟, 王静云, 张雅婷, 等. 医学专业学生临床实践中面临的问题及解决对策[J]. 基层医学论坛, 2017, 21(7): 878-879. doi: 10.19435/j.1672-1721.2017.07.074SU W, WANG J Y, ZHANG Y T, et al. Problems faced by medical students in clinical practice and countermeasures[J]. The Medical Forum, 2017, 21(7): 878-879. doi: 10.19435/j.1672-1721.2017.07.074 [3] 傅晓红, 贾瑱熙, 赵峰, 等. 社区全科医生与专科医生对全科医生学习超声的观点差异及未来便携式超声向基层普及的意见与建议[J]. 中国全科医学, 2021, 24(22): 2832-2837. doi: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.00.149FU X H, JIA Z X, ZHAO, et al. General practitioners'learning ultrasound techniques and future applicability of portable ultrasound device in primary care: Perspectives from general practitioners and sonographers[J]. Chinese General Practice, 2021, 24(22): 2832-2837. doi: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.00.149 [4] 高琼, 姜玉新, 李建初, 等. 基于甲状腺超声学习班问卷调查结果的继续医学教育研究[J]. 中华医学教育杂志, 2018, 38(4): 604-607. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-677X.2018.04.029GAO Q, JIANG Y X, LI J C, et al. Exploring the necessity and importance of continuing medical education based on questionnaires of learning program in thyroid ultrasound[J]. Chinese Journal of Medical Education, 2018, 38(4): 604-607. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-677X.2018.04.029 [5] 钟华, 华兴, 丁俊, 等. 超声诊断学在临床实践教学中的现状与探讨[J]. 临床超声医学杂志, 2018, 20(9): 638-639. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-6978.2018.09.026ZHONG H, HUA X, DING J, et al. The status and discussion of ultrasonic diagnostics in clinical practice teaching[J]. Journal of Clinical Ultrasound in Medicine, 2018, 20(9): 638-639. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-6978.2018.09.026 [6] 韩雪, 兰天, 郑建, 等. 多学科协作教学方式在超声诊断学实践教学中的应用[J]. 中华医学教育杂志, 2020, 40(8): 598-601. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115259-20200119-00078HAN X, LAN T, ZHENG J, et al. The application of multi-disciplinary team teaching mode in ultrasonography practice teaching[J]. Chinese Journal of Medical Education, 2020, 40(8): 598-601. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115259-20200119-00078 [7] 巩雪, 于铭, 刘丽文, 等. 我国乡镇卫生院超声人才继续教育培养模式探讨[J]. 医学教育研究与实践, 2018, 26(5): 753-756. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBYX201805012.htmGONG X, YU M, LIU L W, et al. Discussion on training mode of continuous education of ultrasonic talents in township health centers in China[J]. Medical Education Research and Practice, 2018, 26(5): 753-756. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBYX201805012.htm [8] 王昌明, 杨广鑫, 李选. 基于案例学习教学方法在血管外科医师超声诊断和操作技能教学中的应用[J]. 中华医学教育杂志, 2021, 41(7): 592-596. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115259-20201220-01740WANG C M, YANG G X, LI X. Application of case-based learning in the teaching of ultrasound diagnostics and operation skills during the training of vascular surgeons[J]. Chinese Journal of Medical Education, 2021, 41(7): 592-596. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115259-20201220-01740 [9] 陈露, 高惠, 尹书月, 等. PBL教学法结合角色扮演教学法在小儿超声诊断学临床教学中的应用[J]. 临床超声医学杂志, 2020, 22(2): 152-153. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCCY202002031.htmCHEN L, GAO H, YIN S Y, et al. Application of PBL teaching combined with role-playing teaching method in clinical teaching of pediatric ultrasound diagnosis[J]. Journal of Clinical Ultrasound in Medicine, 2020, 22(2): 152-153. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCCY202002031.htm [10] 朱晓丽, 郑敏娟, 孟欣, 等. 超声心动图医师中长期规范化培训的经验探讨[J]. 临床超声医学杂志, 2019, 21(1): 68-69. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCCY201901075.htmZHU X L, ZHENG M J, MENG X, et al. Experience of long-term standardized training for echocardiographists[J]. Journal of Clinical Ultrasound in Medicine, 2019, 21(1): 68-69. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCCY201901075.htm [11] 邹兵兵, 余昌俊. 多学科诊疗引领模式在胃肠外科临床教学中的应用探讨[J]. 安徽医学, 2016, 37(3): 365-367. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AHYX201603038.htmZOU B B, YU C J. MDT leading model practice for standardization training of residents in clinical teaching of gastrointestinal surgery[J]. Anhui Medical Journal, 2016, 37(3): 365-367. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AHYX201603038.htm [12] 李政, 金航, 孙敏敏, 等. 组织追踪MR技术评价正常人左室形变功能的临床研究[J]. 中国临床医学, 2020, 27(6): 954-958. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCYX202006012.htmLI Z, JIN H, SUN M M, et al. Tissue tracking magnetic resonance for evaluation of left ventricular global myocardial deformation in healthy subjects[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2020, 27(6): 954-958. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCYX202006012.htm [13] 于蕾, 朱家安, 张万蕾, 等. 以岗位胜任力为导向的超声医学住院医师培训体系构建[J]. 中华医学教育探索杂志, 2020, 19(2): 199-200, 202.YU L, ZHU J A, ZHENG W L, et al. Construction of post competency-oriented training system for ultrasound residents[J]. Chinese Journal of Medical Education Research, 2020, 19(2): 199-200, 202. [14] 罗文, 张云飞, 袁佳妮, 等. 基于B-Learning多元化超声医学整合教学法的应用探索[J]. 临床超声医学杂志, 2018, 20(11): 784-786. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCCY201811024.htmLUO W, ZHANG Y F, YUAN J N, et al. Application of B-Learning based integrated teaching method on ultrasound lecture[J]. Journal of Clinical Ultrasound in Medicine, 2018, 20(11): 784-786. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCCY201811024.htm [15] 王峥, 郑敏娟, 刘丽文, 等. 模块化PBL教学法在产前系统超声培训中的应用[J]. 临床超声医学杂志, 2018, 20(12): 859-861. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCCY201812027.htmWANG Z, ZHENG M J, LIU L W, et al. Application of modular PBL teaching method in ultrasound training of prenatal system[J]. Journal of Clinical Ultrasound in Medicine, 2018, 20(12): 859-861. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCCY201812027.htm [16] 童铸廷, 吴怡. PBL教学法在鼻咽癌临床放疗教学中的应用效果[J]. 安徽医学, 2019, 40(06): 703-705. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AHYX201906033.htmTONG Z T, WU Y. The application value of PBL model in clinical radiotherapy teaching of nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Anhui Medical Journal, 2019, 40(06): 703-705. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AHYX201906033.htm [17] 梁冰, 王敏, 郦忆文, 等. 课程整合模式下以器官系统为中心的联合教学查房在全科医学专业实习带教中的应用[J]. 中华全科医学, 2019, 17(10): 1749-1752. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.001047LIANG B, WANG M, LI Y W, et al. Application of organ-systems-centered joint teaching rounds in the practice and teaching of general practice under the mode of curriculum integration[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2019, 17(10): 1749-1752. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.001047 [18] 范兴君, 谷红梅, 齐悦, 等. 基于PBL的对话教学模式在《社区预防与保健》教学中的实践[J]. 中华全科医学, 2022, 20(2): 315-319. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002341FAN X J, GU H M, QI Y, et al. Practice for the course of "community prevention and health care" in the teaching dialogue mode using problem-based learning[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2022, 20(2): 315-319. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002341 [19] 胡小磊, 陈卫东, 孙卫华, 等. PBL联合CBL教学法在内分泌科住院医师规范化培训教学中的应用[J]. 中华全科医学, 2017, 15(7): 1236-1238. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.2017.07.043HU X L, CHEN W D, SUN W H, et al. Application of the teaching method combining PBL with CBL in resident standardization training in the department of endocrinology[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2017, 15(7): 1236-1238. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.2017.07.043 [20] 王先祥, 张义泉, 张震, 等. 多元化教学法在留学生神经外科教学中的应用价值[J]. 安徽医学, 2018, 39(10): 1277-1279. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AHYX201810034.htmWANG X X, ZHANG Y Q, ZHANG Z, et al. The application value of pluralistic teaching method in neurosurgery teaching for international students[J]. Anhui Medical Journal, 2018, 39(10): 1277-1279. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AHYX201810034.htm -





 下载:
下载: