The molecular mechanism of sinomenine hydrochloride treat ulcerative colitis through Hedgehog signalling pathway in mice
-
摘要:
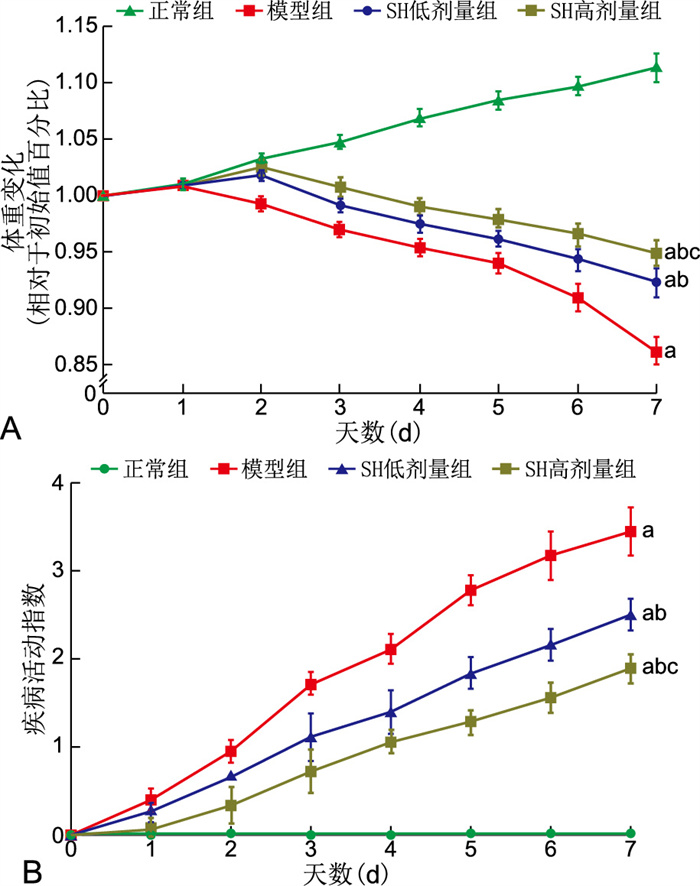
目的 研究盐酸青藤碱(SH)对小鼠溃疡性结肠炎(UC)的保护作用及可能机制。 方法 将24只小鼠采用随机数字表法分为正常组、模型组、SH低、高剂量组(SH 20 mg/kg、60 mg/kg)4组,每组6只;记录疾病活动指数(DAI)和结肠组织病理学评分,检测Shh mRNA及相关蛋白和细胞因子的表达。 结果 与正常组相比,模型组DAI评分[(3.44±0.27)分vs. 0分, P<0.001]升高,组织病理学评分升高[(7.67±0.52)分vs. 0分,P<0.001],Shh mRNA降低(P<0.05),Shh、Smo、Ptch1、Gli1蛋白表达水平降低(均P<0.01),TNF-α、IL-1β、IL-6升高(均P<0.001);与模型组相比, SH低、高剂量组DAI评分[(2.50±0.18)分、(1.89±0.17)分vs. (3.44±0.27)分, P < 0.001]降低, 组织病理学评分降低[(5.17±0.75)分、(3.33±0.52)分vs. (7.67±0.52)分, P < 0.001],Shh、Smo、Ptch1、Gli1蛋白升高(均P<0.001),TNF-α、IL-1β、IL-6降低(均P<0.01)。 结论 SH可治疗小鼠UC,其机制可能是SH上调了Hedgehog信号通路活性,从而降低了TNF-α、IL-1β、IL-6含量。 -
关键词:
- 盐酸青藤碱 /
- 溃疡性结肠炎 /
- 葡聚糖硫酸钠 /
- Hedgehog信号通路
Abstract:Objective To investigate the protective effect and possible mechanism of sinomenine hydrochloride (SH) on ulcerative colitis (UC) in mice. Methods Twenty-four mice were randomly divided into 4 groups: normal group, model group, low and high dose SH group (SH 20 mg/kg, 60 mg/kg), with 6 mice in each group. Disease activity index (DAI) and colon histopathology (HI) scores were recorded, and the expression levels of Shh mRNA and related proteins and cytokines were detected. Results Compared with the normal group, the DAI score [(3.44±0.27) points vs. 0, P < 0.001] and HI score [(7.67±0.52) points vs. 0, P < 0.001] increased, Shh mRNA (P < 0.05), Shh, Smo, Ptch1 and Gli1 protein (all P < 0.01) decreased, and TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 (all P < 0.001) increased in the model group. Compared with the model group, the DAI score [(2.50±0.18) points, (1.89±0.17) points vs. (3.44±0.27) points, P < 0.001], HI score [(5.17±0.75) points, (3.33±0.52) points vs. (7.67±0.52) points, P < 0.001] decreased, Shh, Smo, Ptch1 and Gli1 protein (all P < 0.001) increased, and TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 (all P < 0.01) decreased in the SH treatment group. Conclusion SH can treat ulcerative colitis in mice. The mechanism may be that it up regulates the activity of Hedgehog signalling pathway, thereby reduces the content of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6. -
表 1 各组小鼠结肠组织内Hedgehog信号通路Shh、Smo、Ptch1、Gli1蛋白表达水平比较(x±s)
Table 1. Comparison of the protein expression levels of Shh, Smo, Ptch1 and Gli1 of Hedgehog signaling pathway in colon tissue of mice in each group(x±s)
组别 只数 Shh Smo Ptch1 Gli1 正常组 6 1.00±0.00 1.00±0.00 1.00±0.00 1.00±0.00 模型组 6 0.77±0.08a 0.80±0.09a 0.73±0.09a 0.74±0.10a SH低剂量组 6 1.44±0.10ab 1.35±0.15ab 1.42±0.13ab 1.56±0.16ab SH高剂量组 6 1.83±0.20abc 1.62±0.22abc 1.81±0.09abc 2.05±0.20abc F值 94.771 51.484 132.684 97.811 P值 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 注:与正常组比较,aP < 0.05;与模型组比较,bP < 0.05;与SH低剂量组比较,cP < 0.05。 表 2 各组小鼠血清中细胞因子TNF-α、IL-1β、IL-6表达水平比较(x±s,pg/mL)
Table 2. Comparison of cytokine TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 expression levels in serum of mice in each group (x±s, pg/mL)
1组别 只数 TNF-α IL-1β IL-6 正常组 6 164.61±29.09 21.95±1.56 32.78±6.84 模型组 6 718.53±81.81a 51.62±2.80a 444.07±67.77a SH低剂量组 6 544.72±90.03ab 34.10±2.90ab 345.43±43.40ab SH高剂量组 6 434.11±71.75abc 29.44±3.70abc 236.11±29.35abc F值 62.258 72.606 101.150 P值 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 注:与正常组比较,aP<0.001;与模型组比较,bP<0.01;与SH低剂量组比较,cP<0.05。 -
[1] FLYNN S, EISENSTEIN S. Inflammatory bowel disease presentation and diagnosis[J]. Surg Clin North Am, 2019, 99(6): 1051-1062. doi: 10.1016/j.suc.2019.08.001 [2] 徐峰, 柯希权. 溃疡性结肠炎与肠道微生物关系研究进展[J]. 胃肠病学和肝病学杂志, 2021, 30(9): 969-971. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5709.2021.09.003XU F, KE X Q. Progress of ulcerative colitis and intestinal microorganisms[J]. Chinese Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 2021, 30(9): 969-971. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5709.2021.09.003 [3] NG S C, SHI H Y, HAMIDI N, et al. Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: A systematic review of population-based studies[J]. Lancet, 2017, 390(10114): 2769-2778. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32448-0 [4] 吴开春, 梁洁, 冉志华, 等. 炎症性肠病诊断与治疗的共识意见(2018年·北京)[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2018, 38(9): 796-813. doi: 10.19538/j.nk2018090106WU K C, LIANG J, RAN Z H, et al. Chinese consensus on diagnosis and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease (Beijing, 2018)[J]. Chinese Journal of Practical Internal Medicine, 2018, 38(9): 796-813. doi: 10.19538/j.nk2018090106 [5] FU Y F, LI L, FANG P, et al. Sinomenine ' s protective role and mechanism in stress load-induced heart failure[J]. J Pharm Pharmacol, 2020, 72(2): 209-217. doi: 10.1111/jphp.13181 [6] SINGH D, AGRAWAL A, SINGAL C M S, et al. Sinomenine inhibits amyloid beta-induced astrocyte activation and protects neurons against indirect toxicity[J]. Mol Brain, 2020, 13(1): 30. doi: 10.1186/s13041-020-00569-6 [7] GAO L N, ZHONG B, WANG Y. Mechanism underlying antitumor effects of sinomenine[J]. Chin J Integr Med, 2019, 25(11): 873-878. doi: 10.1007/s11655-019-3151-2 [8] ZHOU Y, LIU H Y, SONG J, et al. Sinomenine alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis via the Nrf2/NQO-1 signaling pathway[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2018, 18(4): 3691-3698. [9] ABRAHAM B P, QUIGLEY E M M. Probiotics in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Gastroenterol Clin North Am, 2017, 46(4): 769-782. doi: 10.1016/j.gtc.2017.08.003 [10] VEENSTRA J P, VEMU B, TOCMO R, et al. Pharmacokinetic analysis of carnosic acid and carnosol in standardized rosemary extract and the effect on the disease activity index of DSS-induced colitis[J]. Nutrients, 2021, 13(3): 773-789. doi: 10.3390/nu13030773 [11] KOJIMA F, SEKIYA H, HIOKI Y, et al. Facilitation of colonic T cell immune responses is associated with an exacerbation of dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in mice lacking microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1[J]. Inflamm Regen, 2022, 42(1): 1. doi: 10.1186/s41232-021-00188-1 [12] KUCHARZIK T. Living guideline on ulcerative colitis[J]. Chirurg, 2022, 93(3): 261-265. doi: 10.1007/s00104-022-01594-y [13] WALTON K D, GUMUCIO D L. Hedgehog signaling in intestinal development and homeostasis[J]. Annu Rev Physiol, 2021, 83: 359-380. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-031620-094324 [14] BUONGUSTO F, BERNARDAZZI C, YOSHIMOTO A N, et al. Disruption of the Hedgehog signaling pathway in inflammatory bowel disease fosters chronic intestinal inflammation[J]. Clin Exp Med, 2017, 17(3): 351-369. doi: 10.1007/s10238-016-0434-1 [15] EICHELE D D, KHARBANDA K K. Dextran sodium sulfate colitis murine model: An indispensable tool for advancing our understanding of inflammatory bowel diseases pathogenesis[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2017, 23(33): 6016-6029. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i33.6016 [16] NEURATH M F, CHIRIAC M T. Targeting immune cell wiring in ulcerative colitis[J]. Immunity, 2019, 51(5): 791-793. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.10.011 [17] 江海燕, 王新月, 王建云, 等. 解毒活血灌肠方联合中药口服治疗溃疡性结肠炎患者的临床研究[J]. 中华全科医学, 2021, 19(11): 1925-1928, 1955. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002202JIANG H Y, WANG X Y, WANG J Y, et al. Clinical study of Jiedu Huoxue Decoction enema combined with oral Chinese medicine in patients with ulcerative colitis[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2021, 19(11): 1925-1928, 1955. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002202 [18] LIU W W, ZHANG Y J, ZHU W N, et al. Sinomenine inhibits the progression of rheumatoid arthritis by regulating the secretion of inflammatory cytokines and monocyte/macrophage subsets[J]. Front Immunol, 2018, 9: 2228. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02228 [19] GAO T L, SHI T S, WIESENFELD-HALLIN Z, et al. Sinomenine facilitates the efficacy of gabapentin or ligustrazine hydrochloride in animal models of neuropathic pain[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2019, 854: 101-108. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.03.061 [20] HELAL M G, ABD ELHAMEED A G. Graviola mitigates acetic acid-induced ulcerative colitis in rats: Insight on apoptosis and Wnt/Hh signaling crosstalk[J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int, 2021, 28(23): 29615-29628. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-12716-0 -





 下载:
下载: