Expression of NLRC5 in cervical cancer and the correlation with the patients ' survival prognosis
-
摘要:
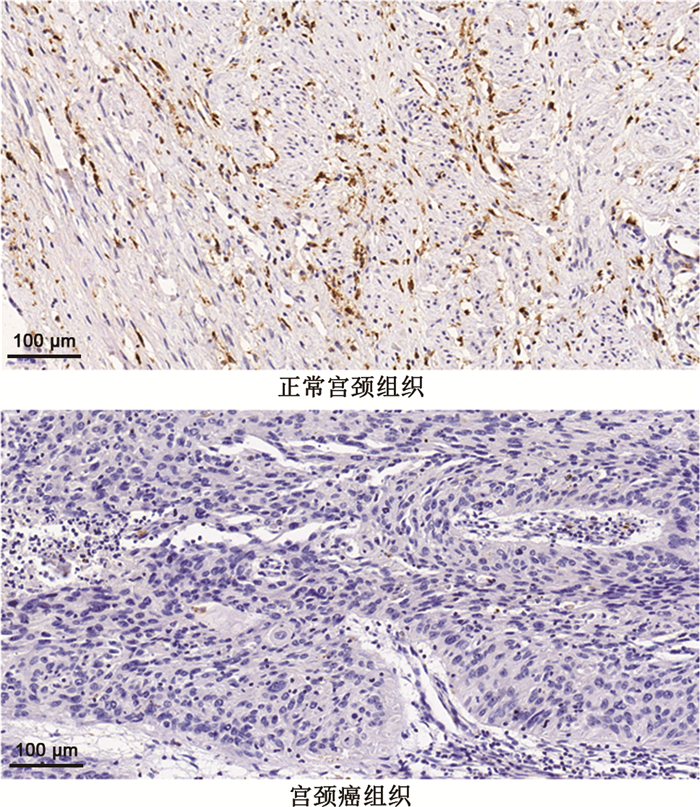
目的 探讨宫颈癌组织及癌旁组织NLRC5(NOD-like receptor family caspase recruitment domain family-containing 5)的表达情况与宫颈癌患者预后的相关性。 方法 选择2013年1月—2016年6月在安徽医科大学第二附属医院进行诊治的宫颈癌患者,共60例,收集宫颈癌手术的癌组织和癌旁组织,采用免疫组化的方法检测宫颈癌组织及癌旁组织中NLRC5的表达并分析其与宫颈癌患者预后的相关性。 结果 在宫颈癌组织中,NLRC5的阳性表达低于癌旁组织[15(25.00)% vs. 50(83.33%), P < 0.05)]。对宫颈癌组织内NLRC5表达与患者临床病理特征进行分析,发现NLRC5的阴性表达与宫颈癌的浸润深度和肿瘤大小相关(χ2=11.769、5.926,均P < 0.05),NLRC5的表达与年龄、病理类型、有无淋巴结转移等没有相关性(均P>0.05)。绘制宫颈癌的生存预后Kaplan-Meier曲线,发现NLRC5阴性表达患者生存期较阳性表达的患者短(P < 0.05)。对宫颈癌预后的相关因素进行单因素或Cox多因素分析,发现NLRC5阴性表达、淋巴结转移、浸润深度是宫颈癌预后的独立影响因素(均P < 0.05)。 结论 与癌旁组织比较,在宫颈癌组织中NLRC5呈现低表达,同时,NLRC5阴性表达是影响宫颈癌患者预后的独立危险因素,这一发现有可能作为宫颈癌诊治的新靶点。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the correlation between the expression of NLRC5 (NOD-like receptor family caspase recruitment domain family-containing 5) in cervical cancer tissue and paracancerous tissue and the prognosis of cervical cancer patients. Methods A total of 60 patients with cervical cancer who were diagnosed and treated in the Second Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University from January 2013 to June 2016 were selected. The cancer tissues and paracancerous tissues of cervical cancer surgery were collected and detected by immunohistochemistry. The expression of NLRC5 in cervical cancer tissues and paracancerous tissues was analyzed, and the correlation between the expression of NLRC5 and the prognosis of cervical cancer patients was analyzed. Results The positive expression of NLRC5 in cervical cancer tissues was lower than that in paracancerous tissues [15(25.00)% vs. 50(83.33%), P < 0.05)]. The expression of NLRC5 in cervical cancer tissue and the clinicopathological characteristics of patients were analyzed, and it was found that the negative expression of NLRC5 was correlated with the depth of invasion and tumor size of cervical cancer (χ2=11.769, 5.926, all P < 0.05). The expression of NLRC5 was not correlated with age, pathological type, lymph node metastasis (all P>0.05). The Kaplan-Meier curve of survival and prognosis of cervical cancer was drawn. It was found that the survival time of patients with negative NLRC5 expression were shorter than those with positive expression (P < 0.05). Univariate or Cox multivariate analysis was performed on the prognostic factors of cervical cancer, and it was found that the negative expression of NLRC5, lymphatic metastasis and depth of invasion were independent risk factors for the prognosis of cervical cancer (all P < 0.05). Conclusion Compared with paracancerous tissues, NLRC5 shows a low expression pattern in cervical cancer tissues. Meanwhile, the negative expression of NLRC5 is an independent risk factor affecting the prognosis of cervical cancer patients. This finding may be used for the diagnosis and treatment of cervical cancer. -
表 1 NLRC5在癌旁组织和癌组织中的表达[例(%)]
Table 1. Expression of NLRC5 in adjacent and cancer tissues[cases(%)]
组别 例数 NLRC5 阳性 阴性 癌组织 60 15(25.00) 45(75.00) 癌旁组织 60 50(83.33) 10(16.67) 注:χ2=41.119,P < 0.001。 表 2 NLRC5表达和宫颈癌临床病理特征的单因素分析(例)
Table 2. Univariate analysis of NLRC5 expression and clinicopathological features of cervical cancer
项目 例数 NLRC5 统计量 P值 阴性 阳性 年龄 0.370a 0.543 ≤45岁 24 19 5 >45岁 36 26 10 病理类型 1.693a 0.193 鳞癌 42 29 13 腺癌 18 16 2 淋巴结转移 < 0.001a 0.999 无 50 38 12 有 10 7 3 分期 0.056b 0.813 Ⅰ 37 28 9 Ⅱ 13 10 3 Ⅲ 10 7 3 癌栓 2.400a 0.121 无 45 31 14 有 15 14 1 浸润深度 11.769a 0.001 浅 29 16 13 深 31 29 2 肿瘤直径 5.926a 0.015 ≤4 cm 36 23 13 >4 cm 24 22 2 注:a为χ2值,b为Hc值。 表 3 宫颈癌预后影响因素的单因素分析
Table 3. Univariate analysis of prognostic impact of cervical cancer
变量 B SE Wald χ2 P值 HR值 95% CI 年龄 0.377 0.410 0.843 0.359 1.457 0.652~3.256 病理类型 -0.290 0.433 0.447 0.504 0.749 0.320~1.750 淋巴结转移 -1.673 0.438 14.591 < 0.001 0.188 0.080~0.443 癌栓 -0.784 0.423 3.441 0.064 0.457 0.200~1.045 浸润深度 -1.381 0.473 8.516 0.004 0.251 0.099~0.636 肿瘤直径 -0.115 0.414 0.077 0.781 0.891 0.396~2.008 NLRC5表达 -1.522 0.739 4.240 0.039 0.218 0.051~0.929 注:赋值方法如下,年龄≤45岁=0,>45岁=1;病理类型为鳞癌=0,腺癌=1;无淋巴结转移=0,有淋巴结转移=1;无癌栓=0,有癌栓=1;浸润深度浅=0,浸润深度深=1;肿瘤直径≤4 cm=0,>4 cm=1;NLRC5表达阳性=0,阴性=1。 表 4 宫颈癌预后影响因素的Cox多因素分析
Table 4. Cox multivariate analysis of prognostic impact of cervical cancer
变量 B SE Wald χ2 P值 HR值 95% CI 淋巴结转移 -2.820 0.573 24.193 < 0.001 0.060 0.019~0.183 浸润深度 -1.954 0.562 12.084 0.001 0.142 0.047~0.426 NLRC5表达 -1.584 0.782 4.099 0.043 0.205 0.044~0.951 -
[1] 张慧慧, 王蓓蓓, 张献文, 等. 伴有盆腔淋巴结转移的宫颈癌新辅助化疗联合放化疗临床疗效及预后因素分析[J]. 中华全科医学, 2021, 19(11): 1823-1826, 1839. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002176ZHANG H H, WANG B B, ZHANG X W, et al. Treatment effect and analysis of prognostic factors of neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by concurrent chemoradiotherapy for advanced cervical cancer with pelvic lymph node metastasis[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2021, 19(11): 1823-1826, 1839. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002176 [2] 张娟, 李娜娜, 陈蕊, 等. TSHR、HPV16 E6蛋白在老年宫颈癌组织中表达及与疾病发生发展的关系[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2021, 41(5): 963-966. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZLXZ202105024.htmZHANG J, LI N N, CHEN R, et al. Expressions of TSHR, HPV16 E6 in cervical cancer tissue from elderly patients and the relationship between the expressions and the development of disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Gerontology, 2021, 41(5): 963-966. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZLXZ202105024.htm [3] TANG F, XU Y D, ZHAO B. NLRC5: New cancer buster?[J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2020, 47(3): 2265-2277. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05253-5 [4] WU Y T, SHI T L, LI J. NLRC5: A paradigm for NLRs in immunological and inflammatory reaction[J]. Cancer Lett, 2019, 451(1): 92-99. [5] 史于传. NLRC5通过激活卵巢癌细胞PI3K/AKT信号通路促进细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭[D]. 合肥: 安徽医科大学, 2021.SHI Y C. NLRC5 promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion by activating PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in ovarian cancer cells[D]. Hefei: Anhui Medical University, 2021. [6] 冯明月, 闫萍. 宫颈上皮内瘤变诊治现状[J]. 河北医科大学学报, 2020, 41(4): 480-483. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3205.2020.04.026FENG M Y, YAN P. Current status of diagnosis and treatment of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia[J]. Journal of Hebei Medical University, 2020, 41(4): 480-483. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3205.2020.04.026 [7] 赵小迎, 郑胡忠, 金纬纬, 等. 宫颈癌临床病理特征与盆腔淋巴结转移的相关性分析[J]. 中华全科医学, 2019, 17(3): 430-432. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.000700ZHAO X Y, ZHENG H Z, JIN W W, et al. Correlation between clinicopathological features and pelvic lymph node metastasis in cervical cancer[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2019, 17(3): 430-432. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.000700 [8] 蒋芳, 向阳. 早期宫颈癌微创手术的现状与未来[J]. 中国妇产科临床杂志, 2021, 22(2): 113-115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FKLC202102002.htmJIANG F, XIANG Y. Minimally invasive surgery for early stage cervical cancer: current status and the future[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology, 2021, 22(2): 113-115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FKLC202102002.htm [9] SCHEFF N N, SALOMAN J L. Neuroimmunology of cancer and associated symptomology[J]. Immunol Cell Biol, 2021, 99(9): 949-61. doi: 10.1111/imcb.12496 [10] LI Y X, CHANG J Y, HE M Y, et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio (MLR) predict clinical outcome in patients with stage ⅡB cervical cancer[J]. J Oncol, 2021, 8(9): 1-14. [11] LAVINIA D, ALESSANDRO T, PAOLO A, et al. Inflammatory biomarkers as promising predictors of prognosis in cervical cancer patients[J]. Oncology, 2021, 99(9): 571-579. [12] ZHANG Z, SUN Y H, CHEN X. NLRC5 alleviated OGD/R-induced PC12-cell injury by inhibiting activation of the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway[J]. J Int Med Res, 2020, 48(8): 1-12 [13] 王媛媛. NLRC5通过NF-κB与p38 MAPK通路调控肺泡巨噬细胞炎症因子分泌的机制研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽医科大学, 2018.WANG Y Y. NLRC5 regulates the secretion of inflammatory cytokines in alveolar macrophages through NF-κB and p38 MAPK pathway[D]. Hefei: Anhui Medical University, 2018. [14] 邵帅, 朱清, 刘洁. Shh信号通路对宫颈癌细胞增殖与凋亡影响的机制研究[J]. 海南医学, 2021, 32(21): 2721-2725. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HAIN202121001.htmSHAO S, ZHU Q, LIU J. Research on the mechanism of Sonic hedgehog signaling pathway on the proliferation and apoptosis of Hela cells[J]. Hainan Medical Journal, 2021, 32(21): 2721-2725. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HAIN202121001.htm [15] 汪欢, 俞广进, 熊奇如. 肝细胞癌患者中NLRC5的表达及其临床意义[J]. 肝胆外科杂志, 2018, 26(2): 149-153. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDWZ201802022.htmWANG H, YU G J, XIONG Q R. Expression of NLRC5 in hepatocellular cacinoma and its clinical significance[J]. Journal of Hepatobiliary Surgery. 2018, 26(2): 149-153. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDWZ201802022.htm [16] 王琴. NLRC5在透明细胞肾细胞癌中的功能与机制研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽医科大学, 2019.WANG Q. Function and mechanism of NLRC5 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma[D]. Hefei: Anhui Medical University, 2019. -





 下载:
下载: