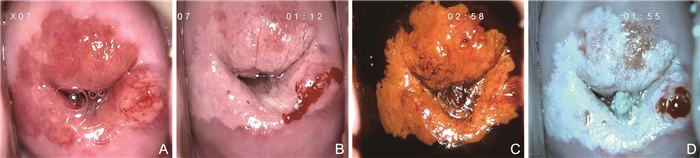
Clinical application value of R-way colposcopy diagnosis system in diagnosing cervical diseases
-
摘要:
目的 评估R-way阴道镜诊断系统在宫颈疾病诊断中的临床应用价值。 方法 2018年1—12月在蚌埠医学院第一附属医院阴道镜门诊就诊的患者中,选取保留有完整图像及病理随访结果的380例患者,应用R-way阴道镜诊断系统对图像进行回顾性分析并给出诊断结果,以宫颈组织病理诊断为“金标准”,比较R-way诊断系统与2011版阴道镜诊断术语对宫颈病变诊断的敏感度、特异度、约登指数及一致性,并计算ROC曲线下面积,评估R-way诊断系统在宫颈疾病诊断方面的临床应用价值。 结果 R-way系统诊断宫颈癌的灵敏度为62.9%,特异度为100.0%,约登指数为69.2%,符合率为98.9%;诊断宫颈高级别上皮内病变的灵敏度为84.9%,特异度为89.5%,约登指数为74.5%,符合率为88.4%;诊断宫颈低级别上皮内病变的灵敏度为76.1%,特异度为79.0%,约登指数为55.1%,符合率为78.2%。设定宫颈高级别以上病变为阳性组,低级别以下病变为阴性组;R-way诊断系统诊断宫颈阳性病变的灵敏度为86.8%,特异度为90.5%;2011版阴道镜诊断术语诊断宫颈阳性病变的灵敏度为73.6%,特异度为90.9%;两者诊断宫颈阳性病变的ROC曲线下面积分别为0.887、0.822。 结论 R-way诊断系统是一种简单易学、稳定有效的客观评价阴道镜图像的诊断系统,具有较高的临床应用和推广价值。 Abstract:Objective To evaluate the clinical value of the R-way colposcopy diagnosis system in diagnosing cervical diseases. Methods From January 2018 to December 2018, amongst the patients who visited the colposcopy clinic of the First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College, 380 patients with complete image and pathological follow-up results were selected. The R-way diagnosis system was used to analyse the images retrospectively and provide diagnosis results. Histopathological diagnosis was taken as the "gold standard" to compare the sensitivity, specificity, Youden index, and consistency test of the R-way diagnostic system and 2011 colposcopy diagnostic terms in the diagnosis of cervical lesions. We further calculated the area under the ROC curve and evaluated the clinical value of the R-way diagnostic system in diagnosing cervical diseases. Results The R-way diagnosis system had a sensitivity of 62.9%, a specificity of 100.0%, Youden index of 69.2%, and a concordance rate of 98.9% for diagnosing cervical cancer. The sensitivity for diagnosing high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL) was 84.9%, the specificity was 89.5%, the Youden index was 74.5%, and the concordance rate was 88.4%. The sensitivity for diagnosing low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (LSIL) was 76.1%, specificity was 79.0%, Youden index was 55.1%, and concordance was 78.2%. With the assumption that HSIL and above lesions were the positive group, LSIL and other lesions were the negative group. The sensitivity of the positive group of the R-way system and colposcopic terminology were 86.8% and 73.6%, respectively, the specificity were 90.5% and 90.9%, and the area under the ROC curve were 0.887 and 0.822. Conclusion The R-way diagnostic system is a simple, easy, stable and effective diagnostic system for objectively evaluating colposcopic images. It has high-potential clinical application and promotion value. -
Key words:
- R-way diagnosis system /
- Cervical diseases /
- Colposcopy /
- Diagnostic techniques
-
表 1 R-way诊断系统与阴道镜诊断术语评价指标(%)
Table 1. Comparison of R-way diagnostic system and colposcopy diagnostic value
项目 检查方法 灵敏度(95% CI) 特异度(95% CI) 阳性预测值(95% CI) 阴性预测值(95% CI) 约登指数 符合率 癌 R-way 69.2(44.1~94.3) 100.0(100.0~100.0) 100.0(100.0~100.0) 98.9(97.9~100.0) 69.2 98.9 阴道镜 61.5(35.1~88.0) 99.7(99.2~100.3) 88.9(68.4~109.4) 98.7(97.5~99.8) 61.3 98.4 HSIL R-way 84.9(77.7~92.2) 89.5(86.0~93.1) 72.5(64.1~80.9) 94.8(92.2~97.5) 74.5 88.4 阴道镜 68.8(59.4~78.2) 89.5(86.0~93.1) 68.1(58.7~77.5) 89.9(86.4~93.4) 58.4 84.5 LSIL R-way 76.1(68.2~84.0) 79.0(74.1~83.9) 60.6(52.5~68.6) 88.7(84.6~92.7) 55.1 78.2 阴道镜 72.6(64.3~80.8) 76.0(70.9~81.2) 56.2(48.1~64.2) 86.8(82.4~91.1) 48.6 75.0 表 2 R-way诊断系统及阴道镜诊断价值比较
Table 2. Comparison of R-way diagnostic system and colposcopy diagnostic value
检查方法 真阳性
(例)假阳性
(例)真阴性
(例)假阴性
(例)灵敏度
(95% CI, %)特异度
(95% CI, %)阳性预测值
(95% CI, %)阴性预测值
(95% CI, %)约登指数
(%)符合率
(%)ROC曲线下面积
(95% CI)R-way诊断系统 92 26 248 14 86.8(80.3~93.2) 90.5(87.0~94.0) 78.0(70.5~85.4) 94.7(91.9~97.4) 77.3 89.5 0.887±0.022(0.844~0.929) 阴道镜诊断术语 78 25 249 28 73.6(65.2~82.0) 90.9(87.5~94.3) 75.7(67.4~84.0) 89.9(86.3~93.4) 64.5 86.1 0.822±0.027(0.769~0.876) -
[1] JOHNSON C A, JAMES D, MARZAN A, et al. Cervical cancer: An overview of pathophysiology and management[J]. Semin Oncol Nurs, 2019, 35(2): 166-174. doi: 10.1016/j.soncn.2019.02.003 [2] 钱德英. 阴道镜下异常图像对宫颈病变筛查意义[J]. 中国实用妇科与产科杂志, 2016, 32(5): 399-402. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSF201605006.htmQIAN D Y. Significance of abnormal images under colposcopy in screening cervical lesions[J]. Chinese Journal of Practical Gynecology and Obstetrics, 2016, 32(5): 399-402. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSF201605006.htm [3] FERLAY J, COLOMBET M, SOERJOMATARAM I, et al. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods[J]. Int J Cancer, 2019, 144(8): 1941-1953. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31937 [4] 刘萍. 中国大陆13年宫颈癌临床流行病学大数据评价[J]. 中国实用妇科与产科杂志, 2018, 34(1): 41-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSF201801014.htmLIU P. Evaluation of big data of clinical epidemiology of cervical cancer in Chinese Mainland in the past 13 years[J]. Chinese Journal of Practical Gynecology and Obstetrics, 2018, 34(1): 41-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSF201801014.htm [5] SIMMS K T, STEINBERG J, CARUANA M, et al. Impact of scaled up human papilloma virus vaccination and cervical screening and the potential for global elimination of cervical cancer in 181 countries, 2020-99: A modelling study[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2019, 20(3): 394-407. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30836-2 [6] 陈春林. 中国宫颈癌临床诊疗与大数据[J]. 中国实用妇科与产科杂志, 2018, 34(1): 25-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSF201801008.htmCHENG C L. Clinical diagnosis, treatment and big data of cervical cancer in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Practical Gynecology and Obstetrics, 2018, 34(1): 25-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSF201801008.htm [7] SHANMUGASUNDARAM S, YOU J. Targeting persistent human papillomavirus infection[J]. Viruses, 2017, 9(8): 229. doi: 10.3390/v9080229 [8] 徐军娟, 裘雅芬, 冯燕. 高危型人乳头瘤病毒对不同程度宫颈病变发生、发展及预后的影响研究[J]. 中华全科医学, 2016, 14(6): 1050-1052. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.2016.06.055XU J J, QIU Y F, FENG Y. Study on the influence of high-risk human papillomavirus on the occurrence, development and prognosis of different degrees of cervical lesions[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2016, 14(6): 1050-1052. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.2016.06.055 [9] 倪昌雪, 王艳, 叶国柳, 等. HPV E6/E7 mRNA检查对宫颈细胞学ASCUS的分流价值[J]. 中华全科医学, 2021, 19(2): 198-201, 255. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.001766NI C X, WANG Y, YE G L, et al. The shunt value of HPV E6/E7 mRNA examination in cervical cytology ASCUS[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2021, 19(2): 198-201, 255. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.001766 [10] 冯慧, 马德勇, 王婷婷, 等. TTR-way在宫颈癌筛查及阴道镜诊断培训中的价值研究[J]. 中国实用妇科与产科杂志, 2017, 33(3): 301-306. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSF201703020.htmFENG H, MA D Y, WANG T T, et al. Value of TTR-way in the training of cervical cancer screening and colposcopy diagnosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Practical Gynecology and Obstetrics, 2017, 33(3): 301-306. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSF201703020.htm [11] CHEN W Q, ZHENG R S, BAADE P D, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2016, 66(2): 115-132. [12] 陈飞, 李舒, 胡惠英, 等. 2017年美国阴道镜和子宫颈病理学会阴道镜检查标准解读[J]. 中国实用妇科与产科杂志, 2018, 34(4): 413-418. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSF201804021.htmCHEN F, LI S, HU H Y, et al. Interpretation of colposcopy examination standard of American Society of colposcopy and cervical pathology in 2017[J]. Chinese Journal of Practical Gynecology and Obstetrics, 2018, 34(4): 413-418. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSF201804021.htm [13] 魏玮, 臧茂娟, 陈国庆. 542例阴道镜图像特点及病理结果分析[J]. 中国妇幼保健, 2018, 33(6): 1221-1223. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZFYB201806008.htmWEI W, ZANG M J, CHENG G Q. Analysis on colposcopic image characteristics and pathological results in 542 cases[J]. Maternal and Child Health Care of China, 2018, 33(6): 1221-1223. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZFYB201806008.htm [14] MORA ENRIQUEZ J A, AMAYA GUIO J, SALAMANCA MORA S, et al. Evaluation of inter observer concordance of the Swede score for digital colposcopic images[J]. Rev Colomb Obstet Ginecol, 2019, 70(2): 94-102. [15] 潘云青. 人乳头状瘤病毒分型联合液基薄层细胞学检查、阴道镜Reid评分对宫颈上皮内瘤变分级诊断效能分析[J]. 中国现代医药杂志, 2021, 23(3): 95-98. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHTY202103039.htmPAN Y Q. Analysis of diagnostic efficacy of HPV typing combined with liquid-based thin-layer cytology and colposcopy Reid score in grading cervical intraepithelial neoplasia[J]. Modern Medicine Journal of China, 2021, 23(3): 95-98. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHTY202103039.htm [16] 邢亚萍, 宋晓霞. HR-HPV在宫颈癌中的分布特点及其与发病年龄的关系[J]. 医药论坛杂志, 2021, 42(13): 75-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYYX202113020.htmXING Y P, SONG X X. Distribution characteristics of HR-HPV in cervical squamous carcinoma and its relationship with age of onset[J]. Journal of Medical Forum, 2021, 42(13): 75-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYYX202113020.htm [17] 吴言, 王军. 临床阴道镜评分体系诊断宫颈鳞状上皮内病变的临床意义[J]. 中国社区医师, 2020, 36(20): 105-106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XCYS202020059.htmWU Y, WANG J. Study on the clinical significance of clinical colposcopy scoring system in diagnosis of cervical squamous intraepithelial lesions[J]. Chinese Community Doctors, 2020, 36(20): 105-106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XCYS202020059.htm [18] KUSHWAH S, KUSHWAH B. Correlation of two colposcopic indices for predicting premalignant lesions of cervix[J]. J Mid-life Health, 2017, 8(3): 118-123. [19] RANGA R, RAI S, KUMARI A, et al. A comparison of the strength of association of Reid colposcopic index and Swede score with cervical histology[J]. J Low Genit Tract Dis, 2017, 21(1): 55-58. [20] 刘芳, 张玉芳, 韩菁, 等. R-way系统对宫颈病变的诊断价值及影响因素分析[J]. 浙江医学, 2020, 42(11): 1117-1121. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJYE202011007.htmLIU F, ZHANG Y F, HAN J, et al. Diagnostic value and influencing factors of R-way system for cervical lesions[J]. Zhejiang Medical Journal, 2020, 42(11): 1117-1121. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJYE202011007.htm -





 下载:
下载: