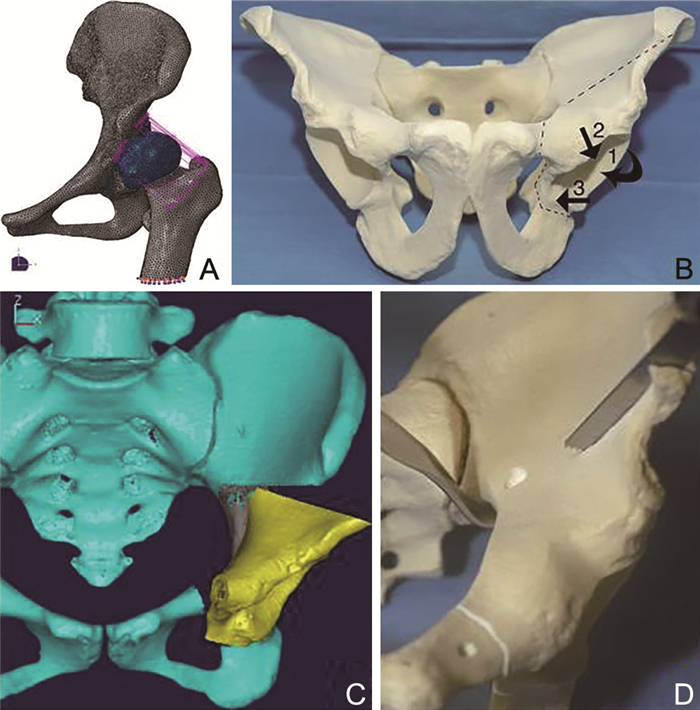
CAD-RP technique combined with three-dimensional finite element analysis in orthopedics practice and exploration in clinical teaching
-
摘要:
目的 探究计算机辅助设计(CAD)技术及快速成型(RP)技术(简称为CAD-RP技术)联合三维有限元分析在骨科临床教学中的效果与可行性。 方法 将2019—2020学年在蚌埠医学院第一附属医院骨科实习的84名临床医学专业学生按随机数字表法分为观察组与对照组,每组各42人,观察组采取结合CAD-RP技术联合三维有限元分析的PBL教学法,对照组则采取传统PBL教学法。在课程完成后开展结课考试及教学满意度调查。考试方式包括骨科专业理论课内容以及临床实践技能操作,满意度调查包括学习兴趣、知识掌握效率、师生互动交流及教学环境等方面。 结果 专业理论知识:观察组成绩为(35.36±2.40)分;对照组成绩为(33.90±2.55)分。临床实践技能:观察组结业考核成绩为(35.21±2.41)分;对照组结业考核成绩为(33.36±2.84)分。满意度:观察组满意率为78.6%(33/42);对照组满意率为45.2%(19/42)。观察组较对照组在考试成绩与教学满意度方面均有所提高(均P<0.05)。 结论 CAD-RP技术联合三维有限元分析在骨科临床教学有重要意义,激发了医学生的学习兴趣,值得推广和采用。 Abstract:Objective To explore the effect and feasibility of computer aided design (CAD) and rapid prototyping (RP) technique combined with three-dimensional (3D) finite element analysis in clinical teaching of orthopedics. Methods Eighty-four clinical medicine students who were practicing in the Department of Orthopedics in the First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College in 2019-2020 were randomly divided into observation group and control group, with 42 students in each group. The observation group adopted the PBL teaching method combined with CAD-RP technology and 3D finite element analysis, while the control group adopted the traditional PBL teaching method. After the completion of the course, the final examination and teaching satisfaction survey carried out. The examination method included the theoretical course content of orthopedics specialty and the operation of clinical practice skills. The satisfaction survey included learning interest, knowledge mastery efficiency, teacher-student interaction and teaching environment. Results Professional theoretical knowledge: the average scores of the observation group and the control group were (35.36±2.40) points and (33.90±2.55) points, respectively. Clinical practice skills: the average score of completion examination in the observation group and the control group were (35.21±2.41) points and (33.36±2.84) points, respectively. Satisfaction: the satisfaction rates of the observation group and the control group were 78.6% (33/42) and 45.2% (19/42), respectively. Compared with the control group, the examination scores and teaching satisfaction were improved in the observation group (all P < 0.05). Conclusion CAD-RP combined with 3D finite element analysis is of great significance in clinical teaching of orthopedics. It has stimulated the learning interest of medical students and is worth promoting and adopting. -
表 1 2组实习医生期末考试综合成绩及绩点比较(x ±s,分)
Table 1. Comparison of the comprehensive scores and grade points of the final examination between two groups of interns(x ±s, points)
组别 人数 期末考试成绩 绩点 观察组 42 85.02±3.40 3.83±0.21 对照组 42 85.33±4.06 3.86±0.24 t值 0.378 0.664 P值 0.706 0.509 表 2 2组实习医生专业理论考试成绩比较(x ±s,分)
Table 2. Comparison of professional theory test scores between two groups of interns(x ±s, points)
组别 人数 专业理论考试 临床实践技能 观察组 42 35.36±2.40 35.21±2.41 对照组 42 33.90±2.55 33.36±2.84 t值 2.687 3.226 P值 0.009 0.002 表 3 2组实习医生教学满意度评价比较[人(%)]
Table 3. Comparison of teaching effect evaluation between two groups of interns[cases(%)]
组别 人数 满意 不满意 观察组 42 33(78.6) 9(21.4) 对照组 42 19(45.2) 23(54.8) 注:2组满意情况比较,χ2=5.182,P=0.022。 -
[1] DONG X S, SONG G F, WU C J, et al. Effectiveness of rehabilitation training combined with acupuncture on aphasia after cerebral hemorrhage: A systematic review protocol of randomized controlled trial[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2019, 98(24): e16006. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016006. [2] KIMIWADA T, HAYASHI T, TAKAHASHI M, et al. Progressive cerebral ischemia and intracerebral hemorrhage after indirect revascularization for a patient with cerebral proliferative angiopathy[J]. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis, 2019, 28(4): 853-858. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2018.11.021 [3] 张培, 高涌, 崔培元, 等. 3D打印联合PBL教学在骨科住院医师规范化培训中的应用[J]. 中华全科医学, 2021, 19(5): 856-859. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.001934ZHANG P, GAO Y, CUI P Y, et al. Application value of 3D printing technology combined with PBL teaching in standardised training of orthopaedic residents[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2021, 19(5): 856-859. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.001934 [4] 张党锋, 马兴, 尹思, 等. 改良传统教具突破骨科教学难点的探索[J]. 临床医药文献电子杂志, 2018, 5(39): 173, 179. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCWX201839149.htmZHANG D F, MA X, YIN S, et al. Exploration of improving traditional teaching AIDS to break through the difficulties in orthopedic teaching[J]. Journal of Clinical Medical Literature(Electronic Edition), 2018, 5(39): 173, 179. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCWX201839149.htm [5] 李静, 石庆平, 彭德峰. PDCA循环在静脉药物配置中心提高抗肿瘤药物配置质量中的应用[J]. 中华全科医学, 2018, 16(12): 2095-2097, 2101. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.000571LI J, SHI Q P, PENG D F. Application of Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle in improving the quality of antitumor drugs intravenous admixture services[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2018, 16(12): 2095-2097, 2101. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.000571 [6] 马婧婧. 新课标背景下PBL教学法在中职思政课中的应用[J]. 现代职业教育, 2021(25): 106-107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDZJ202125053.htmMA J J. Application of PBL teaching method in ideological and political course in secondary vocational schools under the background of new curriculum standard[J]. Modern Vocational Education, 2021(25): 106-107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDZJ202125053.htm [7] 姚新明, 赵咏莉, 何春玲, 等. PBL结合CBL教学法在内分泌科临床实习教学中的应用效果[J]. 安徽医学, 2017, 38(5): 651-654. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AHYX201705034.htmYAO X M, ZHAO Y L, HE C L, et al. Application of PBL combined with CBL teaching method in clinical practice teaching in department of endocrinology[J]. Anhui Medical Journal, 2017, 38(5): 651-654. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AHYX201705034.htm [8] 任静, 祖光然, 姬栋岩. 医工交叉学科发展背景下护理学教研的思考[J]. 教育教学论坛, 2017(3): 239-240. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYJU201703105.htmREN J, ZU G R, JI D Y. The thinking of nursing teaching and research based on the principle development of biomedical engineering[J]. Education Teaching Forum, 2017(3): 239-240. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYJU201703105.htm [9] WANG X Y, LIU S X, PENG J P, et al. Development of a novel customized cutting and rotating template for Bernese periacetabular osteotomy[J]. J Orthop Surg Res, 2019, 14(1): 1-10. [10] 朱晨, 孔荣, 方诗元, 等. 混合型教学模式对骨科教学效果的影响[J]. 安徽医学, 2016, 37(4): 486-488. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AHYX201604036.htmZHU C, KONG R, FANG S Y, et al. The effect of blended teaching mode on orthopedic teaching[J]. Anhui Medical Journal, 2016, 37(4): 486-488. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AHYX201604036.htm [11] 彭林. 引导式教学联合模拟教学在骨科护理解剖学教学中的应用[J]. 解剖学研究, 2019, 41(4): 354-356. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDJP201904041.htmPENG L. Application of guided teaching combined with simulation teaching in orthopedic nursing anatomy teaching[J]. Anatomy Research, 2019, 41(4): 354-356. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDJP201904041.htm [12] 代飞. 探讨虚拟手术训练系统在骨科住院医师临床教学中的应用[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘, 2019, 19(63): 370-371. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WMIA201963223.htmDAI F. To explore the application of virtual surgery training system in clinical teaching of orthopedic residents[J]. World Latest Medicine Information, 2019, 19(63): 370-371. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WMIA201963223.htm [13] 何小艳, 张蔚, 刘静, 等. 探讨三维解剖软件在妇产科CPPT教学中的应用[J]. 中国继续医学教育, 2016, 8(32): 25-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXUY201632014.htmHE X Y, ZHANG W, LIU J, et al. To explore application of 3D anatomical software in gynecology and obstetrics cppt teaching method[J]. China Continuing Medical Education, 2016, 8(32): 25-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXUY201632014.htm [14] 刘涛, 牛国旗, 陈辉, 等. 3D打印结合VR技术在经皮椎弓根穿刺教学中的应用效果[J]. 安徽医学, 2021, 42(6): 692-695. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AHYX202106028.htmLIU T, NIU G Q, CHEN H, et al. The application effect of 3D printing combined virtual reality(VR)technology in teaching of percutaneous pedicle puncture[J]. Anhui Medical Journal, 2021, 42(6): 692-695. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AHYX202106028.htm [15] 张琳琳, 王旭义, 陈晓东. Bernese髋臼周围截骨术术前规划的有限元分析方法研究[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志, 2016, 33(3): 455-460. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWGC201603010.htmZHANG L L, WANG X Y, CHEN X D. Study on finite element analysis method for the pre-operative planning of Bernese periacetabular osteotomy[J]. Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2016, 33(3): 455-460. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWGC201603010.htm [16] WANG X Y, PENG J P, LI D, et al. Does the optimal position of the acetabular fragment should be within the radiological normal range for all developmental dysplasia of the hip? A patient-specific finite element analysis[J]. J Orthop Surg Res, 2016, 11(1): 109. [17] WANG X Y, PENG J P, ZHU J F, et al. Application of three-dimensional computerised tomography reconstruction and image processing technology in individual operation design of developmental dysplasia of the hip patients[J]. Int Orthop, 2016, 40(2): 255-265. [18] 唐佃俊, 李凡东, 郭亚南, 等. 3D打印技术联合PBL在主动脉扩张性疾病教学中的研究[J]. 中华全科医学, 2021, 19(2): 305-307. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.001795TANG D J, LI F D, GUO Y N, et al. Application of three-dimensional printing technology and PBL in teaching about aortic dilated diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2021, 19(2): 305-307. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.001795 [19] MARRO A, BANDUKWALA T, MAK W. Three-dimensional printing and medical imaging: A review of the methods and applications[J]. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol, 2016, 45(1): 2-9. [20] 李忠海, 鲁明, 高淑贤, 等. 3D打印技术在骨盆骨折临床教学中的应用及效果评价[J]. 中国高等医学教育, 2020(4): 75-76. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZOGU202004042.htmLI Z H, LU M, GAO S X, et al. Application and effect evaluation of 3D printing technology in clinical teaching of pelvic fractures[J]. China Higher Medical Education, 2020(4): 75-76. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZOGU202004042.htm -





 下载:
下载: