Correlation analysis between serum Lp-PLA2 level and carotid atherosclerotic plaque
-
摘要:
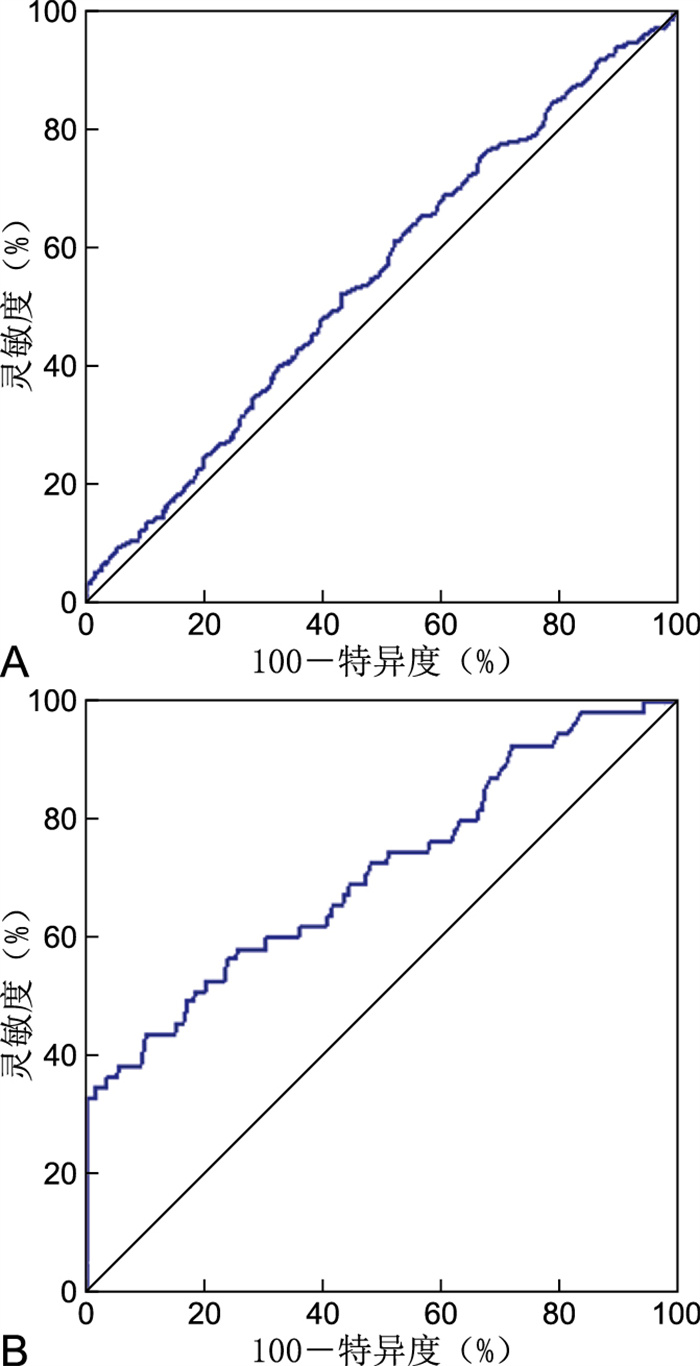
目的 探讨血清脂蛋白相关磷脂酶A2(Lp-PLA2)水平与颈动脉粥样硬化斑块的相关性。 方法 选择2019年6月—2020年12月于南京医科大学第二附属医院行颈动脉超声及Lp-PLA2检测的住院患者1 018例,根据检查结果将患者分为:(1)无斑块(31例)、稳定(376例)和不稳定斑块组(611例);(2)无斑块(31例)、单侧(324例)和双侧颈动脉斑块组(663例);(3)无狭窄(31例)、轻度(932例)、中度(26例)和重度颈动脉狭窄组(29例)。计算所有患者的斑块总面积、稳定斑块面积和不稳定斑块面积。分析Lp-PLA2水平在各组间的差异性及与斑块面积的相关性。 结果 与无斑块组[139.00(96.00,193.00)ng/mL]比较,不稳定斑块组[179.00(123.00,281.00)ng/mL]和双侧斑块组[181.00(120.00,279.00)ng/mL]Lp-PLA2水平明显升高(均P < 0.05)。颈动脉无狭窄及轻度狭窄患者的Lp-PLA2水平与中、重度狭窄患者之间差异有统计学意义(均P < 0.01)。Lp-PLA2与斑块总面积、不稳定斑块面积之间均呈正相关关系(均P < 0.05)。Lp-PLA2对中重度颈动脉狭窄存在较高的诊断价值(AUC=0.710,灵敏度为43.6%,特异度为89.7%,P < 0.001,95% CI: 0.631~0.789)。 结论 Lp-PLA2与颈动脉斑块稳定度、血管狭窄程度、双侧斑块形成及斑块面积,尤其是不稳定斑块面积显著相关,对颈动脉粥样硬化斑块的形成和发展有促进作用。Lp-PLA2对中重度颈动脉狭窄具有较高的诊断价值,可能是大规模临床筛查较好的提示指标。 -
关键词:
- 脂蛋白相关磷脂酶A2 /
- 颈动脉粥样硬化斑块 /
- 颈动脉超声
Abstract:Objective To explore the correlation between lipoprotein associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) and carotid atherosclerotic plaque. Methods A total of 1 018 patients who underwent carotid artery ultrasound and Lp-PLA2 detection from June 2019 to December 2020 in the Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University were selected. Based on the test results, patients were divided into (1) non-carotid plaque group (31 cases), stable group (376 cases) and unstable group (611 cases); (2) non-carotid plaque group (31 cases), unilateral group (324 cases) and bilateral group (663 cases); (3) no stenosis group (31 cases), mild (932 cases), moderate (26 cases) and severe carotid stenosis (29 cases). The total plaque area, stable plaque area, and unstable plaque area of all patients were calculated. The difference of Lp-PLA2 level among groups and the correlation of plaque area were analyzed. Results Compared with the non-plaque group [139.00 (96.00, 193.00) ng/mL], the Lp-PLA2 level in the unstable plaque group [179.00 (123.00, 281.00) ng/mL] and the bilateral plaque group [181.00 (120.00, 279.00) ng/mL] were significantly increased (all P < 0.05). The level of Lp-PLA2 in patients without carotid stenosis and with mild carotid stenosis were significantly different from that in patients with moderate and severe carotid stenosis (all P < 0.01). Lp-PLA2 was positively correlated with total plaque area and unstable plaque area (all P < 0.05). Lp-PLA2 had high diagnostic value for moderate and severe carotid artery stenosis (AUC=0.710, sensitivity was 43.6%, specificity was 89.7%, P < 0.001, 95% CI: 0.631-0.789). Conclusion Lp-PLA2 is significantly correlated with carotid plaque stability, vascular stenosis, bilateral plaque formation and plaque area, especially unstable plaque area, which can promote the formation and development of carotid atherosclerotic plaque. Lp-PLA2 has high diagnostic value for moderate and severe carotid stenosis, and may be a good indicator for large-scale clinical screening. -
表 1 Lp-PLA2与颈动脉斑块稳定度的关系[M(P25, P75), ng/mL]
Table 1. Relationship between Lp-PLA2 and carotid plaque stability[M(P25, P75), ng/mL]
组别 例数 Lp-PLA2 无斑块 31 139.00(96.00,193.00) 稳定斑块 376 161.50(114.00,271.00) 不稳定斑块 611 179.00(123.00,281.00)a H值 11.862 P值 0.003 注:与无斑块组比较,aP < 0.01。 表 2 Lp-PLA2与颈动脉斑块单双侧的关系[M(P25, P75), ng/mL]
Table 2. Relationship of Lp-PLA2 between non-carotid plaque, unilateral and bilateral group[M(P25, P75), ng/mL]
组别 例数 Lp-PLA2 无斑块 31 139.00(96.00,193.00) 单侧 324 157.00(113.25,265.50) 双侧 663 181.00(120.00,279.00)a H值 9.937 P值 0.007 注:与无斑块组比较,aP < 0.01。 表 3 Lp-PLA2与颈动脉狭窄程度的关系[M(P25, P75), ng/mL]
Table 3. Relationship between Lp-PLA2 and degree of carotid stenosis[M(P25, P75), ng/mL]
组别 例数 Lp-PLA2 无狭窄 31 139.00(96.00,93.00) 轻度狭窄 932 167.50(117.00,270.00) 中度狭窄 26 257.50(138.50,394.00)ab 重度狭窄 29 333.00(161.00,430.50)ab H值 34.004 P值 < 0.001 注:与无狭窄组比较,aP < 0.01;与轻度狭窄组比较,bP < 0.01。 表 4 Lp-PLA2与斑块总面积、稳定斑块面积、不稳定斑块面积的相关性分析
Table 4. Correlation analysis of Lp-PLA2 with carotid plaque area
组别 Lp-PLA2 r值 P值 斑块总面积 0.094 0.003 稳定斑块面积 -0.003 0.918 不稳定斑块面积 0.109 < 0.001 表 5 Lp-PLA2对不稳定斑块和中重度颈动脉狭窄的诊断价值
Table 5. Diagnostic value of Lp-PLA2 in unstable plaque and moderate to severe carotid stenosis
组别 AUC 临界值(ng/mL) P值 95% CI 灵敏度(%) 特异度(%) 不稳定斑块 0.552 150.00 0.005 0.516~0.588 61.5 47.7 中重度颈动脉狭窄 0.710 332.00 < 0.001 0.631~0.789 43.6 89.7 -
[1] 王亚楠, 吴思缈, 刘鸣. 中国脑卒中15年变化趋势和特点[J]. 华西医学, 2021, 36(6): 803-807. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYX202106017.htmWANG Y N, WU S M, LIU M. Temporal trends and characteristics of stroke in China in the past 15 years[J]. West China Medical Journal, 2021, 36(6): 803-807. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYX202106017.htm [2] WU S M, WU B, LIU M, et al. Stroke in China: Advances and challenges in epidemiology, prevention, and management[J]. Lancet Neurol, 2019, 18(4): 394-405. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30500-3 [3] MESCHIA J F, BUSHNELL C, BODEN-ALBALA B, et al. Guidelines for the primary prevention of stroke: A statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association[J]. Stroke, 2014, 45(12): 3754-3832. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000046 [4] STAFFORINI D M. Plasma PAF-AH (PLA2G7): Biochemical properties, association with LDLs and HDLs, and regulation of expression[J]. Enzymes, 2015, 38: 71-93. [5] CAO J, YAN P, ZHOU Y J, et al. Clinical utility of the serum level of lipoprotein-related phospholipase A2 in acute ischemic stroke with cerebral artery stenosis[J]. Front Neurol, 2021, 12: 642483. DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2021.642483. [6] 李振洲, 邵玉凤, 陈胜华, 等. 颈动脉斑块稳定性超声评估与血浆脂蛋白相关磷脂酶A2水平的相关性研究[J]. 中国临床医学影像杂志, 2019, 30(3): 166-168, 173. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LYYX201903007.htmLI Z Z, SHAO Y F, CHEN S H, et al. Correlation between stability of carotid plaque evaluated by ultrasound and the level of plasma Lp-PLA2[J]. Journal of China Clinic Medical Imaging, 2019, 30(3): 166-168, 173. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LYYX201903007.htm [7] 张瑾, 潘凤华, 吴晋. 脑梗死患者脂蛋白相关磷脂酶A2水平及其与颈动脉斑块稳定性的相关性研究[J]. 系统医学, 2018, 3(14): 1-3. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTYX201814001.htmZHANG J, PAN F H, WU J. Study on Correlation between the Lipoprotein Associated Phospholipase A2 and Stability of Carotid Artery Plaque of Patients with Cerebral Infraction[J]. Systems Medicine, 2018, 3(14): 1-3. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTYX201814001.htm [8] 郝泽林, 吴建跃, 滕振飞, 等. 急性脑梗死患者血清学指标与神经功能缺损和脑梗死体积及颈动脉斑块性质的相关性研究[J]. 中华全科医学, 2020, 18(11): 1803-1806. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.001623HAO Z L, WU J Y, TENG Z F, et al. Correlation of hs-CRP, MMP-9 and Lp-PLA2 with neurological deficit, cerebral infarction volume and carotid plaque properties in patients with acute cerebral infarction[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2020, 18(11): 1803-1806. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.001623 [9] 中国医师协会神经内科医师分会神经超声专业委员会, 中华医学会神经病学分会神经影像协作组. 中国神经超声的操作规范(三)[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2017, 97(43): 3361-3370. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2017.43.001Neuroultrasound Professional Committee of Chinese Medical Doctor Association, Neuroimaging Collaborative Group of Chinese Society of Neurology. Chinese Code of practice for neuroultrasound(3)[J]. National Medical Journal of China, 2017, 97(43): 3361-3370. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2017.43.001 [10] LIU H M, YAN Y, WANG Y X, et al. Association between high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 and carotid atherosclerosis: A cross-sectional study[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2018, 22(10): 5145-5150. [11] HUANG X Y, WANG A X, LIU X X, et al. Association between high sensitivity C-reactive protein and prevalence of asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis[J]. Atherosclerosis, 2016, 246: 44-49. [12] SASAI M, ISO Y, MIZUKAMI T, et al. Potential contribution of the hepcidin-macrophage axis to plaque vulnerability in acute myocardial infarction in human[J]. Int J Cardiol, 2017, 227: 114-121. [13] DENNIS E A, JIAN C, HSU Y H, et al. Phospholipase A2 enzymes: Physical structure, biological function, disease implication, chemical inhibition, and therapeutic intervention[J]. Chem Rev, 2011, 111(10): 6130-6185. [14] HUANG F B, WANG K, SHEN J H. Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2: The story continues[J]. Med Res Rev, 2020, 40(1): 79-134. [15] LIANG T, WANG S C, ZHANG D T, et al. Evaluation of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2, serum amyloid A, and fibrinogen as diagnostic biomarkers for patients with acute cerebral infarction[J]. J Clin Lab Anal, 2020, 34(3): e23084. DOI: 10.1002/jcla.23084. [16] 陆强彬, 陆梦茹, 朱祖福, 等. 脂蛋白相关磷脂酶A2、脂蛋白(a)与脑梗死进展及头颈部血管狭窄的相关性[J]. 中国动脉硬化杂志, 2018, 26(12): 1270-1272, 1290. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KDYZ201812016.htmLU Q B, LU M R, ZHU Z F, et al. The correlation of lipoprotein associated phospholipase A2 and lipoprotein(a) with progress of cerebral infarction and the vascular stenosis of intracranial and external[J]. Chinese Journal of Arteriosclerosis, 2018, 26(12): 1270-1272, 1290. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KDYZ201812016.htm [17] ALSULAIMANI S, GARDENER H, ELKIND M, et al. Elevated homocysteine and carotid plaque area and densitometry in the Northern Manhattan Study[J]. Stroke, 2013, 44(2): 457-461. [18] WEI L L, KE Z Y, ZHAO Y, et al. The elevated lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 activity is associated with the occurrence and recurrence of acute cerebral infarction[J]. Neuroreport, 2017, 28(6): 325-330. [19] 王亚飞, 李惠勉. 动脉粥样硬化血栓形成性脑梗死患者血清Lp-PLA2水平变化及其意义[J]. 山东医药, 2018, 58(11): 72-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYY201811022.htmWANG Y F, LI H M. Changes and significance of serum LP-PLA2 levels in patients with atherosclerotic thrombotic cerebral infarction[J]. Shandong Medical Journal, 2018, 58(11): 72-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYY201811022.htm [20] STEFANO A D, MA NN UCCI L, TAMBURI F, et al. Lp-PLA2, a new biomarker of vascular disorders in metabolic diseases[J]. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol, 2019, 33: 205873841982715. DOI: 10.1177/2058738419827154. -





 下载:
下载: