Application of pelvic floor ultrasound combined with MRI in treating stress urinary incontinence with Fu's subcutaneous needling
-
摘要:
目的 采用经会阴盆底超声联合盆底MRI观察浮针治疗轻中度压力性尿失禁前后的不同指标的变化,为浮针治疗压力性尿失禁疗效判断提供客观依据。 方法 纳入2017年1月—2020年4月就诊于浙江中医药大学附属第二医院临床诊断为轻中度压力性尿失禁的患者100例,采用随机数字表法分为对照组(50例)和实验组(50例),对照组进行凯格尔运动,实验组进行浮针治疗和凯格尔运动。研究对象治疗前后均行盆底超声及盆底MRI检查,比较2组治疗前后膀胱颈移动度(BND)、膀胱后角(Av)、尿道倾斜角(θv)、尿道旋转角(θ)、肛提肌裂孔面积(Sv)和尿道内口开放情况、肛提肌、尿道括约肌的连续性及厚度、尿道周围韧带、尿道旁韧带、耻骨尿道韧带和尿道下韧带形态及肌肉的T2WI信号值的差异。 结果 治疗前,2组所有超声和MRI指标比较差异无统计学意义(均P>0.05);2组治疗后比较,BND[对照组(24.71±4.84)mm, 实验组(30.01±6.40)mm]、Av、θv、θ、Sv、耻骨直肠肌厚度[对照组(3.19±0.14)mm, 实验组(3.32±0.10)mm]、耻骨直肠肌T2WI信号值、尿道括约肌T2WI信号值差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。静息状态下,2组尿道内口漏斗化差异有统计学意义[对照组22例(44.0%), 实验组6例(13.3%),P<0.05]。 结论 轻中度压力性尿失禁患者经浮针治疗后,部分膀胱、尿道及盆底肌的参数和功能发生了改变。盆底超声联合MRI检查能辅助评估浮针治疗的疗效。 Abstract:Objective To observe the changes of different indicators before and after the treatment of mild to moderate stress urinary incontinence with Fu's subcutaneous needling using transperineal pelvic floor ultrasound combined with pelvic floor MRI, and provide an objective basis for judging the efficacy of Fu's subcutaneous needling in treating stress urinary incontinence. Methods A total of 100 patients with mild to moderate stress urinary incontinence that were diagnosed in the Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University from January 2017 to April 2020 were randomly divided into control group (n=50) and experimental group (n=50). The control group received the Kegel exercise, meanwhile, the experimental group received Fu's subcutaneous needling and Kegel exercise. Patients were examined by pelvic floor ultrasound and MRI before and after treatment. The bladder neck descent (BND), posterior angle of the bladder (Av), the tilt angle of the urethra (θv), rotation angle of the urethra (θ), area of the levator hiatus (Sv) and the opening of the urethral orifice, the continuity and thickness of levator anus and urethral sphincter, the morphology and muscle T2WI signal values of peri-urethral ligament, para-urethral ligament, pubic urethral ligament, hypospadias ligament of the two groups were compared before and after the treatment. Results Before the treatment, there was no significant difference found in ultrasound and MRI indicators between the two groups (all P > 0.05). Compare the two groups after treatment, there were significant differences in BND [control group (24.71±4.84) mm; experimental group (30.01±6.40) mm], Av, θv, θ, Sv, pubic sphincter thickness [control group (3.19±0.14) mm; experimental group (3.32±0.10) mm], the thickness of urethral sphincter T2WI signal value and urethral sphincter T2WI signal value (P < 0.05). Meanwhile, in the resting state, there were statistically significant differences in funnelization of the internal urethral orifice between the two groups [control group 22 cases (44.0%), experimental group 6 cases (13.3%), P < 0.05]. Conclusion After Fu's subcutaneous needling treatment, some parameters and functions of the bladder, urethra and pelvic floor muscle are changed in patients with mild to moderate stress urinary incontinence. Therefore, pelvic floor ultrasound combined with MRI can be used to evaluate the efficacy of Fu's subcutaneous needling therapy. -
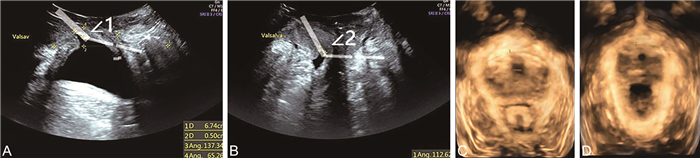
图 1 压力性尿失禁患者治疗前后盆底超声图像
注:患者,女性,62岁。A示治疗前患者盆底超声检查最大Valsalva状态下膀胱内口扩张,膀胱后角∠1=137°;B示治疗后患者盆底超声检查最大Valsalva状态下膀胱内口未见扩张,膀胱后角∠2=112°;C示治疗前患者盆底超声检查最大Valsalva状态下肛提肌裂孔最大面积为20.45 cm2;D示治疗后患者盆底超声检查最大Valsalva状态下肛提肌裂孔最大面积为13.08 cm2。
Figure 1. Ultrasound image of pelvic floor before and after treatment of a patient with stress urinary incontinence
表 1 2组治疗前最大Valsalva状态下超声及静息状态下磁共振观察指标比较
Table 1. Comparison of ultrasonic indicators in the maximum Valsalva state and MRI indicators In the resting state before treatment between the two groups
项目 实验组(45例) 对照组(50例) 统计量 P值 BND(x±s,mm) 30.01±6.40 28.33±5.41 1.391a 0.173 Av(x±s,°) 139.56±23.49 134.94±22.80 0.973a 0.334 θv(x±s,°) 50.07±22.66 48.77±22.69 0.280a 0.782 θ(x±s,°) 50.84±22.00 50.01±22.71 0.181a 0.864 Sv(x±s,cm2) 22.47±5.25 20.59±6.27 1.574a 0.121 尿道内口漏斗化[例(%)] 39(86.7) 40(80.0) 0.752b 0.393 耻骨直肠肌(左,x±s) 3.96±0.32 4.01±0.26 -0.660a 0.514 耻骨直肠肌(右,x±s) 2.47±0.11 2.46±0.13 0.901a 0.373 耻骨直肠肌T2WI信号值(左,x±s) 118.72±6.86 119.17±6.17 -0.343a 0.741 耻骨直肠肌T2WI信号值(右,x±s) 129.28±6.51 128.89±5.87 0.312a 0.760 髂尾肌(左,x±s) 5.70±0.17 5.71±0.18 -0.061a 0.952 髂尾肌(右,x±s) 3.07±0.12 3.09±0.12 -0.463a 0.652 髂尾肌T2WI信号值(左,x±s) 60.27±1.97 60.10±1.66 0.421a 0.673 髂尾肌T2WI信号值(右,x±s) 61.06±1.43 61.45±1.34 -1.384a 0.171 耻尾肌(x±s) 4.36±0.12 4.32±0.11 1.552a 0.124 耻尾肌T2WI信号值(x±s) 74.68±1.43 74.70±1.44 -0.091a 0.932 尿道括约肌(x±s) 4.15±0.12 4.16±0.12 0.654a 0.521 尿道括约肌T2WI信号值(x±s) 114.36±5.79 116.68±6.60 -1.810a 0.071 注:a为t值, b为χ2值。 表 2 2组治疗后最大Valsalva状态下超声及静息状态下磁共振观察指标比较
Table 2. Comparison of ultrasonic indicators in the maximum Valsalva state and MRI indicators In the resting state after treatment between the two groups
项目 实验组(45例) 对照组(50例) 统计量 P值 BND(x±s,mm) 19.96±7.31 24.71±4.84 -3.763a <0.001 Av(x±s,°) 131.25±17.43 140.85±16.96 -2.722a 0.008 θv(x±s,°) 29.94±16.70 40.43±20.01 -2.754a 0.007 θ(x±s,°) 29.94±16.70 40.58±19.87 -2.811a 0.006 Sv(x±s,cm2) 17.86±4.37 20.04±4.47 -2.400a 0.020 尿道内口漏斗化[例(%)] 6(13.3) 22(44.0) 10.712b 0.001 耻骨直肠肌(左,x±s) 5.16±0.25 5.08±0.33 2.263a 0.030 耻骨直肠肌(右,x±s) 3.32±0.10 3.19±0.14 4.904a <0.001 耻骨直肠肌T2WI信号值(左,x±s) 102.41±2.77 105.98±1.97 -7.280a <0.001 耻骨直肠肌T2WI信号值(右,x±s) 101.45±2.56 109.15±5.12 -9.111a <0.001 髂尾肌(左,x±s) 5.70±0.16 5.67±0.16 1.102a 0.280 髂尾肌(右,x±s) 3.01±0.13 3.01±0.12 0.074a 0.940 髂尾肌T2WI信号值(左,x±s) 60.31±1.59 59.77±1.71 1.622a 0.110 髂尾肌T2WI信号值(右,x±s) 60.27±2.30 59.66±2.09 1.374a 0.170 耻尾肌(x±s) 4.32±0.13 4.35±0.14 0.722a 0.470 耻尾肌T2WI信号值(x±s) 74.92±2.01 74.58±1.78 0.891a 0.380 尿道括约肌(x±s) 4.41±0.13 4.12±0.17 9.223a <0.001 尿道括约肌T2WI信号值(x±s) 86.34±6.34 86.34±6.34 -3.024a 0.003 注:a为t值, b为χ2值。 -
[1] 罗振恺, 矫宾宾, 张萌, 等. 女性压力性尿失禁治疗新进展[J]. 医学综述, 2019, 25(12): 2411-2415. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2019.12.023LUO Z K, JIAO B B, ZHANG M, et al. New progress of female stress urinary incontinence[J]. Medical Recapitulate, 2019, 25(12): 2411-2415. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2019.12.023 [2] 杨晓波, 安军明, 李书晓, 等. 热敏灸联合Kegel锻炼对轻中度女性单纯压力性尿失禁患者盆底结构及功能改变的可视化研究[J]. 针灸临床杂志, 2021, 37(2): 44-48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJLC202102012.htmYANG X B, AN J M, LI S X, et al. A visual study on the changes of pelvic floor structure and function in female patients with mild and moderate SUI treated by heat-sensitive moxibustion combined with kegel exercise[J]. Journal of Clinical Acupuncture and Moxibustion, 2021, 37(2): 44-48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJLC202102012.htm [3] XU L, DING M, FENG H, et al. Clinical observation of deep electroacupuncture at Baliao points for female stress urinary incontinence[J]. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2020, 18(2): 111-115. doi: 10.1007/s11726-020-1164-1 [4] 方盛, 时宽, 吕晓丹. 头体针对女性轻、中度单纯性压力性尿失禁的临床疗效观察[J]. 浙江中医药大学学报, 2021, 45(1): 79-82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BHON202101017.htmFANG S, SHI K, LYU X D. Observation of clinical effect of head and body acupuncture on mild and moderate female simple stress urinary incontinence[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, 2021, 45(1): 79-82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BHON202101017.htm [5] 万红棉, 颜承凤. 针刺横骨联合温针灸曲骨治疗女性压力性尿失禁33例[J]. 中国针灸, 2020, 40(10): 1065-1066. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZE202010012.htmWAN H M, YAN C F. Acupuncture at Henggu(KI 11) combined with warm acupuncture at Qugu(CV 2) for 33 cases of female stress urinary incontinence[J]. Chinese Acupuncture & Moxibustion, 2020, 40(10): 1065-1066. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZE202010012.htm [6] 王子臣, 杨晓锋, 左晓玲, 等. 沈氏芒针治疗女性压力性尿失禁的临床研究[J]. 河北中医药学报, 2019, 34(1): 34-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HZYX201901011.htmWANG Z C, YANG X F, ZUO X L, et al. Clinical study of Shen's Awn Needle in treatment of female stress urinary incontinence[J]. Journal of Hebei Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacology, 2019, 34(1): 34-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HZYX201901011.htm [7] 夏漫城, 双卫兵. 女性压力性尿失禁新型保守治疗方式的研究进展[J]. 海南医学院学报, 2020, 26(4): 316-320. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNYY202004014.htmXIA M C, SHUANG W B. Research progress of new conservative treatment for female stress urinary incontinence[J]. Journal of Hainan Medical University, 2020, 26(4): 316-320. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNYY202004014.htm [8] 王孟琦, 王峰. 近20年来针灸治疗压力性尿失禁的临床研究进展[J]. 中医药学报, 2019, 47(6): 73-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXB201906018.htmWANG M Q, WANG F. Clinical research progress of acupuncture and moxibustion in treating SUI in recent 20 years[J]. Acta Chinese Medicine and Pharmacology, 2019, 47(6): 73-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXB201906018.htm [9] 杨明, 叶和松, 秦远, 等. 针灸联合生物反馈治疗女性轻中度压力性尿失禁[J]. 中国中西医结合外科杂志, 2018, 24(3): 290-293. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZX201803008.htmYANG M, YE H S, QIN Y, et al. Clinical observation of acupuncture combined with pelvic floor biofeedback in treatment of mild-to-moderate female stress urinary incontinence[J]. Chinese Journal of Surgery of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine, 2018, 24(3): 290-293. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZX201803008.htm [10] 符仲华. 浮针医学纲要[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2016: 107-154.FU Z H. Medical Compendium of floating needles[M]. Beijing: People'S Medical Publishing House, 2016: 107-154. [11] 肖汀, 张新玲, 毛永江, 等. 盆底超声在压力性尿失禁诊断中的应用研究[J]. 中华超声影像学杂志, 2017, 26(7): 618-622. https://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11065-1021886772.htmXIAO T, ZHANG X L, MAO Y J, et al. The research of pelvic floor ultrasound in diagnosis of stress urinary incontinence[J]. Chinese Journal of Ultrasonography, 2017, 26(7): 618-622. https://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11065-1021886772.htm [12] 李敏, 王飚, 刘潇, 等. 盆底MRI在女性压力性尿失禁诊疗中的应用价值[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2020, 54(4): 345-346, 349.LI M, WANG B, LIU X, et al. The value of MRI in assessment of the functional disorders of stress urinary incontinence in women[J]. Chinese Journal of Radiology, 2020, 54(4): 345-346, 349. [13] LI N, CUI C, CHENG Y, et al. Association between magnetic resonance imaging findings of the pelvic floor and de novo stress urinary incontinence after vaginal delivery[J]. Korean J Radiol, 2018, 19(4): 715-723. [14] KOBI M, FLUSBERG M, PARODER V, et al. Practical guide to dynamic pelvic floor MRI[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2018, 47(5): 1155-1170. [15] 周艳梅, 罗穗豫, 郝凯, 等. 女性压力性尿失禁患者MRI表现特征[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志, 2019, 17(2): 90-93. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CTMR201902028.htmZHOU Y M, LUO S Y, HAO K, et al. MRI findings of stress urinary incontinence in female[J]. Chinese Journal of CT and MRI, 2019, 17(2): 90-93. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CTMR201902028.htm [16] 冯海兵. 经会阴三维超声盆底超声、MRI检查在诊断女性盆底功能障碍性疾病的临床价值[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志, 2021, 19(3): 118-120. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CTMR202103040.htmFENG H B. Clinical Value of perineal threedimensional ultrasound pelvic floor ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in the diagnosis of female pelvic floor dysfunction[J]. Chinese Journal of CT and MRI, 2021, 19(3): 118-120. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CTMR202103040.htm [17] VAN GEELEN H, OSTERGARD D, SAND P. A review of the impact of pregnancy and childbirth on pelvic floor function as assessed by objective measurement techniques[J]. Int Urogynecol J, 2018, 29(3): 327-338. [18] 吕悦, 陈英红, 张娟娟. 盆底超声在初产妇产后压力性尿失禁的应用研究[J]. 医药论坛杂志, 2022, 43(4): 64-66. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYYX202204017.htmLYU Y, CHEN Y H, ZHANG J J. Application of pelvic floor ultrasound in puerperal stress urinary incontinence[J]. Journal of Medical Forum, 2022, 43(4): 64-66. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYYX202204017.htm [19] 余颖莹, 陶肖樱, 金贝, 等. 四维盆底超声评估针灸治疗产后女性盆底功能障碍疗效的价值[J]. 中华全科医学, 2020, 18(1): 102-104, 133. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.001179YU Y Y, TAO X Y, JIN B, et al. Evaluation of the therapeutic efficacy of acupuncture and moxibustion on postpartum female pelvic floor dysfunction by four-dimensional pelvic floor ultrasound[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2020, 18(1): 102-104, 133. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.001179 [20] 单华英, 徐亚芬, 陆艳, 等. 盆底超声在女性压力性尿失禁中的应用及初产妇产后盆底肌肉训练的疗效评估[J]. 中华全科医学, 2019, 17(9): 1557-1560. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.000997SHAN H Y, XU Y F, LU Y, et al. Application of pelvic floor ultrasound in female stress incontinence and evaluation of efficacy of postpartum pelvic floor muscle training[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2019, 17(9): 1557-1560. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.000997 [21] 刘佳, 叶细荣. 智能盆底超声联合多平面成像技术在产后压力性尿失禁筛查中的应用[J]. 国际泌尿系统杂志, 2020, 40(3): 505-508.LIU J, YE X R. The application of intelligent pelvic floor ultrasound combined with multiplanar imaging in screening of postpartum stress urinary incontinence[J]. International Journal of Urology and Nephrology, 2020, 40(3): 505-508. -





 下载:
下载: