Value of vesical imaging reporting and data system combined with intravoxel incoherent motion sequences in the evaluation of muscle invasion in bladder cancer
-
摘要:
目的 探讨膀胱影像报告和数据系统(VI-RADS)及体素内不相干运动(IVIM)在评估膀胱癌肌层浸润中的价值。 方法 回顾性分析2018年6月—2022年2月在滁州市第一人民医院手术及病理检查证实的膀胱癌患者共50例(52处病灶),均在本院行膀胱磁共振常规多参数(包括T2WI、DWI、DCE序列)及IVIM序列扫描,其中,非肌层浸润性膀胱癌(NMIBC)30处病灶,肌层浸润性膀胱癌(MIBC)22处病灶。依据VI-RADS对MR各序列图像进行评分,计算不同截断值诊断MIBC的敏感度、特异度、阳性预测值、阴性预测值及准确率;测量病灶IVIM各参数值(ADCst、D、D*及f值);分别绘制ROC曲线评价VI-RADS、IVIM参数及其联合对肌层浸润的诊断效能。 结果 IVIM序列内ADCst、D及f值在NMIBC组均高于MIBC组,差异有统计学意义(均P<0.01),其AUC分别为0.904、0.889和0.780(均P<0.01)。以VI-RADS≥4分作为截断值预测肌层浸润性膀胱癌,约登指数最大,为0.603,AUC为0.871;其联合ADCst及D值时,约登指数提升为0.636,AUC为0.916。 结论 VI-RADS≥4分及ADCst、D和f值减低均提示膀胱癌侵犯肌层可能性较大,而VI-RADS联合ADCst及D值组合可明显提高诊断效能。 -
关键词:
- 膀胱影像报告和数据系统 /
- 体素内不相干运动 /
- 扩散加权成像 /
- 膀胱癌 /
- 肌层侵犯
Abstract:Objective To investigate the value of vesical imaging reporting and data system (VI-RADS) and intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) in the diagnosis of muscle invasive bladder cancer (MIBC). Methods A total of 50 cases (52 tumours) with surgery and pathologically confirmed bladder cancer at the First People' s Hospital of Chuzhou from June 2018 to February 2022 were analysed retrospectively. All patients underwent routine multiparameter MRI scan (including T2WI, DWI and DCE sequence) and IVIM sequence before surgery. Among the cases, 30 lesions were non-MIBC (NMIBC), and 22 were MIBC. The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value and accuracy of different cut-off values in diagnosing MIBC were calculated by scoring MR images according to VI-RADS. IVIM parameters (ADCst, D, D* and f values) were measured. The diagnostic efficacy of VI-RADS, IVIM parameters and their combinations in muscle invasion was evaluated by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Results The ADCst, D and f values of the NMIBC group were significantly higher than those of the MIBC group (all P < 0.01), and the areas under curve (AUC) were 0.904, 0.889 and 0.780, respectively (all P < 0.01). Using VI-RADS score ≥ 4 as the cut-off, muscle invasion was predicted with the highest Youden index of 0.603 and AUC of 0.871. When the VI-RADS combined with ADCst and D values, the Yoden index rose to 0.636, and the AUC was 0.916. Conclusion The VI-RADS ≥ 4 and ADCst, D and f values decline, which indicate the greater possibility of muscle invasion of bladder cancer, and the combination of VI-RADS and ADCst and D values can significantly improve the diagnostic efficacy. -
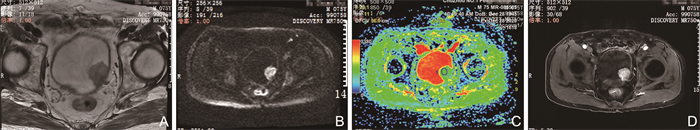
图 4 VI-RADS 1分及4分多发病灶
注:A~F为男性患者,86岁。A为fs T2WI示膀胱两侧后壁肿块,左侧大小为1.7 cm×2.5 cm,邻近肌层低信号欠连续,SC3;右侧0.86 cm×0.87 cm,邻近肌层信号连续,SC1。B为DWI相应肿块呈高信号,左侧肿瘤邻近肌层及输尿管内见高信号,DW4;右侧肌层连续完整,DW1。C、D为左侧肿瘤,ADCst值为0.898×10-3mm2/s,D值为0.652×10-3mm2/s。E、F为右侧肿瘤,ADCst值为1.290×10-3mm2/s,D值为0.836×10-3mm2/s。左、右侧病灶评分为4分及1分,提示左侧MIBC,右侧NMIBC,与病理一致。
Figure 4. VI-RADS 1 and 4 for multi-onset lesions
表 1 膀胱癌多参数MRI的VI-RADS评分标准
Table 1. VI-RADS scoring criteria for multiparametric MRI in bladder cancer
T2WI、DCE、DWI序列 VI-RADS评分 SC 1+DC 1+DWI 1 1分(浸润肌层极不可能存在) SC 2+DC 2+DWI 2 2分(浸润肌层不太可能存在) SC 3+DC 2+DWI 2 2分(浸润肌层不太可能存在) SC 3+DC 3和(或)DWI 3 3分(浸润肌层的存在模棱两可) SC 3+DC 4和(或)DWI 4 4分(浸润肌层可能存在) SC 4+DC 4和(或)DWI 4 4分(浸润肌层可能存在) SC 4+DC 5和(或)DWI 5 5分(浸润肌层极有可能存在) SC 5+DC 5和(或)DWI 5 5分(浸润肌层极有可能存在) SC 5+DC 4和(或)DWI 4 4分(浸润肌层极可能存在) 表 2 NMIBC及MIBC组间IVIM各参数值比较
Table 2. Comparison of IVIM parameters between NMIBC and MIBC groups
组别 病灶数 ADCst(×10-3 mm2/s) D(×10-3 mm2/s) f D*(×10-3 mm2/s) NMIBC 30 1.39±0.22 1.03±0.24 0.53±0.14 12.12±6.64 MIBC 22 0.91±0.19 0.67±0.12 0.36±0.17 9.87±5.59 t值 5.112 4.077 4.885 0.445 P值 <0.001 <0.001 0.031 0.662 表 3 IVIM各参数值对MIBC的诊断效能
Table 3. The diagnostic efficacy of IVIM parameters for MIBC
参数 阈值 敏感度(%) 特异度(%) 准确率(%) AUC P值 ADCst 1.18×10-3 mm2/s 86.51 83.22 85.42 0.904 <0.001 D 1.07×10-3 mm2/s 79.62 85.35 83.31 0.889 <0.001 f 0.41 75.12 71.29 77.62 0.780 0.003 表 4 不同VI-RADS评分预测MIBC的诊断效能
Table 4. The diagnostic efficacy of different VI-RADS scores to predict MIBC
VI-RADS评分(截断值) 例数 约登指数 敏感度(%) 特异度(%) PPV(%) NPV(%) 准确性(%) ≥1分 22 0 100.0 0 42.3 0 42.3 ≥2分 22 0.167 100.0 16.7 46.8 100.0 51.9 ≥3分 20 0.476 90.9 56.7 60.6 89.5 71.2 ≥4分 14 0.603 63.6 96.7 93.3 78.4 82.7 5分 4 0.182 18.2 100.0 100.0 62.5 65.4 表 5 VI-RADS 2~4分联合ADCst/D值对MIBC的诊断效能
Table 5. The diagnostic efficacy of VI-RADS 2-4 score combined with ADCst / D value on MIBC
VI-RADS评分 IVIM参数 约登指数 敏感度(%) 特异度(%) ≥2分 ADCst/D 0.167 100.0 16.7 ≥3分 ADCst/D 0.476 90.9 56.7 ≥4分 ADCst/D 0.636 63.6 100.0 -
[1] BRAY F, FERLAY J, SOERJOMATARAM I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660 [2] 李立强, 郭园园, 岳晓娥, 等. 二次等离子电切术在非肌层浸润性膀胱肿瘤中的应用[J]. 中华全科医学, 2020, 18(10): 1629-1632. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.001578LI L Q, GUO Y Y, YUE X E, et al. Application of the repeat plasmakinetic resection in non-muscular invasive bladder tumor[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2020, 18(10): 1629-1632. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.001578 [3] 薛学义, 许宁, 吴宇鹏. 肌层浸润性膀胱癌的临床治疗进展[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2017, 32(10): 771-774. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCMW201710010.htmXUE X Y, XU N, WU Y P. Advances in clinical management of muscle invasive bladder cancer[J]. Journal of Clinical Urology, 2017, 32(10): 771-774. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCMW201710010.htm [4] PANEBIANCO V, NARUMI Y, ALTUN E, et al. Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for bladder cancer: Development of VI-RADS (Vesical Imaging-Reporting And Data System)[J]. Eur Urol, 2018, 74: 294-306. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2018.04.029 [5] 王良, QIUBAI L, VARGAS H A. 膀胱影像报告和数据系统解读[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2019, 53(3): 164-169. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1005-1201.2019.03.002WANG L, QIUBAI L, VARGAS H A. China interpretation of vesical imaging-reporting and data system guideline for the management of bladder cancer[J]. Chinese Journal of Radiology, 2019, 53(3): 164-169. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1005-1201.2019.03.002 [6] 夏威利, 张孝先, 王立峰, 等. 膀胱癌邻近肌层表观扩散系数值及其比值诊断肌层浸润性膀胱癌的价值[J]. 实用放射学杂志, 2019, 35(2): 245-248. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1671.2019.02.019XIA W L, ZHANG X X, WANG L F, et al. Application of ADC value and ADC ratio in the diagnosis of muscular invasive bladder cancer[J]. Journal of Practical Radiology, 2019, 35(2): 245-248. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1671.2019.02.019 [7] 张苗苗, 陈雁, 丛欣莹, 等. MR体素内不相干运动成像评价膀胱尿路上皮癌病理分级及肌层侵犯[J]. 中国医学影像技术, 2018, 34(4): 595-600. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXX201804041.htmZHANG M M, CHEN Y, CONG X Y, et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion MRI for prediction of histological grade and muscle invasion in bladder urothelial carcinoma[J]. Chinese Journal of Medical Imaging Technology, 2018, 34(4): 595-600. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXX201804041.htm [8] WANG Z Y, SHANG Y Y, LUAN T, et al. Evaluation of the value of the VI-RADS scoring system in assessing muscle infiltration by bladder cancer[J]. Cancer Imaging, 2020, 20(1): 26. doi: 10.1186/s40644-020-00304-3 [9] BABJUK M, BURGER M, COMPERAT E M, et al. European association of urology guidelines on non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (TaT1 and carcinoma in situ)-2019 update[J]. Eur Urol, 2019, 76(5): 639-657. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2019.08.016 [10] WANG H J, LUO C, ZHANG F, et al. Multiparametric MRI for bladder Cancer: Validation of VI-RADS for the detection of detrusor muscle invasion[J]. Radiology, 2019, 291(3): 668-674. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2019182506 [11] 鄂天娇, 冯峰, 王小林, 等. 膀胱癌影像报告及数据系统对膀胱癌肌层浸润的诊断价值[J]. 中国医学计算机成像杂志, 2021, 27(1): 20-26. E T J,FENG F, WANG X L, et al. Diagnostic V alue of Vesical Imaging Reporting and Data System for Detecting Muscle Invasion of Bladder Cancer[J]. Chinese Computed Medical Imaging, 2021, 27(1): 20-26. [12] 王铃, 石林, 郑石磊, 等. 膀胱影像报告和数据系统对膀胱癌组织病理学特征的诊断价值[J]. 中国医学影像学杂志, 2021, 29(11): 1109-1113, 1115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5185.2021.11.012WANG L, SHI L, ZHENG S L, et al. Diagnosis of Vesical Imaging Reporting and Data System in Histopathological Characteristics of Bladder Cancer[J]. Chinese Journal of Medical Imaging, 2021, 29(11): 1109-1113, 1115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5185.2021.11.012 [13] 张添辉, 程凤燕, 罗润标, 等. 基于VI-RADS评分比较不同MRI序列组合诊断肌层浸润型膀胱癌的效能[J]. 临床放射学杂志, 2020, 39(4): 725-729. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCFS202004023.htmZHANG T H, CHENG F Y, LUO R B, et al. The Value of Different MRI Sequences Combination in the Diagnosis of Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Based on Vesical Imaging-Reporting and Data System[J]. Journal of Clinical Radiology, 2020, 39(4): 725-729. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCFS202004023.htm [14] 严植, 郝金钢, 尚芸芸. VI-RADS评分对膀胱癌精准治疗的价值[J]. 昆明医科大学学报, 2022, 43(3): 74-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KMYX202203013.htmYAN Z, HAO J G, SHANG Y Y. Value of VI-RADS Scoring System in Precision Treatment of Bladder Cancer[J]. Journal of Kunming Medical University, 2022, 43(3): 74-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KMYX202203013.htm [15] PANER G P, MONTIRONI R, AMIN M B. Challenges in pathologic staging of bladder cancer: Proposals for fresh approaches of assessing pathologic stage in light of recent studies and observations pertaining to bladder Histoanatomic variances[J]. Adv Anat Pathol, 2017, 24(3): 113-127. [16] 徐肖攀, 杜鹏, 徐桓, 等. 基于多模态MRI影像组学策略构建膀胱癌肌层浸润预测模型研究[J]. 中国医学装备, 2020, 17(9): 5-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXZB202009002.htmXU X P, DU P, XU H, et al. Study on constructing prediction model of muscle-invasive status of bladder cancer based on multimodal MRI radiomics strategy[J]. China Medical Equipment, 2020, 17(9): 5-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXZB202009002.htm [17] 夏迎洪, 朱海旭, 曲源, 等. 3.0T磁共振表观扩散系数和病灶面积预测膀胱癌肌层和非肌层浸润研究[J]. 中国医学装备, 2022, 19(4): 60-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXZB202204012.htmXIA Y H, ZHU H D, QU Y, et al. Study on the value of 3.0T MRI ADC and lesion area in predicting MIBC and NMIBC of bladder cancer[J]. China Medical Equipment, 2022, 19(4): 60-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXZB202204012.htm [18] 李陇超, 常鸿志, 杨艳蓉, 等. 膀胱影像报告和数据系统对初发和复发膀胱癌肌层浸润预测价值的对比研究[J]. 影像诊断与介入放射学, 2021, 30(1): 44-48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXZD202101011.htmLI L C, CHANG H Z, YANG Y R, et al. Comparative study using Vesical Imaging-Reporting and Data System(VI-RADS)score in predicting muscle invasion of primary and recurrent bladder cancer[J]. Diagnostic Imaging & Interventional Radiology, 2021, 30(1): 44-48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXZD202101011.htm -





 下载:
下载: