Study on the magnetic resonance colonography combined with fecal calprotectin in the diagnosis of ulcerative colitis
-
摘要:
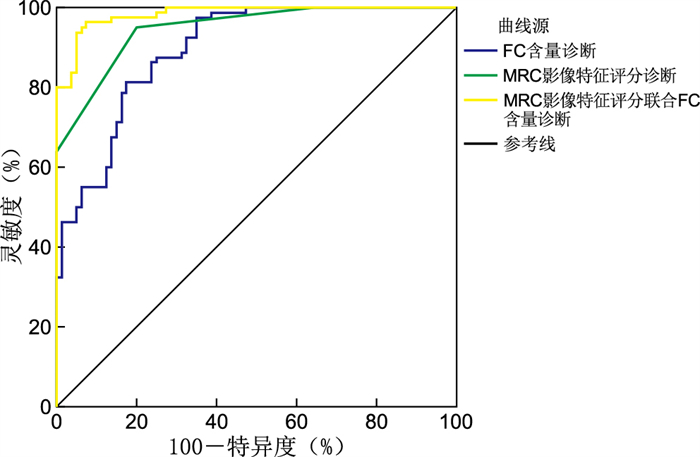
目的 观察磁共振结肠成像(MRC)与粪钙卫蛋白(FC)联合用于溃疡性结肠炎(UC)诊断及病情评估的临床价值。 方法 以2019年6月—2022年6月衢州市中医医院收治的80例UC患者和80例同期健康受试者为研究对象,均进行结肠镜、MRC检查和FC检测。比较不同活动程度UC患者及健康受试者MRC影像特征及FC含量差异,以结肠镜检查结果为金标准,评价MRC影像特征评分、FC含量及两者联合诊断UC的诊断效能。 结果 健康受试者及不同活动程度UC患者出现黏膜强化、肠壁增厚、肠壁分层强化、梳齿征、肠壁淋巴结肿大、黏膜及黏膜下层缺损和DWI信号增强等MRC影像特征比例差异均有统计学意义(均P < 0.05),且不同UC活动程度患者肠壁分层强化、梳齿征、肠壁淋巴结肿大等MRC影像特征出现比例差异均有统计学意义(均P < 0.05)。健康受试者及不同活动程度UC患者FC比较差异有统计学意义(P < 0.01),UC患者FC为(3 186.11±291.80)μg/g,显著高于健康受试者[(2 699.47±249.67)μg/g, P < 0.05],而不同活动程度UC患者之间FC比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。MRC影像特征评分、FC、MRC影像特征评分联合FC诊断UC的ROC曲线下面积分别为0.956、0.895、0.984。 结论 MRC和FC作为2种无创诊断技术,可作为结肠镜病理检查的替代或辅助手段用于UC的诊断和病情评估,且两者联合应用可提高UC的诊断效能。 Abstract:Objective To observe the clinical value of magnetic resonance colonography (MRC) combined with fecal calprotectin (FC) in the diagnosis and evaluation of ulcerative colitis (UC). Methods A total of 80 UC patients and 80 healthy subjects during the same period admitted to Quzhou Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine from June 2019 to June 2022 were selected as the research objects. All the subjects were examined by colonoscopy, MRC and FC. The MRC image characteristics and FC content of UC patients with different activity levels and healthy subjects were compared. The results of colonoscopy were used as the gold standard to evaluate the efficacy of MRC imaging feature score, FC content and their combination in the diagnosis of UC. Results There were statistically significant differences in the proportions of MRC imaging features such as mucosal enhancement, intestinal wall thickening, intestinal wall layering enhancement, comb tooth sign, intestinal wall lymph node enlargement, mucosal and submucosal defects and DWI signal enhancement in healthy subjects and UC patients with different activity levels (all P < 0.05), and there were statistically significant differences in the proportion of MRC imaging features such as intestinal wall stratification enhancement, comb tooth sign, intestinal wall lymph node enlargement in UC patients with different activity levels (P < 0.05). The difference of FC content between healthy subjects and UC patients with different activity levels was statistically significant (P < 0.01). The FC content of UC patients was (3 186.11±291.80) μg/g, significantly higher than that of healthy subjects [(2 699.47±249.67) μg/g, P < 0.05], while the FC content in UC patients with different activity levels was not statistically significant (P>0.05). The area under the ROC curve of MRC image feature score, FC content and MRC image feature score combined with FC content in diagnosing UC were 0.956, 0.895 and 0.984, respectively. Conclusion MRC and FC, as two non-invasive diagnostic techniques, can be used as an alternative or auxiliary means of colonoscopy pathology for UC diagnosis and disease evaluation. The combined application of MRC and FC can improve the diagnostic efficiency of UC. -
表 1 健康受试者及不同活动程度UC患者MRC影像特征比较[例(%)]
Table 1. Comparison of MRC image characteristics between healthy subjects and UC patients with different degrees of activity [cases (%)]
组别 例数 黏膜强化 肠壁增厚 肠壁分层强化 梳齿征 肠壁淋巴结肿大 黏膜及黏膜下层缺损 DWI信号增强 健康受试者 80 23(28.75) 27(33.75) 13(16.25) 15(18.75) 8(10.00) 10(12.50) 19(23.75) 轻度UC 26 23(88.46) 24(92.31) 11(42.31) 14(53.85) 9(34.62) 17(65.38) 21(80.77) 中度UC 35 32(91.43) 33(94.28) 24(68.57) 27(77.14) 20(57.14) 25(71.43) 30(85.71) 重度UC 19 18(94.74) 18(94.74) 18(94.74) 17(89.47) 14(73.68) 14(73.68) 17(89.47) χ2值 10.788 18.968 53.854 52.739 43.304 54.936 60.836 P值 0.013 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 表 2 MRC影像特征评分及FC诊断UC的ROC曲线分析
Table 2. ROC curve analysis of MRC image feature score and FC content in diagnosis of UC
诊断方式 AUC SE P值 渐近95% CI MRC影像特征评分 0.956 0.013 < 0.001 0.930~0.983 FC含量 0.895 0.024 < 0.001 0.849~0.942 MRC影像特征评分联合FC含量 0.984 0.007 < 0.001 0.971~0.998 -
[1] 江学良. 溃疡性结肠炎中西医结合诊疗进展[J]. 中华消化病与影像杂志(电子版), 2021, 11(3): 144. doi: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-2015.2021.03.011JIANG X L. Progress in diagnosis and treatment of ulcerative colitis with integrated Chinese and Western Medicine[J]. Chinese Journal of Digestive Diseases and Iimaging (Electronic Edition), 2021, 11(3): 144. doi: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-2015.2021.03.011 [2] 苏晓路, 董弛, 张静, 等. 溃疡性结肠炎临床病理特点及鉴别诊断[J]. 生物医学转化, 2022, 3(2): 66-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWZH202202009.htmSU X L, DONG C, ZHANG J, et al. Clinicopathological features and differential diagnosis of ulcerative colitis[J]. Biomedical Transformation, 2022, 3(2): 66-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWZH202202009.htm [3] 阎鹏光, 李景南. 溃疡性结肠炎的规范诊治[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2021, 60(6): 567-570. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112138-20210316-00216AN P G, LI J N. The standard diagnosis and treatment of ulcerative colitis[J]. Chinese Journal of Internal Medicine, 2021, 60(6): 567-570. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112138-20210316-00216 [4] 刘海燕, 陈军贤, 徐平珍. 溃疡性结肠炎患者尿液NGAL、MMP-9检测的临床意义[J]. 中华全科医学, 2019, 17(5): 776-778. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.000789LIU H Y, CHEN J X, XU Pi Z. Clinical significance of urine NGAL and MMP-9 in the patients of ulcerative colitis[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2019, 17(5): 776-778. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.000789 [5] 王松, 刘流, 张开光. 单核细胞和单核细胞/淋巴细胞比值对判断溃疡性结肠炎严重程度的临床价值[J]. 中华全科医学, 2020, 18(6): 895-898, 1065. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.001386WANG S, LIU L, ZHANG K G. Clinical value of monocytes and monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio in determining the severity of ulcerative colitis[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2020, 18(6): 895-898, 1065. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.001386 [6] 李军苗, 朱雄文, 吴贵阳, 等. MSCT与MRI术前诊断结肠癌及评价术后复发的价值分析[J]. 中国现代医生, 2018, 56(27): 112-115, 119. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDYS201827032.htmLI J M, ZHU X W, WU G Y, et al. The value of MSCT and MRI in preoperative diagnosis of colon cancer and evaluation of postoperative recurrence[J]. Chinese Modern Doctor, 2018, 56(27): 112-115, 119. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDYS201827032.htm [7] 赵利芳. 磁共振成像与多层螺旋CT诊断结肠癌致肠梗阻的临床价值分析[J]. 中国肛肠病杂志, 2021, 41(10): 1-3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1174.2021.10.001ZHAO L F. MRI and multi-slice spiral CT in the diagnosis of intestinal obstruction incuced by colonic cancer: clinical value analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Coloproctology, 2021, 41(10): 1-3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1174.2021.10.001 [8] 杨爽, 陈英敏. MRC联合DCE-MRI定量参数在结肠癌分期及分级中的应用[J]. 影像研究与医学应用, 2019, 3(8): 5-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXYY201908002.htmYANG S, CHENG Y M. The application of MRC combined with DCE-MRI quantitative parameters in staging and grading of colon cancer[J]. Journal of Imaging Research and Medical Applications, 2019, 3(8): 5-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXYY201908002.htm [9] 朱叶珊, 沈春艳, 费亚军, 等. 磁共振成像对溃疡性结肠炎诊断的研究进展[J]. 医学美学美容, 2018, 27(5): 136.ZHU Y S, SHEN C Y, FEI Y J. Research progress of magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of ulcerative colitis[J]. Journal of Medical Aesthetice and Cosmetology, 2018, 27(5): 136. [10] DONG X, LUO J F, LAN P X, et al. Magnetic resonance colonography with intestine-absorbable nanoparticle contrast agents in evaluation of colorectal inflammation[J]. Eur Radiol, 2021, 31(7): 4615-4624. [11] SONOYAMA H, KAWASHIMA K, ISHIHARA S, et al. Capabilities of fecal calprotectin and blood biomarkers as surrogate endoscopic markers according to ulcerative colitis disease type[J]. J Clin Biochem Nutr, 2019, 64(3): 265-270. [12] STEVENS T W, GECSE K, TURNER J R, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of fecal calprotectin concentration in evaluating therapeutic outcomes of patients with ulcerative colitis[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 19(11): 2333-2342. [13] 尹鑫, 褚卫建, 李岩岩. 溃疡性结肠炎患者血清钙卫蛋白、白细胞介素-17及C反应蛋白水平的变化及其临床意义[J]. 现代实用医学, 2021, 33(8): 1009-1011. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NBYX202108012.htmYIN X, CHU W J, LI Y Y. Changes and clinical significance of serum calprotectin, interleukin-17 and C-reactive protein levels in patients with ulcerative colitis[J]. Modern Practical Medicine, 2021, 33(8): 1009-1011. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NBYX202108012.htm [14] 周凤霞, 陈少军, 查志刚, 等. 血清核周型抗中性粒细胞胞质抗体和粪钙卫蛋白对儿童溃疡性结肠炎病情预测的价值[J]. 中国医师进修杂志, 2020, 43(3): 215-216, 220.ZHOU F X, CHEN S J, ZHA Z G, et al. Clinical significance of the serum perinuclear antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody and fecal calprotectin in prediction the severity of ulcerative colitis in children[J]. Chinese Journal of Postgraduates of Medicine, 2020, 43(3): 215-216, 220. [15] 孟祥鹿, 孙际伟, 王欢, 等. MRC结合FC对溃疡性结肠炎活动程度的诊断效能[J]. 天津医药, 2020, 48(7): 635-641. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJYZ202007014.htmMENG X L, SUN J W, WANG H, et al. The diagnostic efficiency of MRC combined with fecal calprotectin in the activity of ulcerative colitis[J]. Tianjin Medical Journal, 2020, 48(7): 635-641. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJYZ202007014.htm -





 下载:
下载: