Diagnostic value of rapid on-site evaluation of biopsy specimens during medical thoracoscopy for undiagnosed pleural effusion
-
摘要:
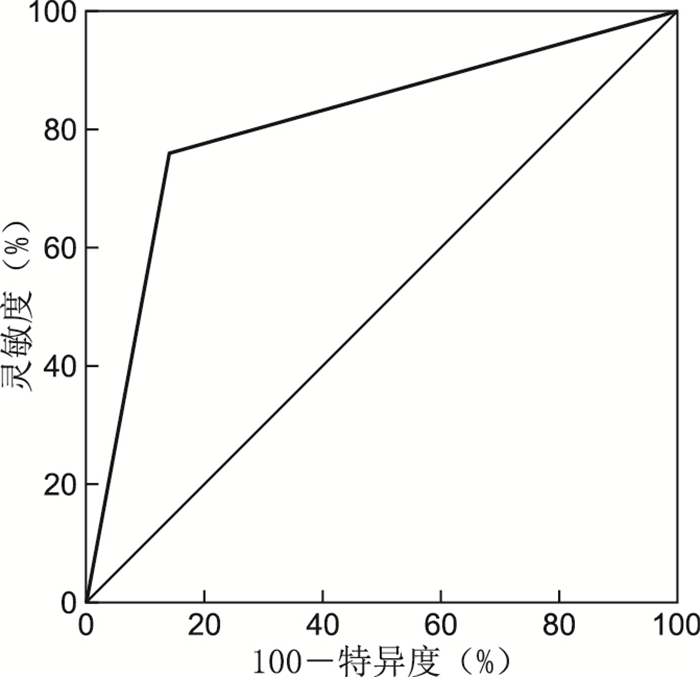
目的 探讨内科胸腔镜检查中镜下表现及多部位活检结合快速现场评价技术(简称ROSE技术)对不明原因胸腔积液的诊断价值。 方法 回顾性分析解放军第903医院2016年6月—2017年12月因不明原因胸腔积液行内科胸腔镜检查的124例患者的临床资料,通过观察胸腔镜下胸膜变化,术中活检组织的快速现场细胞学表现,并对照最终的病理诊断,对内科胸腔镜检查联合ROSE技术在临床应用中的安全性、有效性及准确性进行系统分析和评价。 结果 124例行胸腔镜检查的患者中良性病变77例,恶性病变41例,诊断不明确者6例。胸腔镜镜下诊断恶性病变的阳性预测值为73.81%,阴性预测值为86.84%,灵敏度为75.60%,特异度为85.71%,与病理诊断符合率为82.2%。胸腔镜联合ROSE技术诊断恶性胸腔积液的阳性预测值为82.98%,阴性预测值为97.18%,灵敏度为95.12%,特异度为89.61%,胸腔镜联合ROSE技术与最终病理结果的一致性较好(Kappa值为0.825,P<0.001)。 结论 内科胸腔镜在胸腔积液中具有检出率高、准确性高的特点, 而ROSE技术与最终病理结果具有较好的一致性,二者联合进一步提高了不明原因胸腔积液的诊断效率,值得在临床推广应用。 Abstract:Objective This study aims to investigate the diagnostic value of manifestations in medical thoracoscopy and multi-site biopsy combined with rapid on-site evaluation (ROSE) in undiagnosed pleural effusion. Methods The clinical data of 124 patients with undiagnosed pleural effusion who underwent medical thoracoscopy from June 2016 to December 2017 in the 903th Hospital of People's Liberation Army were analyzed retrospectively. The safety, effectiveness and accuracy of thoracoscopy combined with ROSE in clinical application were systematically analyzed and evaluated by observing pleural changes under thoracoscope, rapid field cytological manifestations of biopsies during operation and comparing with the final pathological diagnosis. Results Among the 124 patients who underwent thoracoscopy, 77 cases were benign, 41 cases were malignant, and 6 cases were uncertain. The positive predictive value was 73.81%, the negative predictive value was 86.84%, the sensitivity was 75.60%, the specificity was 85.71%, and the coincidence rate with pathological diagnosis was 82.2%. The positive predictive value, negative predictive value, sensitivity and specificity were 82.98%, 97.18%, 95.12% and 89.61% in the diagnosis of malignant pleural effusion by thoracoscopy combined with ROSE (Kappa value was 0.825, P < 0.001), respectively. Conclusion Medical thoracoscopy have the characteristics of high detection rate and high accuracy in pleural effusion, and ROSE technique have a good consistency with the final pathological results. The combination of the two techniques can further improve the diagnostic efficiency of undiagnosed pleural effusion, which is worthy of clinical application. -
Key words:
- Pleural effusion /
- Rapid on-site evaluation /
- Medical thoracoscopy
-
表 1 胸腔积液的特征胸腔镜下主要特点
Table 1. Features of pleural effusion main features of thoracoscopy
项目 良性疾病(77例) 恶性疾病(41例) 统计量 P值 胸腔积液特征[例(%)] 单侧 69(89.61) 35(85.37) 0.461a 0.498 双侧 8(10.39) 6(14.63) 黄色 65(84.42) 10(24.39) 41.619a < 0.001 血性 12(15.58) 31(75.61) 包裹性 20(25.97) 3(7.32) 5.935a 0.015 镜下主要表现[例(%)] 胸膜增厚 10(12.99) 23(56.10) 24.683a < 0.001 胸膜充血、水肿 31(40.26) 11(26.83) 2.105a < 0.001 黏膜粗糙 11(14.29) 1(2.44) 4.110a 0.042 多发结节 41(53.25) 32(78.05) 6.976a 0.008 广泛粘连 68(88.31) 4(9.76) 69.410a < 0.001 纤维素渗出 37(48.05) 2(4.88) 22.538a < 0.001 肺不张 38(49.35) 20(48.78) 0.003a 0.956 总活检个数(x±s, 个) 6.99±1.78 6.04±2.03 2.524b 0.326 ROSE标本个数(x±s, 个) 2.04±1.77 2.28±1.45 0.791b 0.774 相关实验室检查(x±s) CRP(mg/L) 82.88±4.38 39.04±4.38 51.772b 0.002 ADA(U/L) 32.15±4.38 25.89±2.88 9.317b 0.239 LDH(U/L) 485.85±146.15 362.67±40.01 6.925b 0.224 胸水CEA(ng/mL) 137.27±80.72 142.18±73.17 0.335b 0.923 胸腔镜下初步诊断[例(%)] 恶性 11(14.29) 37(90.24) 63.969a < 0.001 良性 66(85.71) 4(9.76) 注:a为χ2值,b为t值。 表 2 胸腔镜与病理检查对良恶性胸腔积液的诊断结果(例)
Table 2. Diagnosis of benign and malignant pleural effusion by thoracoscopy and pathology (cases)
胸腔镜 病理检查 合计 恶性 良性 恶性 31 11 42 良性 10 66 76 合计 41 77 118 表 3 胸腔镜联合ROSE技术诊断与病理检查对良恶性胸腔积液的诊断结果(例)
Table 3. Diagnosis of benign and malignant pleural effusion by thoracoscopy combined with ROSE technique and pathological examination (cases)
胸腔镜联合ROSE技术 病理检查 合计 恶性 良性 恶性 39 8 47 良性 2 69 71 合计 41 77 118 表 4 单用胸腔镜与胸腔镜联合ROSE技术诊断恶性胸腔积液的诊断价值比较
Table 4. Comparison of the diagnostic value of thoracoscopy and thoracoscopy combined with ROSE in the diagnosis of malignant pleural effusion
诊断方法 灵敏度(%) 特异度(%) 阳性预测值(%) 阴性预测值(%) AUC P值 95% CI 胸腔镜 75.60 85.71 73.81 86.84 0.807 <0.001 0.717~0.896 胸腔镜联合ROSE技术 95.12 89.61 82.98 97.18 0.924 <0.001 0.868~0.979 -
[1] DUYSINX B, HEINEN V, CORHAY J L, et al. Medicalthoracoscopy in respiratory medicine: the liège university hospital experience[J]. Rev Mal Respir, 2019, 36(6): 688-696. doi: 10.1016/j.rmr.2019.02.007 [2] LIN O, RUDOMINA D, FERATOVIC R, et al. Rapid on-site evaluation using telecytology: a major cancer center experience[J]. Diagn Cytopathol, 2019, 47(1): 15-19. doi: 10.1002/dc.23925 [3] LI C, XIE W, CAO J, et al. Detailed procedureand clinical application overview of rapid on site evaluation in diagnostic interventional pulmonology[J]. J Res Med Sci, 2020, 25: 35. doi: 10.4103/jrms.JRMS_21_18 [4] GUPTA N, KLEIN M, CHAU K, et al. Adequate at rapid on-site evaluation (ROSE), but inadequate on final cytologic diagnosis: analysis of 606 cases of endobronchial ultrasound-guided trans bronchial needle aspirations (EBUS-TBNA)[J]. Diagn Cytopathol, 2019, 47(5): 367-373. doi: 10.1002/dc.24121 [5] GUARINO C, MOLLICA M, CESARO C, et al. Diagnostic yield of rapid on-site evaluation transbronchial needle aspiration versus conventional transbronchial needle aspiration: a single center experience[J]. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis, 2020, 90(1): 73-77. [6] UMEDA Y, OTSUKA M, NISHIKIORI H, et al. Feasibility of rapid on-site cytological evaluation of lung cancer by a trained pulmonologist during bronchoscopy examination[J]. Cytopathology, 2019, 30(6): 628-633. doi: 10.1111/cyt.12771 [7] 李真, 孟婕, 胡成平, 等. 412例胸膜疾病胸腔镜下的表现与诊断分析[J]. 中国内镜杂志, 2015, 21(9): 897-900. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGNJ201509002.htmLI Z, MENG J, HU C P, et al. Manifestations and diagnostic analysis of 412 cases of thoracoscopic pleural disease[J]. China Journal of Endoscopy, 2015, 21(9): 897-900. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGNJ201509002.htm [8] ANEVLAVIS S, FROUDARAKIS M E. Advances in pleuroscopy[J]. Clin Respir J, 2018, 12(3): 839-847. doi: 10.1111/crj.12597 [9] LEE P, FOLCH E. Thoracoscopy: advances and increasing role for interventional pulmonologists[J]. Semin Respir Crit Care Med, 2018, 39(6): 693-703. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1676978 [10] 熊洁, 任小平, 魏声泓, 等. 内科胸腔镜对老年患者渗出性胸腔积液的诊断价值及安全性[J]. 临床肺科杂志, 2017, 22(1): 11-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCFK201701005.htmXIONG J, REN X P, WEI S H, et al. Diagnostic value and safety of medical thoracoscopy in elderly patients with exudative pleural effusion[J]. Journal of Clinical Pulmonary Medicine, 2017, 22(1): 11-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCFK201701005.htm [11] 朱新程, 王炯. 内科胸腔镜对不明原因胸腔积液诊断价值及恶性胸腔积液镜下表型特征[J]. 临床肺科杂志, 2019, 24(3): 491-494. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6663.2019.03.027ZHU X C, WANG J. Diagnostic value and morphological features for unexplained and malignant pleural effusion under medical thoracoscopy examination[J]. Journal of Clinical Pulmonary Medicine, 2019, 24(3): 491-494. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6663.2019.03.027 [12] SHAIKH F, LENTZ R J, FELLER-KOPMAN D, et al. Medical thoracoscopy in the diagnosis of pleural disease: a guide for the clinician[J]. Expert Rev Respir Med, 2020, 14(10): 987-1000. doi: 10.1080/17476348.2020.1788940 [13] 吕彦天, 陈颖, 徐莉, 等. 内科胸腔镜在不同原因胸腔积液诊断中的作用[J]. 临床肺科杂志, 2019, 24(2): 234-238. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6663.2019.02.010LYU Y T, CHEN Y, XU L, et al. Role of medical thoracoscopy in diagnosis of pleural effusion in different causes[J]. Journal of Clinical Pulmonary Medicine, 2019, 24(2): 234-238. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6663.2019.02.010 [14] 舒媚, 吴振兴, 朱振亮, 等. 血清肿瘤标志物联合检测在肺癌诊断中的价值[J]. 中华全科医学, 2016, 14(6): 1019-1021. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.2016.06.045SHU M, WU Z X, ZHU Z L, et al. Value of combined detection of serum tumor markers in the diagnosis of lung cancer[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2016, 14(6): 1019-1021. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.2016.06.045 [15] 国家卫计委海峡两岸医药卫生交流协会呼吸病学专业委员会, 中华医学会结核病学分会呼吸内镜专业委员会, 中国医师协会儿科学分会内镜专业委员会(筹), 等. 诊断性介入肺脏病学快速现场评价临床实施指南[J]. 天津医药, 2017, 45(4): 441-448. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJYZ201704025.htmNational Health and Family Planning Commission Cross-Straits Medical and Health Exchange Association Respiratory professional Committee, Professional Committee of Respiratory endoscopy of Tuberculosis Branch of Chinese Medical Association, Endoscopy Professional Committee of Pediatrics Branch of Chinese Medical Doctor Association (preparation), et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines for rapid Field Evaluation in diagnostic interventional pulmonary medicine[J]. Tianjin Medical Journal, 2017, 45(4): 441-448. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJYZ201704025.htm [16] GUARINO C, MOLLICA M, CESARO C, et al. Diagnostic yield of rapid on-site evaluation transbronchial needle aspiration versus conventional transbronchial needle aspiration: a single center experience[J]. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis, 2020, 90(1144): 73-77. [17] WAN T, LI Y, HU Q F, et al. Diagnostic value of rapid on-site evaluation during endobronchial ultrasound with a guide sheath for peripheral pulmonary lesions[J]. Cytopathology, 2020, 31(1): 16-21. [18] LIN C K, JAN I S, YU K L, et al. Rapid on-site cytologic evaluation by pulmonologist improved diagnostic accuracy of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial biopsy[J]. J Formos Med Assoc, 2021, 120(6): 1414-1415. [19] GLINSKI L, SHETTY D, ILES S, et al. Single slide assessment: a highly effective cytological rapid on-site evaluation technique for endobronchial and endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration[J]. Cytopathology, 2019, 30(2): 164-172. [20] WANG H S, REN T, WANG X, et al. Rapid on-site evaluation of touch imprints of biopsies improves the diagnostic yield of transbronchial biopsy for endoscopically nonvisible malignancy: a retrospective study[J]. Jpn J Clin Oncol, 2021, 51(4): 622-629. [21] 胡旭钢, 王剑, 宋嘉, 等. 结核性胸膜炎的内科胸腔镜表现及快速现场评价特点分析[J]. 中国内镜杂志, 2019, 25(12): 65-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGNJ201912013.htmHU X G, WANG J, SONG J, et al. Performance and diagnostic value of medical thoracoscopy and rapid on-site evaluation for tuberculous pleurisy[J]. China Journal of Endoscopy, 2019, 25(12): 65-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGNJ201912013.htm [22] 朱萌, 黄礼年. 内科胸腔镜在不明原因胸腔积液诊治中的应用价值分析[J]. 中国现代医药杂志, 2020, 22(3): 36-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHTY202003018.htmZHU M, HUANG L N. The application value of medical thoracoscopy in unexplained pleural effusion[J]. Modern Medicine Journal of China, 2020, 22(3): 36-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHTY202003018.htm [23] MCDONALD C M, PIERRE C, DE PERROT M, et al. Efficacy and cost of awake thoracoscopy and video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery in the undiagnosed pleural effusion[J]. Ann Thorac Surg, 2018, 106(2): 361-367. -





 下载:
下载: