Effects of peripheral magnetic stimulation and transcranial magnetic stimulation on upper extremity motor function in patients with cerebral infarction
-
摘要:
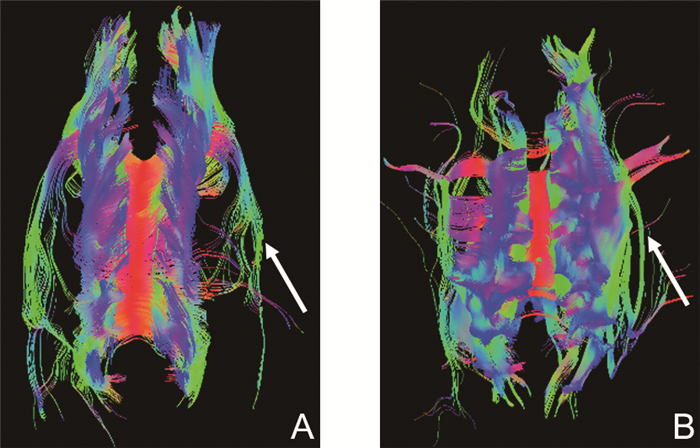
目的 应用外周磁刺激联合中枢磁刺激的康复方法,观察该方法对脑梗死患者上肢运动功能的恢复效果。 方法 选取2020年9月—2021年11月在郑州大学第二附属医院住院的脑梗死患者共42例为研究对象,经评定均存在上肢运动功能障碍,采用随机数字表法分为对照组(20例)与观察组(22例)。2组均给予常规康复治疗,对照组给予中枢磁刺激治疗,观察组在对照组的基础上加用外周磁刺激治疗。治疗前、后采用上肢Fugl-Meyer运动功能评分量表(UL-FMA)评估患者上肢运动功能恢复情况,采用改良Barthel指数(MBI)评估患者日常生活能力,采用弥散张量成像评估患者受损神经纤维束修复情况。 结果 治疗4周后,观察组UL-FMA评分[32.50(15.75, 46.50)分]、MBI[76.50(59.50, 91.25)分]均较治疗前明显提高(均P<0.05),对照组UL-FMA评分[29.50(10.25, 40.00)分]、MBI[89.00(50.00, 90.00)分]均较治疗前明显提高(均P<0.05);观察组治疗前后UL-FMA评分差值[12.00(9.75, 13.25)分]与对照组[7.00(5.00, 9.00)分]比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);观察组治疗前后MBI差值[18.50(10.00, 22.50)分]与对照组[10.00(7.00, 13.75)分]比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。2组患者受损的神经纤维束密度均有所增加。 结论 外周磁刺激联合中枢磁刺激促进了脑梗死患者上肢运动功能的恢复,提高了患者的日常生活能力。 Abstract:Objective To observe the effect of peripheral magnetic stimulation and transcranial magnetic stimulation on the recovery of upper limb motor function in patients with cerebral infarction. Methods A total of 42 patients with cerebral infarction who were admitted to the Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University from September 2020 to November 2021 were included in the study. They were assessed for upper limb motor dysfunction, and divided into the control group (n=20) and observation group (n=22) by using the random number table method. Both groups received routine rehabilitation treatment, and the control group was given transcranial magnetic stimulation. On the basis of the control group, the observation group was given peripheral magnetic stimulation. Before and after the treatment, upper limber Fugl-Meyer assessment of motor recovery (UL-FMA) was used to evaluate patients' upper limb motor function, the modified Barthel index (MBI) was used to evaluate patients' ability of daily living, and diffusion tensor imaging data were used to evaluate the repair of damaged nerve fibre bundles. Results After 4 weeks of treatment, the UL-FMA score [32.50 (15.75, 46.50) points] and MBI [76.50 (59.50, 91.25) points] in the observation group were significantly higher than those before treatment (all P < 0.05), while the UL-FMA score [29.50 (10.25, 40.00) points] and MBI [89.00 (50.00, 90.00) points] in the control group were significantly higher than those before treatment (all P < 0.05). The difference of UL-FMA scores before and after treatment [12.00 (9.75, 13.25) scores] in the observation group was statistically significant compared with the UL-FMA deviations before and after treatment [7.00 (5.00, 9.00) scores] in the control group (P < 0.05). The difference of MBI before and after treatment [18.50 (10.00, 22.50) scores] in the observation group was statistically significant compared with the MBI deviations [10.00(7.00, 13.75) scores] in the control group (P < 0.05). The density of damaged nerve fibre bundles increased in both groups. Conclusion Transcranial magnetic stimulation combined with peripheral magnetic stimulation promote the upper limb motor function in patients after cerebral infarct and improve patients' activities of daily living. -
表 1 2组脑梗死合并上肢运动功能障碍患者一般资料比较
Table 1. Comparison of general data of cerebral infarction patients with upper limb motor dysfunction between two groups
组别 例数 性别(例) 年龄(x±s, 岁) 病程(x±s, d) 病灶侧(例) Brunnstrom分期(例) 男性 女性 左 右 Ⅱ Ⅲ Ⅳ 对照组 20 14 6 59.55±8.86 8.93±4.01 5 15 7 6 7 观察组 22 16 6 62.18±10.24 7.23±0.66 5 17 7 8 7 统计量 0.038a 0.886b -1.879b 0.030a 0.191c P值 0.845 0.381 0.075 0.863 0.909 注:a为χ2值,b为t值,c为Z值。 表 2 2组脑梗死合并上肢运动功能障碍患者治疗前后MBI指数比较[M(P25, P75), 分]
Table 2. Comparison of MBI index of cerebral infarction patients with upper limb motor dysfunction before and after treatment between two groups [M(P25, P75), points]
组别 例数 治疗前 治疗后 差值 Z值 P值 对照组 20 77.50(35.00, 84.25) 89.00(50.00, 90.00) 10.00(7.00, 13.75) -3.925 < 0.001 观察组 22 57.50(35.00, 80.00) 76.50(59.50, 91.25) 18.50(10.00, 22.50) -4.111 < 0.001 Z值 -0.914 -0.865 -2.780 P值 0.361 0.387 0.005 表 3 2组脑梗死合并上肢运动功能障碍患者治疗前后UL-FMA评分比较[M(P25, P75), 分]
Table 3. Comparison of UL-FMA scores of cerebral infarction patients with upper limb motor dysfunction before and after treatment between two groups [M(P25, P75), points]
组别 例数 治疗前 治疗后 差值 Z值 P值 对照组 20 20.50(4.00, 35.50) 29.50(10.25, 40.00) 7.00(5.00, 9.00) -3.937 < 0.001 观察组 22 20.00(4.00, 34.25) 32.50(15.75, 46.50) 12.00(9.75, 13.25) -4.120 < 0.001 Z值 -0.218 -1.312 -4.757 P值 0.827 0.190 < 0.001 -
[1] 范晨雨, 谢鸿宇, 吴毅, 等. 早期康复训练促进脑卒中神经重塑机制的研究进展[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2020, 35(11): 1377-1380. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1242.2020.11.021FAN C Y, XIE H Y, WU Y, et al. Research progress of early rehabilitation training promoting neuroremodeling in stroke[J]. Chinese Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine, 2020, 35(11): 1377-1380. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1242.2020.11.021 [2] 肖长林, 潘翠环, 陈艳, 等. 高频重复经颅磁刺激对脑卒中患者手功能康复的疗效[J]. 中国康复理论与实践, 2018, 24(2): 179-183. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9771.2018.02.012XIAO Z L, PAN C H, CHEN Y, et al. Effect of high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on hand function in patients after stroke[J]. Chinese Journal of Rehabilitation Theory and Practice, 2018, 24(2): 179-183. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9771.2018.02.012 [3] 杨青, 陈树耿, 邓盼墨, 等. 周围神经肌肉磁刺激联合重复经颅磁刺激治疗脑卒中慢性期手功能障碍1例报道[J]. 中国康复理论与实践, 2018, 24(12): 1384-1387. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9771.2018.12.005YANG Q, CHEN S G, DENG P M, et al. Peripheral magnetic stimulation and repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for upper limb motor rehabilitation in chronic stroke: a case report[J]. Chinese Journal of Rehabilitation Theory and Practice, 2018, 24(12): 1384-1387. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9771.2018.12.005 [4] BEAULIEU L D, MASSÉ-ALARIE H, CAMIRÉ-BERNIER S, et al. After-effects of peripheral neurostimulation on brain plasticity and ankle function in chronic stroke: the role of afferents recruited[J]. Neurophysiol Clin, 2017, 47(4): 275-291. doi: 10.1016/j.neucli.2017.02.003 [5] 邓晓青, 廖亮华, 黄秀红, 等. 高、低频重复经颅磁刺激在脑梗死患者运动功能康复中的应用效果[J]. 数理医药学杂志, 2019, 32(5): 775-776. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4337.2019.05.067DENG X Q, LIAO L H, HUANG X H, et al. Effect of high and low frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on motor function rehabilitation of patients with cerebral infarction[J]. Journal of Mathematical Medicine, 2019, 32(5): 775-776. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4337.2019.05.067 [6] 刘进, 蔡倩, 徐亮, 等. 低频重复经颅磁刺激联合任务导向性镜像疗法对脑梗死患者上肢运动功能的影响[J]. 中国康复理论与实践, 2018, 24(11): 1320-1323. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9771.2018.11.012LIU J, CAI Q, XU L, et al. Effects of low-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation combined with task-oriented mirror therapy on upper limbs function in patients with cerebral infarction[J]. Chinese Journal of Rehabilitation Theory and Practice, 2018, 24(11): 1320-1323. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9771.2018.11.012 [7] 曹扬, 李丹. 重复经颅磁刺激对脑梗死患者下肢运动功能的影响及可行性分析[J]. 大医生, 2020, 5(24): 24-26.CAO Y, LI D. Effect and feasibility analysis of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on motor function of lower limbs in patients with cerebral infarction[J]. Doctor, 2020, 5(24): 24-26. [8] 李阳, 陈树耿, 王传凯, 等. 重复外周磁刺激对脑卒中患者上肢痉挛和运动功能的即刻影响[J]. 中国康复理论与实践, 2018, 24(12): 1376-1379. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9771.2018.12.003LI Y, CHEN S G, WANG C K, et al. Immediate effects of repetitive peripheral magnetic stimulation on upper limb spasticity and motor function for stroke patients[J]. Chinese Journal of Rehabilitation Theory and Practice, 2018, 24(12): 1376-1379. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9771.2018.12.003 [9] 徐榕, 朱光跃, 王勇, 等. 外周磁刺激结合经颅磁刺激对脑卒中后上肢痉挛的影响[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2021, 36(8): 943-948. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1242.2021.08.007XU R, ZHU G Y, WANG Y, et al. The effect of peripheral magnetic stimulation combined with transcranial magnetic stimulation on upper limb spasm after stroke[J]. Chinese Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine, 2021, 36(8): 943-948. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1242.2021.08.007 [10] 马明, 蔡倩, 徐亮, 等. 重复性外周神经磁刺激对脑卒中患者上肢屈肘肌痉挛的影响[J]. 中华物理医学与康复杂志, 2017, 39(2): 127-130. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-1424.2017.02.011MA M, CAI Q, XU L, et al. Repetitive magnetic stimulation can reduce elbow flexor spasticity after stroke[J]. Chinese Journal of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 2017, 39(2): 127-130. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-1424.2017.02.011 [11] 刘浩, 贾延兵, 魏静, 等. 重复外周磁刺激在康复治疗中的应用及研究进展[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2021, 36(5): 631-637. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1242.2021.05.024LIU H, JIA Y B, WEI J, et al. Application and research progress of repeated peripheral magnetic stimulation in rehabilitation therapy[J]. Chinese Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine, 2021, 36(5): 631-637. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1242.2021.05.024 [12] YANG C, CHEN P, DU W, et al. Musculoskeletal ultrasonography assessment of functional magnetic stimulation on the effect of glenohumeral subluxation in acute poststroke hemiplegic patients[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2018, 2018: 6085961. DOI: 10.1155/2018/6085961 [13] 刘盼月, 段淑荣, 曹国娟, 等. 脑梗死后HIF-1α及下游因子VEGF、SDF-1对神经干细胞作用的研究进展[J]. 脑与神经疾病杂志, 2018, 26(6): 393-396. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LYSJ201806015.htmLIU P Y, DUAN S R, CAO G J, et al. Research progress of HIF-1α and its downstream factors VEGF and SDF-1 on neural stem cells after cerebral infarction[J]. Journal of Brain and Nervous Diseases, 2018, 26(6): 393-396. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LYSJ201806015.htm [14] 朱炜楷, 沈会, 张朋新, 等. 针刺对脑缺血再灌注模型大鼠脑缺血皮质区神经血管单元微血管再生的影响[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2020, 35(4): 398-403, 419. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1242.2020.04.003ZHU W K, SHEN H, ZHANG P X, et al. Effects of the acupuncture on the brain angiogenesis of neurovascular unit around the cerebral ischemic cortex in rats with cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine, 2020, 35(4): 398-403, 419. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1242.2020.04.003 [15] 任珊, 王志群, 刘明, 等. 基于DTI的联合血栓通注射液治疗脑梗死患者神经重塑机制的研究[J]. 医学影像学杂志, 2018, 28(11): 1803-1807, 1836. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYXZ201811012.htmREN S, WANG Z Q, LIU M, et al. A study on the mechanism of neural remodeling of patients with ischemic stroke with Xueshuantong injection based on DTI[J]. Journal of Medical Imaging, 2018, 28(11): 1803-1807, 1836. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYXZ201811012.htm [16] 李文锋, 余秋华. 脑梗死急性期患者开展早期神经康复对其脑功能重塑的效果分析[J]. 按摩与康复医学, 2019, 10(11): 10-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1879.2019.11.005LI W F, YU Q H. Effect of early neurological rehabilitation on brain function remodeling in patients with acute cerebral infarction[J]. Chinese Manipulation & Rehabilitation Medicine, 2019, 10(11): 10-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1879.2019.11.005 [17] 李若阳, 朱静, 李彦橙, 等. 基于扩散张量成像初探苍艾挥发油对大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤的神经保护作用[J]. 四川大学学报(医学版), 2020, 51(5): 636-642. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYK202005010.htmLI R Y, ZHU J, LI Y C, et al. Basic research on neuroprotective effect of volatile oil of cang ai after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury based on diffusion tensor imaging[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Medical Sciences), 2020, 51(5): 636-642. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYK202005010.htm [18] 汪国余, 施一鸣, 王增献, 等. 头颅核磁共振用于诊断缺血性脑卒中后血管性痴呆的临床观察[J]. 中华全科医学, 2021, 19(6): 998-1000, 1025. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.001970WANG G Y, SHI Y M, WANG Z X, et al. Observe on the clinical effect of MRI in vascular dementia after ischemic stroke[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2021, 19(6): 998-1000, 1025. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.001970 [19] 陶峰, 朱洁, 王传杰, 等. 改良强制性运动疗法联合低频重复经颅磁刺激对脑卒中患者偏瘫上肢运动功能的影响[J]. 中国临床医学, 2021, 28(4): 556-561.TAO F, ZHU J, WANG C J, et al. Effect of modified constraint-induced movement therapy combined with low-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on upper limb motor function in stroke patients with hemiplegia[J]. Chinese Journal Of Clinical Medicine, 2021, 28(4): 556-561. [20] 陈明磊, 何超明, 林康, 等. 脑梗死后不同时期神经纤维束与肢体肌力的相关性[J]. 贵州医科大学学报, 2019, 44(10): 1233-1236. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYYB201910025.htmCHEN M L, HE C M, LIN K, et al. Correlation between Nerve Fiber Bundles and Limb Muscle Strength in Different Periods after Cerebral Infarction[J]. Journal of Guizhou Medical University, 2019, 44(10): 1233-1236. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYYB201910025.htm -





 下载:
下载: