The level and significance of HIGD-1A and HIGD-1B protein in patients with acute coronary syndrome
-
摘要:
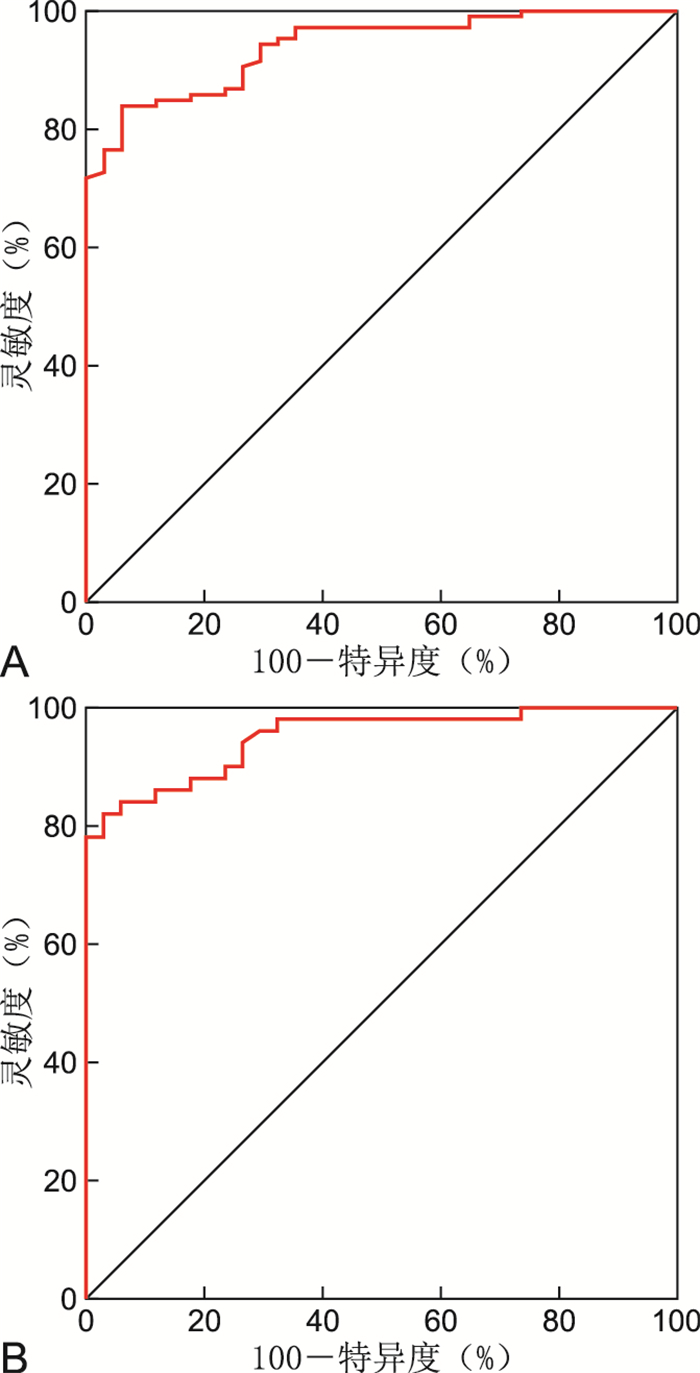
目的 通过检测急性冠脉综合征(ACS)患者血清缺氧诱导基因结构域蛋白-1A(HIGD-1A)、缺氧诱导基因结构域蛋白-1B(HIGD-1B)蛋白水平,分析其与急性冠脉综合征发生发展的关系。 方法 选择2019年9月—2021年9月就诊于蚌埠医学院第一附属医院心血管内科经冠状动脉造影确诊为ACS的患者106例,包括急性心肌梗死(AMI)患者50例、不稳定型心绞痛(UAP)患者56例,稳定型心绞痛(SAP)患者20例,选取同时期冠脉造影未见异常的患者34例作为正常组,采用ELISA法检测HIGD-1A、HIGD-1B蛋白,评估各组间差异。 结果 ACS组血清HIGD-1B蛋白与正常组比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.001)。ACS组、SAP组、正常组血清HIGD-1A蛋白差异无统计学意义(P=0.123)。根据Gensini积分,将冠脉病变程度分为轻度病变组29例,中度病变组40例,重度病变组37例,不同病变程度ACS患者HIGD-1B水平差异有统计学意义(P<0.001)。经Pearson相关性分析,ACS患者HIGD-1B水平与Gensini积分成正相关关系(r=0.685,P<0.001)。绘制ROC曲线,血清HIGD-1B水平预测急性冠脉综合征的AUC为0.940,灵敏度为84.0%,特异度为94.1%,约登指数为0.781,具有一定的诊断参考价值。 结论 急性冠脉综合征患者血清HIGD-1B蛋白显著升高,且与冠脉严重程度成正相关关系,这对于ACS的诊断具有重要意义。 -
关键词:
- 急性冠脉综合征 /
- 缺氧诱导基因结构域蛋白-1A /
- 缺氧诱导基因结构域蛋白-1B
Abstract:Objective To detect serum hypoxia induced genetic structure domain protein-1A (HIGD-1A) and hypoxia induced genetic structure domain protein-1B (HIGD-1B) protein levels in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and analyze their relationship with the development of ACS. Methods A total of 106 patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) diagnosed by coronary angiography in the Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, the First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College from September 2019 to September 2021 were selected, including 50 patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI), 56 patients with unstable angina pectoris (UAP), and 20 patients with stable angina pectoris (SAP). Thirty-four patients with normal coronary angiography during the same period were selected as the normal group. The protein levels of HIGD-1A and HIGD-1B were detected by ELISA to evaluate the differences between the groups. Results Serum HIGD-1B protein was statistically significant between the ACS and control group (P < 0.001). There was no significant difference in HIGD-1A protein among ACS group, SAP group and normal group (P=0.123). According to Gensini score, the degree of coronary artery disease was divided into mild group (n=29), moderate group (n=40) and severe group (n=37). There was a significant difference in HIGD-1B level among patients with different degrees of coronary artery disease in ACS group (P < 0.001). Pearson correlation analysis showed that HIGD-1B level was positively correlated with Gensini score in ACS group (r=0.685, P < 0.001). When drawing ROC curve, the AUC of serum HIGD-1B level in predicting acute coronary syndrome was 0.940, the sensitivity was 84.0%, the specificity was 94.1%, and the Youden index was 0.781, which had certain diagnostic reference value. Conclusion The serum HIGD-1B protein is significantly elevated in patients with acute coronary syndromes and positively correlated with coronary severity, which is of great significance for the diagnosis of ACS. -
表 1 3组受试者的基线资料比较
Table 1. Comparison of baseline data among the three groups of subjects
组别 例数 性别
(男/女,例)吸烟
(有/无,例)年龄
(x±s,岁)空腹血糖
(x±s,mmol/L)甘油三酯
(x±s,mmol/L)尿酸
(x±s,μmol/L)肌酐
(x±s,μmol/L)ACS组 106 66/40 56/50 63.91±11.12 6.42±2.78 1.82±0.81 313.30±73.07 69.26±12.72 SAP组 20 14/6 12/8 61.90±10.26 5.52±1.06 1.89±0.83 335.45±82.07 67.50±10.85 正常组 34 22/12 18/16 59.00±9.97 5.94±3.28 1.88±1.31 298.00±67.52 68.35±8.49 统计量 0.453a 0.359a 2.714b 1.090b 0.096b 1.659b 0.229b P值 0.797 0.836 0.069 0.339 0.909 0.194 0.796 注:a为χ2值,b为F值。 表 2 Gensini积分算法
Table 2. Gensini integral algorithm
病变血管位置 系数 病变狭窄程度比例 得分 左主干 5.0 未见异常 0 左前降支近段 2.5 ≤25% 左前降支中段 1.5 1 左前降支远段 1.0 左回旋支近段 2.5 26%~50% 2 左回旋支远段 1.0 后侧支 0.5 51%~75% 4 第一对角支 1.0 76%~90% 第二对角支 0.5 8 右冠近段 1.0 91%~99% 右冠中段 1.0 16 右冠远段 1.0 后降支 1.0 100% 32 表 3 ACS组、SAP组、正常组血清HIGD-1A、HIGD-1B比较(x±s,ng/mL)
Table 3. Comparison of serum HIGD-1A and HIGD-1B among ACS group, SAP group and normal group(x±s, ng/mL)
组别 例数 HIGD-1A HIGD-1B ACS组 106 2.67±0.90 4.46±1.76ab SAP组 20 2.26±0.63 2.51±0.82 正常组 34 2.53±0.78 1.67±0.84 F值 2.125 78.041 P值 0.123 <0.001 注:与正常组比较,aP < 0.05;与SAP组比较, bP < 0.05。 表 4 不同病变程度ACS患者血清HIGD-1B水平比较(x±s,ng/mL)
Table 4. Comparison of serum HIGD-1B levels in ACS patients with different degrees of lesion(x±s, ng/mL)
组别 例数 HIGD-1B 轻度病变组 29 3.02±1.22 中度病变组 40 3.96±0.91a 重度病变组 37 6.12±1.48ab F值 45.501 P值 <0.001 注:与轻度病变组比较,aP < 0.05;与中度病变组比较,bP < 0.05。 表 5 血清HIGD-1B对ACS、AMI的预测价值
Table 5. Predictive value of serum HIGD-1B for ACS and AMI
组别 AUC 95% CI SE P值 截断值
(ng/mL)灵敏度
(%)特异度
(%)约登指数 ACS组 0.940 0.903~0.976 0.019 < 0.001 2.943 84.0 94.1 0.781 AMI组 0.950 0.907~0.992 0.022 < 0.001 3.168 82.0 97.1 0.791 -
[1] TRUTTER L, BIGEH A, PECCI C, et al. Diagnostic and management dilemmas in women presenting with acute coronary syndromes[J]. Curr Cardiol Rep, 2020, 22(12): 163. doi: 10.1007/s11886-020-01410-1 [2] BHATT D L, LOPES R D, HARRINGTON R A. Diagnosis and treatment of acute coronary syndromes: a review[J]. JAMA, 2022, 327(7): 662-675. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.0358 [3] DONG Y, CHEN H, GAO J, et al. Molecular machinery and interplay of apoptosis and autophagy in coronary heart disease[J]. J Mol Cell Cardiol, 2019, 136: 27-41. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2019.09.001 [4] 王娟, 范西真, 吴晓飞. 急性冠脉综合征的诊治与管理[J]. 中华全科医学, 2021, 19(7): 1073-1074. http://www.zhqkyx.net/article/id/aa90c0ac-e729-4f80-9cfa-d82edb47ae2eWANG J, FAN X Z, WU X F. Diagnosis, treatment and management of acute coronary syndrome[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2021, 19(7): 1073-1074. http://www.zhqkyx.net/article/id/aa90c0ac-e729-4f80-9cfa-d82edb47ae2e [5] LI T, XIAN W J, GAO Y, et al. Higd-1a protects cells from lipotoxicity under high-fat exposure[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2019, 2019: 6051262. DOI: 10.1155/2019/6051262. [6] TIMON-GOMEZ A, BARTLEY-DIER E L, FONTANESI F, et al. Higd-driven regulation of cytochrome c oxidase biogenesis and function[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(12): 2620. doi: 10.3390/cells9122620 [7] XU Z, SUN J, MAO Y, et al. Hig1 domain family member 1A disrupts proliferation, migration, and invasion of colon adenocarcinoma cells[J]. Bioengineered, 2021, 12(2): 10501-10511. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1999368 [8] TIMON-GOMEZ A, GARLICH J, STUART R A, et al. Distinct roles of mitochondrial higd-1A and higd-2A in respiratory complex and supercomplex biogenesis[J]. Cell Rep, 2020, 31(5): 107607. DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107607. [9] GUO J, YANG C, ZHANG S, et al. Mir-375 induces ros and apoptosis in ST cells by targeting the higd-1A gene[J]. Gene, 2019, 685: 136-142. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.10.086 [10] CHENG Z, WANG G, ZHU W, et al. LEF1-AS1 accelerates tumorigenesis in glioma by sponging mir-489-3p to enhance higd1A[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11(8): 690. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02823-0 [11] NAGAO T, SHINTANI Y, HAYASHI T, et al. Higd1a improves respiratory function in the models of mitochondrial disorder[J]. FASEB J, 2020, 34(1): 1859-1871. doi: 10.1096/fj.201800389R [12] ZHU J Y, CHEN M, MU W J, et al. Higd1a facilitates exercise-mediated alleviation of fatty liver in diet-induced obese mice[J]. Metabolism, 2022, 134: 155241. DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2022.155241. [13] LOPEZ L, ZULUAGA M J, LAGOS P, et al. The expression of hypoxia-induced gene 1(higd1a) in the central nervous system of male and female rats differs according to age[J]. J Mol Neurosci, 2018, 66(3): 462-473. doi: 10.1007/s12031-018-1195-y [14] CHEN B, XU F, GAO Y, et al. DNA damage-induced translocation of mitochondrial factor HIGD1A into the nucleus regulates homologous recombination and radio/chemo-sensitivity[J]. Oncogene, 2022, 41(13): 1918-1930. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02226-9 [15] BAEK S H, MAIORINO E, KIM H, et al. Single cell transcriptomic analysis reveals organ specific pericyte markers and identities[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2022, 9: 876591. DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.876591. [16] ZHOU Y, XU B, ZHOU Y, et al. Identification of key genes with differential correlations in lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2021, 9: 675438. DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.675438. [17] SORIANO M E, SCORRANO L. The interplay between Bcl-2 family proteins and mitochondrial morphology in the regulation of apoptosis[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2010, 687: 97-114. [18] LIU Y L, YANG L Q, YIN J M, et al. MicroRNA-15b deteriorates hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis by downregulating Bcl-2 and MAPK3[J]. J Investig Med, 2018, 66(1): 39-45. doi: 10.1136/jim-2017-000485 [19] PANG Y, ZHU Z D, WEN Z H, et al. Higd 1b inhibits hypoxia induced mitochondrial fragmentation by regulating OPA1 cleavage in cardiomyocytes[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2021, 24(2): 549. DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12188. [20] CAO M Y, YU C, YAO Z H, et al. Atractylodesin Ⅲ maintains mitochondrial function and inhibits caspase-3 activity to reverse apoptosis of cardiomyocytes in AMI rats[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2019, 12(1): 198-204. [21] KESAVARDHANA S, MALIREDDI R K S, KANNEGANTI T D. Caspases in cell death, inflammation, and pyroptosis[J]. Annu Rev Immunol, 2020, 38: 567-595. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-073119-095439 -





 下载:
下载: