Chlorogenic acid effects of intestinal epithelial barrier function with septic rats through TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway
-
摘要:
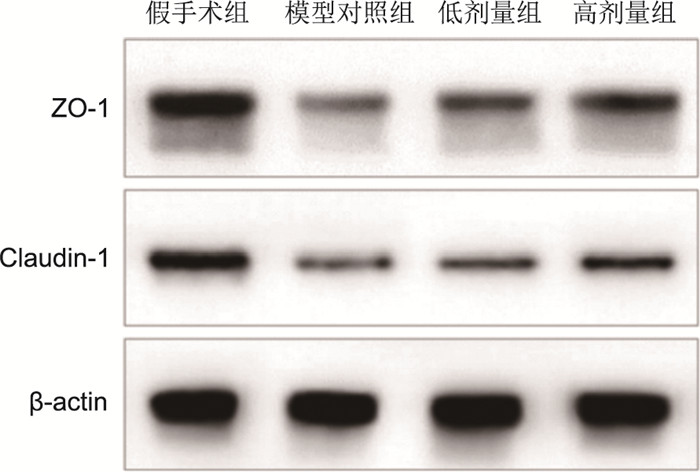
目的 观察绿原酸通过调控TLR4/NF-κB信号通路减轻脓毒症(sepsis)大鼠肠道氧化应激损伤、改善肠上皮细胞屏障功能的作用。 方法 选取SD大鼠60只,采用随机数字表法分成假手术组、模型对照组、绿原酸(低、高剂量)组,每组15只。术后24 h,应用酶联免疫吸附法(ELISA)检测大鼠血清中肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)、白细胞介素-6(IL-6)、IL-10;比色法测定小肠组织中一氧化氮(NO)、超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、丙二醛(MDA)水平;采用Western blotting法测定小肠组织中的蛋白表达[密封蛋白-1(Claudin-1)、闭锁连接蛋白-1(ZO-1)及TLR-4/NF-κB通路相关的蛋白]。 结果 与模型对照组[(4.45±0.14)分]比较,低剂量组[(4.17±0.22)分]、高剂量组[(1.95±0.08)分]Chiu评分明显下降(t=4.159、60.048,均P < 0.001);高剂量组血清TNF-α、IL-6、IL-10水平及小肠组织中NO、MDA含量均显著降低(均P < 0.05),SOD含量、Claudin-1、ZO-1蛋白表达量及MyD88、TLR-4蛋白与p-NF-κB p65(Ser536)水平均显著升高(均P < 0.05)。 结论 绿原酸可经抑制TLR4/NF-kB信号转导途径,减轻脓毒症大鼠的炎症反应程度及小肠组织的氧化应激损伤,进而促进大鼠的肠道屏障功能改善。 -
关键词:
- 绿原酸 /
- TLR4/NF-κB信号通路 /
- 肠道菌群 /
- 肠上皮细胞屏障功能
Abstract:Objective To observe the effect of chlorogenic acid on reducing intestinal oxidative stress injury and improving intestinal cell barrier function through TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in septic rats. Methods Sixty SD rats were randomly divided into four groups by the random number table method: sham operation group, model control group and chlorogenic acid (low and high dose) group, with 15 rats in each group. 24 hours after operation, the levels of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin (IL-6) and IL-10 were detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), the levels of nitric oxide (NO), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and malondialdehyde (MDA) in small intestine were measured by colorimetry, and western blot was used to detect claudin-1, ZO-1 and TLR-4/NF-κB pathway related protein expression. Results Compared with the model control group, Chiu score in low dose group (4.17±0.22) and high dose group (1.95±0.08) decreased significantly (t=4.159, 60.048, all P < 0.01). The levels of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-10 and the contents of NO and MDA in the small intestine in high dose group were significantly decreased (all P < 0.05), the content of SOD, the expression of Claudin-1, ZO-1 protein, MyD88, TLR-4 protein and p-NF-κB p65 (Ser536) increased significantly (all P < 0.05). Conclusion Chlorogenic acid can reduce serum inflammatory response, reduce oxidative damage of small intestine in septic rats through inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB signal transduction, and then improve intestinal barrier function. -
表 1 4组脓毒症大鼠血清TNF-α、IL-6和IL-10水平比较(x±s,pg/mL)
Table 1. Comparison of serum TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 levels in four septic rats(x±s, pg/mL)
组别 只数 TNF-α IL-6 IL-10 假手术组 15 41.38±9.02 76.09±20.36 7.04±2.03 模型对照组 15 106.48±14.25 249.61±31.58 20.16±5.84 低剂量组 15 97.47±15.18 237.68±28.39 18.72±4.25 高剂量组 15 74.29±10.80 202.73±25.44 15.66±3.19 F值 80.142 132.320 31.185 P值 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 表 2 4组脓毒症大鼠小肠组织NO、SOD和MDA水平比较(x±s)
Table 2. Comparison of the levels of NO, SOD, and MDA in small intestinal tissue of septic rats among the four groups(x±s)
组别 只数 NO(μmol/L) SOD(U/mL) MDA(nmol/mL) 假手术组 15 39.65±7.38 43.97±9.81 98.37±11.86 模型对照组 15 110.22±13.91 19.62±5.74 210.08±17.63 低剂量组 15 77.36±10.13 23.65±7.19 198.71±20.39 高剂量组 15 65.36±8.87 38.93±9.06 123.08±13.15 F值 119.970 31.446 175.821 P值 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 -
[1] 张静雯, 庞燕, 耿男, 等. 病毒性脓毒症的研究进展与启发[J]. 中国急救医学, 2021, 41(3): 270-274. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1949.2021.03.017ZHANG J W, PANG Y, GENG N, et al. Research progress and inspiration of viral sepsis[J]. Chinese Journal of Critical Care Medicine, 2021, 41(3): 270-274. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1949.2021.03.017 [2] RUDD K E, JOHNSON S C, AGESA K M, et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990—2017: analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study[J]. Lancet, 2020, 395(10219): 200-211. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32989-7 [3] 李雅琳, 李东风. 脓毒症患者的肠屏障功能损伤变化情况探究[J]. 中国现代医生, 2021, 59(9): 122-124, 133. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDYS202109039.htmLI Y L, LI D F. Investigation on the changes of intestinal barrier dysfunction in patients with sepsis[J]. Modern Chinese Doctor, 2021, 59(9): 122-124, 133. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDYS202109039.htm [4] MIAO M, XIANG L. Pharmacological action and potential targets of chlorogenic acid[J]. Adv Pharmacol, 2020, 87: 71-88. [5] 窦彩霞, 李海花, 孙泽阳, 等. 核转录因子-κB/β-连环蛋白信号通路介导肠产毒性大肠杆菌引致IPEC-J2细胞损伤[J]. 动物营养学报, 2020, 32(12): 5893-5902. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DWYX202012042.htmDOU C X, LI H H, SUN Z Y, et al. Nuclear Transcription Factor-κB/β-Catenin signaling pathway mediates enterotoxigenic escherichia coli causing IPEC-J2 cell injury[J]. Chinese Journal Of Animal Nutrition, 2020, 32(12): 5893-5902. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DWYX202012042.htm [6] CUI W J, HU G X, PENG J, et al. Quercetin exerted protective effects in a rat model of sepsis via inhibition of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and downregulation of high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) protein expression[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2019, 25: 5795-5800. doi: 10.12659/MSM.916044 [7] SINGER M, DEUTSCHMAN C S, SEYMOUR C W, et al. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3)[J]. JAMA, 2016, 315(8): 801-810. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287 [8] 张卉, 冯永文, 姚咏明. 深刻理解烧创伤脓毒症发病机制的网络效应[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2020, 100(12): 881-882, 885. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20191129-02603ZHANG H, FENG Y W, YAO Y M. A profound understanding of the pathogenesis network in sepsis[J]. National Medical Journal of China, 2020, 100(12): 881-882, 885. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20191129-02603 [9] 曾小娜, 尹连红, 许丽娜. 脓毒症性急性肾损伤发病机制[J]. 生理科学进展, 2020, 51(2): 122-126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0559-7765.2020.02.011ZENG X N, YIN L H, XU L N. Pathogenesis of sepsis induced acute renal injury[J]. Progress in Physiological Sciences, 2020, 51(2): 122-126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0559-7765.2020.02.011 [10] 江勉君, 史忠亮, 毛凯凤, 等. 氧化应激在脓毒症中的发病机制[J]. 医学综述, 2020, 26(5): 856-860. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2020.05.005JANG M J, SHI Z L, MAO K F, et al. Pathogenesis of oxidative stress in sepsis[J]. Medical Recapitulate, 2020, 26(5): 856-860. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2020.05.005 [11] 何亮伟, 耿婷, 李艳静, 等. 谷胱甘肽反应性代谢物引起药物性肝损伤的机制研究进展[J]. 中国药房, 2017, 28(7): 990-994. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYA201707036.htmHE L W, GENG T, LI Y J, et al. Research Progress on the mechanism of drug-induced liver injury caused by glutathione reactive metabolites[J]. China Pharmacy, 2017, 28(7): 990-994. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYA201707036.htm [12] 刘世强. 绿原酸对断奶应激大鼠免疫功能和肠道屏障功能的影响[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2013.LIU S Q. Effects of chlorogenic acid on immune function and intestinal barrier function in weaning stress rats[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2013. [13] 黄芳. 绿原酸对镉暴露大鼠肠道屏障的保护作用及机制[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2018.HUANG F. Protective effect and mechanism of chlorogenic acid on intestinal barrier in cadmium exposed rats[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2018. [14] 古丽菲热·塔依尔, 杨春波, 李祥, 等. 脓毒症肠道损伤模型中NLRP3炎症小体活化介导炎症反应及细胞凋亡[J]. 中华危重病急救医学, 2021, 33(7): 855-860. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20210323-00725GU LFR·TYE, YANG C B, LI X, et al. Activation of NOD-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome mediates inflammatory response and apoptosis in septic intestinal injury model[J]. Chinese Critical Care Medicine, 2021, 33(7): 855-860. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20210323-00725 [15] 张夏子, 何先弟, 汪华学, 等. 鲍曼不动杆菌脓毒症大鼠体内miR-155和Th17表达的关系[J]. 中华全科医学, 2019, 17(9): 1478-1481. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.000974ZHANG X Z, HE X D, WANG H X, et al. Expression of microRNA-155 and Th17 in rats with sepsis caused by Acinetobacter baumannii and their relationship[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2019, 17(9): 1478-1481. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.000974 [16] WANG Z, ZHONG C S, CAO Y Y, et al. LncRNA DANCR improves the dysfunction of the intestinal barrier and alleviates epithelial injury by targeting the miR-1306-5p/PLK1 axis in sepsis[J]. Cell Biol Int, 2021, 45(9): 1935-1944. [17] SUBRAMANIAN S, GENG H, TAN X D. Cell death of intestinal epithelial cells in intestinal diseases[J]. Sheng Li Xue Bao, 2020, 72(3): 308-324. [18] GAO W Y, WANG C H, YU L, et al. Chlorogenic acid attenuates dextran sodium sulfate-induced ulcerative colitis in mice through MAPK/ERK/JNK Pathway[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2019, 2019: 6769789. DOI: 10.1155/2019/6769789. [19] JIANG Y D, SONG J, XU Y, et al. Piezo1 regulates intestinal epithelial function by affecting the tight junction protein claudin-1 via the ROCK pathway[J]. Life Sci, 2021, 275: 119254. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119254. [20] CUI L, GUAN X N, DING W B, et al. Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi polysaccharide ameliorates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis by improving intestinal barrier function and modulating gut microbiota[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2021, 166: 1035-1045. [21] ZUSSO M, LUNARDI V, FRANCESCHINI D, et al. Ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin attenuate microglia inflammatory response via TLR4/NF-κB pathway[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2019, 16(1): 148. -





 下载:
下载: