Analysis of influencing factors in 106 children with sleep disorders and the related management strategies
-
摘要:
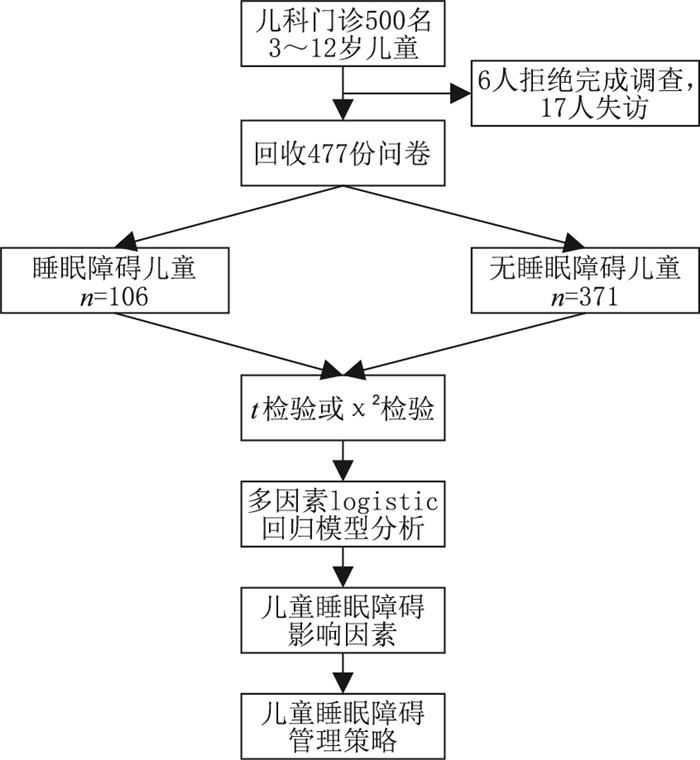
目的 研究儿童睡眠障碍的相关影响因素,为制定预防和减少儿童睡眠障碍的干预措施提供科学依据。 方法 选取2020年1月—2022年1月石家庄市人民医院门诊500名儿童作为研究对象,采用多导睡眠监测、儿童睡眠习惯问卷和睡眠日记综合评估和诊断儿童睡眠障碍。对儿童家长进行问卷调查,包括人口统计数据和与睡眠障碍潜在危险因素相关的信息因素,按照是否有睡眠障碍,分为睡眠障碍组和无睡眠障碍组。分别使用单因素和多因素logistic回归分析研究导致儿童睡眠障碍的影响因素。 结果 本研究共回收477份问卷,其中106例儿童患有睡眠障碍,371例儿童无睡眠障碍,单因素分析显示2组儿童体重、是否肥胖、是否早产儿、父母是否打鼾、有无过敏性鼻炎、夜间环境有无噪音、有无哮喘病史、睡前1 h是否看电子产品、睡前1 h是否活动、睡前1 h是否饮食比较差异有统计学意义(均P < 0.05)。多因素logistic回归分析显示肥胖、有过敏性鼻炎、夜间环境噪音、有哮喘病史、睡前1 h看电子产品、睡前1 h活动、睡前1 h饮食是儿童睡眠障碍的独立危险因素(均P < 0.05)。 结论 肥胖、过敏性鼻炎、夜间环境噪音、哮喘病史、睡前1 h看电子产品、睡前1 h活动、睡前1 h饮食会影响睡眠, 减少并预防儿童睡眠障碍对促进儿童身心发育具有重要临床意义。 Abstract:Objective To study the prevalence of sleep disorders in children and analyze related influencing factors from various aspects, so as to provide a scientific basis for the development of interventions to prevent and reduce sleep disorders in children. Methods A total of 500 children from the outpatient department of Shijiazhuang People's Hospital between January 2020 and October 2022 were selected as the research subjects, using polysomnography, children's sleep habits questionnaire (CSHQ) and sleep diary to comprehensively assess and diagnose children's sleep disorders. Parents are asked to complete a questionnaire about their child's sleep time and sleep habits, including demographic data and informative factors related to potential risk factors for sleep disorders, and are divided into sleep disorder group and non-sleep disorder group. Univariate and Logistic regression were used to analyze the factors influencing children's sleep disturbance and to suggest intervention strategies. Results A total of 477 questionnaires were received for this study, including 106 children with sleep disorders and 371 children without sleep disorders. Univariate analysis showed that the differences between the 2 groups of children were statistically significant with regard to weight, obesity, preterm birth, parents' snoring, allergic rhinitis, presence of noise in the night-time environment, history of asthma, watching electronic devices, being active, or eating 1 hour before bedtime (all P < 0.05). Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that obesity, allergic rhinitis, night-time noise, history of asthma, watching electronic devices, being active, or eating 1 hour before bedtime were independent risk factors for sleep disorders in children (all P < 0.05). Conclusion Independent risk factors for sleep disorders in children include obesity, allergic rhinitis, nocturnal ambient noise, history of asthma, watching electronic devices, being active, or eating 1 hour before bedtime. Reducing and preventing the incidence of sleep disorders in children has important clinical implications for their physical and mental development. -
Key words:
- Children /
- Sleep disorders /
- Sleep time /
- Influencing factors
-
表 1 睡眠障碍组与无睡眠障碍组儿童一般资料比较
Table 1. Comparison of general data of children between sleep disorder group and no sleep disorder group
项目 睡眠障碍组
(106例)无睡眠障碍组
(371例)统计量 P值 性别(例) 0.652a 0.419 男 57 183 女 49 188 年龄(x±s,岁) 7.85±2.94 8.03±1.26 0.921b 0.357 体重(x±s,kg) 24.73±2.46 23.73±1.88 4.489b < 0.001 是否肥胖(例) 24.580a < 0.001 是 21 18 否 85 353 是否母乳喂养(例) 3.533a 0.059 是 100 363 否 6 8 是否早产儿(例) 4.196a 0.041 是 10 16 否 96 355 注:a为χ2值,b为t值。 表 2 2组儿童父母因素、环境因素比较(例)
Table 2. Comparison of parental factors and environmental factors between the two groups (case)
项目 睡眠障碍组
(106例)无睡眠障碍组
(371例)χ2值 P值 父母教育水平 高 46 201 3.838 0.051 低 60 170 父母是否打鼾 是 35 86 4.215 0.040 否 71 285 接触吸烟环境 是 27 74 1.508 0.219 否 79 297 睡眠体位 仰位 83 302 0.509 0.476 俯位 23 69 过敏性鼻炎 是 26 32 19.520 < 0.001 否 80 339 打鼾家族史 有 22 55 2.142 0.143 无 84 316 夜间环境噪音 有 25 26 23.731 < 0.001 无 81 345 哮喘病史 有 15 29 3.950 0.047 无 91 342 睡前看电子产品 是 32 58 11.414 < 0.001 否 74 313 睡前1 h活动 是 21 28 13.452 < 0.001 否 85 343 睡前1 h饮食 是 18 23 12.218 < 0.001 否 88 348 表 3 儿童睡眠障碍的多因素logistic回归分析
Table 3. Multivariate logistic regression analysis of sleep disorders in children
变量 B SE Wald χ2 P值 OR值 95% CI 体重 -0.317 0.283 1.255 0.257 0.728 0.441~1.847 肥胖 0.718 0.329 4.758 0.033 2.050 1.067~3.908 早产儿 1.382 0.783 3.115 0.070 3.983 0.859~18.467 父母打鼾 0.503 0.321 2.455 0.129 1.654 0.882~3.102 过敏性鼻炎 1.827 0.265 47.530 < 0.001 6.215 3.798~10.444 夜间环境噪音 1.124 0.253 19.734 < 0.001 3.077 1.874~5.050 哮喘病史 1.762 0.573 9.456 0.005 5.824 1.895~17.904 睡前玩电子产品 2.287 0.892 6.571 0.008 9.845 1.714~56.543 睡前1 h活动 0.501 0.254 3.889 0.010 1.650 1.004~2.713 睡前1 h饮食 2.163 0.753 8.251 0.009 8.697 1.989~49.948 -
[1] KAPOOR V, FERRI R, STEIN M A, et al. Restless sleep disorder in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder[J]. J Clin Sleep Med, 2021, 17(4): 639-643. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.8984 [2] HOWARTH T P, GENTIN N, REYES-CHICUELLAR N, et al. Sleep quality and obstructive sleep apnoea in Indigenous and non-indigenous Australian children[J]. Sleep Med, 2022, 98: 68-78. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2022.06.014 [3] MCDONAGH M S, HOLMES R, HSU F. Pharmacologic treatments for sleep disorders in children: a systematic review[J]. J Child Neurol, 2019, 34(5): 237-247. doi: 10.1177/0883073818821030 [4] 葛飞飞, 张迪, 姚惠玲, 等. 儿童睡眠障碍性疾病的研究进展[J]. 中国儿童保健杂志, 2020, 28(2): 165-166, 214. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ERTO202002016.htmGE F F, ZHANG D, YAO H L, et al. Research progress on sleep disorders in children[J]. Chinese Journal of Children's Health Care, 2020, 28(2): 165-166, 214. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ERTO202002016.htm [5] 李若宁. 儿童睡眠障碍与维生素D相关性的研究进展[J]. 国际儿科学杂志, 2022, 49(4): 262-265. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4408.2022.04.011LI R N. Research progress on the relationship between sleep disorders and vitamin D in children[J]. International Journal of Pediatrics, 2022, 49(4): 262-265. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4408.2022.04.011 [6] RUSSO K, GREENHILL J, BURGESS S. Home (Level 2) polysomnography is feasible in children with suspected sleep disorders[J]. Sleep Med, 2021, 88: 157-161. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2021.10.024 [7] SCHNAPP A, HAREL M, CAYAM-RAND D, et al. A placebo-controlled trial of cannabinoid treatment for disruptive behavior in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder: effects on sleep parameters as measured by the CSHQ[J]. Biomedicines, 2022, 10(7): 1685. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10071685 [8] 刘静. 儿童中枢性睡眠呼吸暂停研究进展[J]. 国际儿科学杂志, 2021, 48(12): 803-807. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4408.2021.12.003LIU J. Research progress on central sleep apnea in children[J]. International Journal of Pediatrics, 2021, 48(12): 803-807. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4408.2021.12.003 [9] AGOSTINI A, CENTOFANTI S. Normal sleep in children and adolescence[J]. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am, 2021, 30(1): 1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.chc.2020.08.011 [10] WINSOR A A, RICHARDS C, BISSELL S, et al. Sleep disruption in children and adolescents with epilepsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Sleep Med Rev, 2021, 57: 101416. DOI: 10.1016/j.smrv.2021.101416. [11] 黄思艳, 秦岭, 刘海润, 等. 睡眠与儿童青少年语言发展[J]. 中华行为医学与脑科学杂志, 2021, 30(5): 476-480. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn371468-20200930-01758HUANG S Y, QIN L, LIU H R, et al. Sleep and Language Development of Children and Adolescents[J]. Chinese Journal of Behavioral Medicine and Brain Science, 2021, 30(5): 476-480. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn371468-20200930-01758 [12] 李生慧. 将睡眠纳入儿童青少年发育与健康评价体系[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2021, 42(6): 805-809. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XIWS202106004.htmLI S H. Incorporating sleep into the development and health evaluation system of children and adolescents[J]. Chinese School Health, 2021, 42(6): 805-809. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XIWS202106004.htm [13] 曾祥宇, 黄彦, 刘斯博, 等. 睡眠时长、饮食习惯与学龄儿童肥胖的关系[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2021, 25(5): 600-604, 611. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JBKZ202105019.htmZENG X Y, HUANG Y, LIU S B, et al. The relationship between sleep duration, eating habits and obesity in school-age children[J]. Chinese Journal of Disease Control, 2021, 25(5): 600-604, 611. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JBKZ202105019.htm [14] SÁNCHEZ-LÓPEZ A M, NOACK-SEGOVIA J P, NÙÑEZ-NEGRILLO A M, et al. Childhood obesity and its influence on sleep disorders: kids-play study[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2020, 17(21): 7948. DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17217948. [15] MELINDA T F, SEKARTINI R. Association between obesity and sleep disorders in primary school children: a cross-sectional study[J]. Med J Indones, 2019, 28(2): 167-173. doi: 10.13181/mji.v28i2.2645 [16] D' ELIA C, GOZAL D, BRUNI O, et al. Allergic rhinitis and sleep disorders in children-coexistence and reciprocal interactions[J]. J Pediatr (Rio J), 2022, 98(5): 444-454. doi: 10.1016/j.jped.2021.11.010 [17] LEE K S, LIM D H, SHEEN Y H, et al. The relationship between sleep disturbances and allergic rhinitis in Korean children and adolescents[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2022, 149(2): AB127. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2021.12.433. [18] 耿雅轩. 儿童阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征认知功能损害的研究进展[J]. 国际儿科学杂志, 2021, 48(4): 249-252. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4408.2021.04.008GENG Y X. Research progress on cognitive impairment in children with obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome[J]. International Journal of Pediatrics, 2021, 48(4): 249-252. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4408.2021.04.008 [19] WANG R, MIHAICUTA S, TIOTIU A, et al. Asthma and obstructive sleep apnoea in adults and children-an up-to-date review[J]. Sleep Med Rev, 2022, 61: 101564. DOI: 10.1016/j.smrv.2021.101564. [20] 周作玲, 陈希胜. 阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征相关肝损害的危险因素研究[J]. 中华全科医学, 2020, 18(11): 1860-1863. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.001639ZHOU Z L, CHEN X S. Risk factors for obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome-related liver damage[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2022, 18(11): 1860-1863. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.001639 [21] LEE J, PARK J, LEE J, et al. Effect of noise on sleep and autonomic activity in children according to source[J]. J Korean Med Sci, 2021, 36(37): e234. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e234 [22] STAPLES A D, HOYNIAK C, MCQUILLAN M E, et al. Screen use before bedtime: consequences for nighttime sleep in young children[J]. Infant Behav Dev, 2021, 62: 101522. DOI: 10.1016/j.infbeh.2020.101522. [23] WARD A L, JOSPE M, MORRISON S, et al. Bidirectional associations between sleep quality or quantity, and dietary intakes or eating behaviors in children 6-12 years old: a systematic review with evidence mapping[J]. Nutr Rev, 2021, 79(10): 1079-1099. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuaa125 [24] 何梦藻, 赵烨钧, 金剑, 等. 儿童阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征的糖脂代谢变化分析[J]. 中华全科医学, 2017, 15(2): 264-266, 281. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.2017.02.025HE M Z, ZHAO Y J, JIN J, et al. Analysis of glucose and lipid metabolism changes in children with obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2017, 15(2): 264-266, 281. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.2017.02.025 [25] 周倩兰. 哮喘儿童睡眠障碍的机制及研究进展[J]. 国际儿科学杂志, 2021, 48(10): 682-685.ZHOU Q L. The mechanism and research progress of sleep disorders in children with asthma[J]. International Journal of Pediatrics, 2021, 48(10): 682-685. -





 下载:
下载: