Value of dynamic enhanced imaging radiomics in differentiating benign and malignant parotid gland neoplastic lesions
-
摘要:
目的 腮腺肿瘤类型复杂,动态增强扫描定性分析鉴别腮腺肿瘤的良恶性较为困难,本研究利用腮腺动态增强的定量参数图像进行影像组学分析,判断动态增强成像在鉴别腮腺肿瘤良恶性中的价值。 方法 回顾性分析新疆维吾尔自治区人民医院2019年1月—2022年4月病理证实的51例腮腺占位性病灶磁共振图像,共54个病灶,其中多形性腺瘤12个,Warthin瘤19个,恶性肿瘤8个,其余非肿瘤病变15个。腮腺动态增强图像生成转运常数(Ktrans)、血管外细胞外容积分数(Ve)、血浆容积分数(Vp)、回流常数(Kep)定量位图,通过FAE软件提取影像学特征,建立鉴别腮腺病变良恶性诊断的影像组学模型,并用AUC、敏感性、特异性、准确度等指标对影像组学模型进行评价,判断腮腺良恶性肿瘤样病变鉴别的效能。同时,将多形性腺瘤、腺淋巴瘤和非肿瘤性病变分别与恶性腮腺瘤进行影像组学比较分析。 结果 腮腺动态增强定量图像通过特征提取进行影像组学分析,判断腮腺肿块良恶性的AUC、准确度、敏感性、特异度分别为0.612、0.844、0.500、0.875。多形性腺瘤、腺淋巴瘤和非肿瘤性病变分别与恶性腮腺肿瘤对照进行影像组学分析时,AUC、准确度、敏感性、特异性分别为0.736、0.781、0.909、0.714,0.886、0.880、0.933、0.857,0.805、0.781、0.700、0.818。 结论 利用动态增强功能定量图像进行影像组学分析能够初步判断腮腺肿瘤的良恶性,而在区分不同病理亚型的良性腮腺瘤、非肿瘤性病变与恶性腮腺肿瘤中,影像组学的评估效能更好。 Abstract:Objective The classification of parotid gland tumors is complex, qualitative analysis of dynamic enhancement scan is difficult to distinguish benign and malignant parotid tumors. To determine the clinical value of dynamic enhanced imaging in distinguishing the benign and malignant parotid gland mass through radiomics analysis of quantitative parameter images. Methods Magnetic resonance images of 51 cases of parotid gland mass confirmed by pathology in People's Hospital of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region from January 2019 to April 2022 were retrospectively analyzed, including 12 pleomorphic adenomas, 19 Warthin tumors, 8 malignant tumors, and 15 non-neoplastic lesions. Quantitative parametric maps of transfer constant (Ktrans), extracellular volume fraction (Ve), plasma volume fraction (Vp), and outflow rate constant (Kep) were generated from dynamic enhancement images of parotid gland, and the imaging features were extracted by FAE software to establish a radiomics model for the diagnosis of benign and malignant parotid lesions. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy were used to evaluate the radiomics model and assess the efficacy of distinguishing benign and malignant parotid gland lesions. At the same time, pleomorphic adenoma, Warthin tumors and non-neoplastic lesions were separately compared with malignant parotid adenoma in terms of radiomics. Results Feature extraction and radiomics analysis of dynamic enhanced images were performed to determine the efficacy of benign and malignant parotid gland mass. The AUC, accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity were 0.612, 0.844, 0.500 and 0.875, respectively. When pleomorphic adenoma, Warthin's tumor and non-neoplastic lesions were separately compared with malignant parotid tumors, the AUC, accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity were 0.736, 0.781, 0.909, 0.714, and 0.886, 0.880, 0.933, 0.857, and 0.805, 0.781, 0.700, 0.818. Conclusion Radiomics analysis using dynamic enhanced quantitative images can preliminarily determine the benign and malignant parotid gland tumors. The better performance of radiomics is achieved in distinguishing different pathological subtypes of benign parotid tumors, non-neoplastic lesions and malignant parotid tumors. -
Key words:
- Magnetic resonance imaging /
- Head and neck /
- Parotid adenoma /
- Radiomics /
- Dynamic enhancement
-
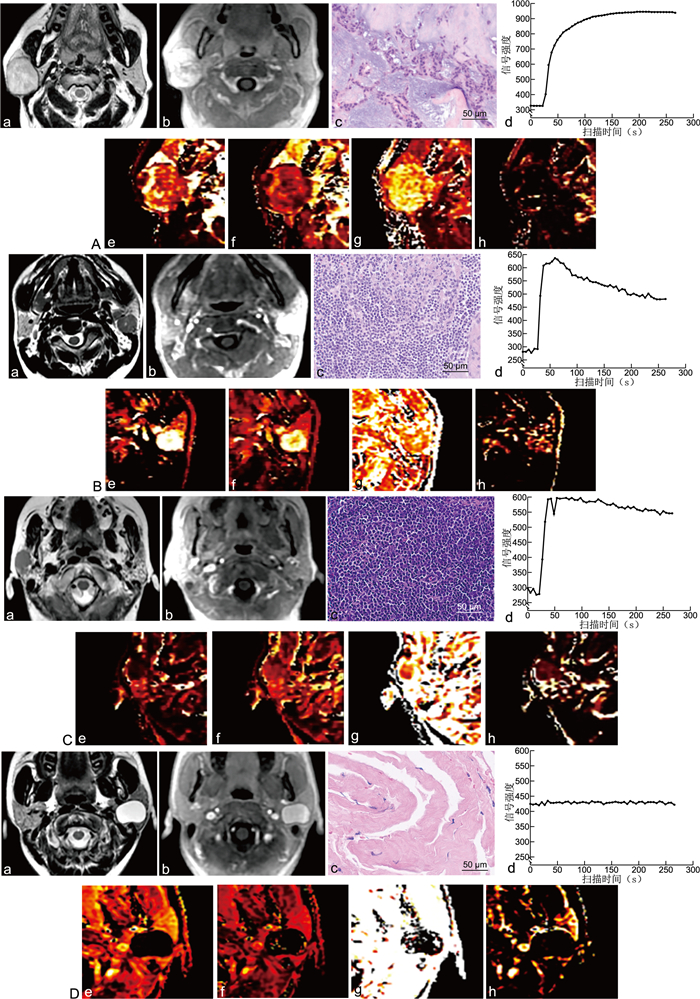
图 1 4种病理类型腮腺占位病灶的影像学表现与病理图像
注:标注a、b、c、d、e、f、g、h分别代表T2加权图像、动态增强图像、病理图像(HE染色,×400)、动态增强时间信号强度曲线和Ktrans、Kep、Ve、Vp。A为多形性腺瘤,其动态增强曲线表现为平台型,Ktrans和Kep值中等,而Ve相对较高。B为Warthin瘤,动态增强表现为快进快出廓清型,Ktrans和Kep值均较高,而Ve相对中等。C为恶性腮腺瘤,同样表现为廓清型动态增强曲线,Ktrans局限性增高,Kep值中等,而Ve相对较高。D为腮腺囊肿,动态增强无强化表现。
Figure 1. Imaging findings and pathological images of four pathological types of parotid gland occupying lesions
表 1 4种病理类型腮腺肿瘤的动态增强定量后处理结果比较(x±s)
Table 1. Comparison of dynamic contrast-enhanced quantitative post-processing results for four pathological types of parotid tumors(x±s)
参数 多形性腺瘤 腺淋巴瘤 其他良性病变 恶性肿瘤 F值 P值 Ktrans 0.668±0.325 0.923±0.677 0.585±0.465 0.767±0.633 1.161 0.334 Kep 0.767±0.378 1.658±1.284 0.985±1.100 0.981±0.645 2.368 0.082 Ve 0.891±0.109 0.601±0.224 0.636±0.211 0.791±0.264 5.818 0.002 Vp 0.127±0.099 0.135±0.080 0.070±0.049 0.101±0.080 1.899 0.142 表 2 定量动态增强数据良恶性肿瘤分组与病理亚型分组结果
Table 2. Results of grouping benign and malignant tumors and pathological subtypes based on quantitative dynamic enhancement data
组别 病理类型 病灶数 层数 训练集 测试集 良恶性肿瘤影像组学对比分析 良性 46 268 180 88 恶性 8 40 32 8 多形性腺瘤与恶性肿瘤对比分析 多形性腺瘤 12 69 48 21 恶性肿瘤 8 40 29 11 腺淋巴瘤与恶性肿瘤对比分析 腺淋巴瘤 19 113 78 35 恶性肿瘤 8 40 25 15 其他良性病变与恶性肿瘤对比 其他良性病变 15 86 64 22 恶性肿瘤 8 40 30 10 表 3 良性与恶性腮腺瘤逻辑回归模型预测结果
Table 3. Predicted results of the logistic regression model for benign and malignant parotid adenomas
类别 AUC ACC SEN SPEC PPV NPV 训练集 0.887 0.807 0.813 0.806 0.426 0.960 测试集 0.612 0.844 0.500 0.875 0.267 0.951 表 4 多形性腺瘤、腺淋巴瘤、其他良性病灶与恶性肿瘤的测试集动态增强定量数据分析结果
Table 4. Analysis results of dynamic contrast-enhanced quantitative data of the test set for pleomorphic adenoma, adenolymphoma, other benign lesions and malignant tumors
项目 多形性腺瘤vs. 恶性肿瘤 腺淋巴瘤vs. 恶性肿瘤 其他良性病灶vs.恶性肿瘤 采用模型 ANOVA_13_GPa RFE_9_LDAb ANOVA_6_GPc 筛选特征(个) 13 9 6 AUC 0.736 0.886 0.805 ACC 0.781 0.880 0.781 SENS 0.909 0.933 0.700 SPEC 0.714 0.857 0.818 PPV 0.625 0.737 0.636 NPV 0.938 0.968 0.857 注:a为ANOVA_13_GP,采用ANOVA筛选的13个特征通过高斯过程回归(gaussian process,GP)分类;b为RFE_9_LDA,采用RFE筛选的9个特征通过线性判别分析(linear discriminant analysis,LDA)分类;c为ANOVA_6_GP,采用ANOVA筛选的6个特征通过高斯过程回归分类。 -
[1] 唐晨虎, 马东, 孙伟, 等. 1.5T MR影像特征与腮腺肿瘤病人良恶性诊断的关系及病理结果对比[J]. 分子影像学杂志, 2021, 44(1): 127-131. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZYX202101025.htmTANG C H, MA D, SUN W, et al. Relationship between 1.5 T MR imaging features and the diagnosis of parotid tumor patients[J]. Journal of Molecular Imaging, 2021, 44(1): 127-131. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZYX202101025.htm [2] ABDEL RAZEK A A K, MUKHERJI S K. State-of-the-art imaging of salivary gland tumors[J]. Neuroimaging Clin N Am, 2018, 28(2): 303-317. doi: 10.1016/j.nic.2018.01.009 [3] COUDERT H, MIRAFZAL S, DISSARD A, et al. Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging of parotid tumors: a systematic review[J]. Diagn Interv Imaging, 2021, 102(3): 121-130. doi: 10.1016/j.diii.2020.08.002 [4] 王海滨, 王理, 张乐星. 动态增强磁共振成像在腮腺肿瘤的诊断优势及研究进展[J]. 肿瘤学杂志, 2018, 24(6): 601-605. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1004-4221.2018.06.014WANG H B, WANG L, ZHANG L X, et al. Research progress on diagnostic advantages of dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in parotid gland tumors[J]. Journal of Chinese Oncology, 2018, 24(6): 601-605. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1004-4221.2018.06.014 [5] XU Z F, ZHENG S Y, PAN A Z, et al. A multiparametric analysis based on DCE-MRI to improve the accuracy of parotid tumor discrimination[J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2019, 46(11): 2228-2234. doi: 10.1007/s00259-019-04447-9 [6] NADA A, HADY D, YOUSSEF A, et al. Accuracy of combined quantitative diffusion-weighted MRI and routine contrast-enhanced MRI in discrimination of benign and malignant salivary gland tumors[J]. Neuroradiol J, 2020, 33(3): 216-223. doi: 10.1177/1971400920913973 [7] 俞顺, 石清磊, 苏家威, 等. DCE-MRI定量参数在不同病理类型腮腺肿瘤鉴别诊断中的初步研究[J]. 磁共振成像, 2017, 8(9): 654-661. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CGZC201709005.htmYU S, SHI Q L, SU J W, et al. An initial study using the quantitative parameters of dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI in differential diagnosis for parotid tumors with different pathological types[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2017, 8(9): 654-661. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CGZC201709005.htm [8] ZHENG Y M, LI J, LIU S, et al. MRI-Based radiomics nomogram for differentiation of benign and malignant lesions of the parotid gland[J]. Eur Radiol, 2021, 31(6): 4042-4052. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07483-4 [9] PILUDU F, MARZI S, RAVANELLI M, et al. MRI-based radiomics to differentiate between benign and malignant parotid tumors with external validation[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 656918. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.656918. [10] 吴艳, 谢元亮, 张树桐, 等. 基于T2WI影像组学及联合诊断模型鉴别腮腺多形性腺瘤与腺淋巴瘤[J]. 放射学实践, 2020, 35(12): 1525-1531. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FSXS202012008.htmWU Y, XIE Y L, ZHANG S T, et al. Radiomic analysis based on MR-T2WI and combined diagnostic model for identification of pleomorphic adenoma from adenolymphoma of parotid gland[J]. Radiologic Practice, 2020, 35(12): 1525-1531. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FSXS202012008.htm [11] GÜNDÜZ E, ALÇIN Ö F, KIZILAY A, et al. Radiomics and deep learning approach to the differential diagnosis of parotid gland tumors[J]. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2022, 30(2): 107-113. doi: 10.1097/MOO.0000000000000782 [12] DEBUS C, FLOCA R, INGRISCH M, et al. MITK-ModelFit: a generic open-source framework for model fits and their exploration in medical imaging-design, implementation and application on the example of DCE-MRI[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2019, 20(1): 31. doi: 10.1186/s12859-018-2588-1 [13] SONG Y, ZHANG J, ZHANG Y D, et al. FeAture Explorer (FAE): a tool for developing and comparing radiomics models[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(8): e0237587. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237587. [14] 江晓勇, 杨志辉, 陈希希, 等. 不同类型腮腺肿瘤的临床特点及远期复发情况分析[J]. 中华全科医学, 2019, 17(5): 790-792, 796. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.000793JIANG X Y, YANG Z H, CHEN X X, et al. Analysis of clinical characteristics and long-term recurrence of different types of parotid tumors[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2019, 17(5): 790-792, 796. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.000793 [15] GÖKÇE E, BEYHAN M. Advanced magnetic resonance imaging findings in salivary gland tumors[J]. World J Radiol, 2022, 14(8): 256-271. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v14.i8.256 [16] 胡涛, 刘琼, 邹玉坚, 等. 扩散峰度成像及动态增强MRI鉴别腮腺多形性腺瘤与Warthin瘤[J]. 放射学实践, 2021, 36(9): 1089-1094. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FSXS202109009.htmHU T, LIU Q, ZOU Y J, et al. Application value of DKI and DCE-MRI in the differential diagnosis of parotid pleomorphic adenoma and Warthin tumor[J]. Radiologic Practice, 2021, 36(9): 1089-1094. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FSXS202109009.htm [17] ZHENG N, LI R, LIU W J, et al. The diagnostic value of combining conventional, diffusion-weighted imaging and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI for salivary gland tumors[J]. Br J Radiol, 2018, 91(1089): 20170707. DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20170707. [18] YABUUCHI H, KAMITANI T, SAGIYAMA K, et al. Characterization of parotid gland tumors: added value of permeability MR imaging to DWI and DCE-MRI[J]. Eur Radiol, 2020, 30(12): 6402-6412. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07004-3 [19] CHANG Y J, HUANG T Y, LIU Y J, et al. Classification of parotid gland tumors by using multimodal MRI and deep learning[J]. NMR Biomed, 2021, 34(1): e4408. DOI: 10.1002/nbm.4408. [20] HUANG N, XIAO Z B, CHEN Y, et al. Quantitative dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI and readout segmentation of long variable echo-trains diffusion-weighted imaging in differentiating parotid gland tumors[J]. Neuroradiology, 2021, 63(10): 1709-1719. doi: 10.1007/s00234-021-02758-z -





 下载:
下载: