Construction of an online and offline blended teaching model for introduction to general practice
-
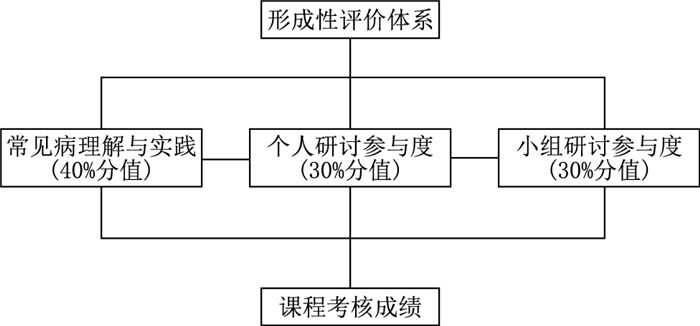
摘要: 《全科医学概论》是农村订单定向免费医学生的一门专业课程,这门课程对于学生深入认识我国基层医疗和分级诊疗体系,强化专业知识等起到非常重要的作用。目前,为进一步顺应现代化医学教育变革,本研究践行“以学为中心”的教学理念,以《全科医学概论》课程为改革对象,结合先进的线上教学技术,通过重新整合课程体系,融入课程思政教育内容,进行线上线下混合式教学模式顶层设计;在教学实践时,线上教学以简洁化、模块化、高效化为主,线下教学以案例式、互动式、探索式为主,两者紧密衔接,互为补充。结果显示,线上线下教学模式的巧妙融合可进一步重塑教师和学生在课堂中所承担的角色,从本质上促进课堂教学内容和教学模式的逐步转型,并且在丰富课程内涵建设的同时,采用适合的形成性评价体系,将层层教学环节和内容设计入评价考核体系中,为更多专业的医学生树立正确的全科医疗知识,激励并引导学生的学习主动性、内驱力和胜任力,教师通过课前准备、课中实施和课后反思,促使自身不断提升教学热情度、拓展教学思路和追求教育革新。此次教学模式的构建值得更多医学专业教师进一步借鉴学习。Abstract: Introduction to General Practice is a professional course for rural-oriented medical students. This course plays a very important role for students to have a deeper understanding of China' s primary care, hierarchical diagnosis and treatment system, and to strengthen their professional knowledge. To further adapt to modern medical education reform and respond rapidly to emergencies such as novel coronavirus pneumonia outbreaks. This research is based on the concept of "putting learning at the center". This study took Introduction to General Practice as the object of reform, combined advanced online teaching technology, reintegrated the curriculum system and incorporated the content of the Civic Education course, and carried out the top-level design of the online and offline blended teaching model. In teaching practice, online teaching is based on simplicity, modularity and efficiency, while offline teaching is based on case-based, interactive and exploratory, and they are closely related and complementary. The results showed that the clever integration of online and offline teaching modes could further reshape the roles of teachers and students in the classroom, and essentially promote the gradual transformation of teaching contents and modes. Moreover, while enriching the internal construction of the curriculum, a suitable formative evaluation system was used to design the layers of teaching links and contents in the evaluation and assessment system, so as to establish the correct knowledge of general medical care for more professional medical students, and to motivate and guide the students' learning initiative, internal drive and competence. Through the preparation before class, implementation during teaching and reflection after class, the teachers motivated themselves to continuously improve their teaching enthusiasm, expand their teaching ideas and pursue educational innovation. The construction of this teaching model is worthy of further learning by more medical faculty.
-
Key words:
- Teaching reform /
- Blended teaching /
- General Practice
-
表 1 《全科医学概论》课程教学体系构建
Table 1. The teaching system construction of Introduction to General Practice course
项目 一年级 二年级 三年级 教学侧重点 理论知识研讨 多学科联系 基层实践服务 医学人文教育 常见病处理 培养创新思维 教学活动形式 小组讨论 团队实践服务 专业竞赛实践活动 心得分享 三级医联体机构见习 理论联系实际 表 2 《全科医学概论》课程教学内容设置
Table 2. The teaching content setting of Introduction to General Practice course
课程模块 课程设置 课程学时 课程内容 绪论 课程学习介绍 1学时 介绍课程的网络共享资源和学习方法 信息化应用 全科医学信息化操作基础 1学时 1.电子化病例档案的建立;2.如何利用信息化智能通信设备完成医联体转诊服务;3.利用智能信息化技术进行基本医疗信息查询,科学研究目标制定等 全科医学基础理论 以人为中心的健康照顾 2学时 强调以人为中心,进行健康照顾的设计讲解,展示课程知识点 以家庭为中心的健康照顾 2学时 强调以家庭为中心,进行健康照顾的设计讲解,展示课程知识点 以社区为范围的健康照顾 2学时 强调以社区为范围,进行健康照顾的设计讲解,展示课程知识点 以预防为导向的健康照顾 2学时 强调以预防为导向,进行健康照顾的设计讲解,展示课程知识点 全科医学疾病诊疗 高血压的全科医学处理 2学时 从高血压疾病的预防、诊断到双向转诊等,进行全科医学处理策略的设计和讲解 冠心病、脑卒中的全科医学处理 2学时 从心脑血管疾病的预防、诊断到双向转诊等,进行全科医学处理策略的设计和讲解 糖尿病的全科医学处理 2学时 从糖尿病的预防、诊断到双向转诊等,进行全科医学处理策略的设计和讲解 慢性阻塞性肺疾病的全科医学处理 2学时 从慢性阻塞性肺疾病的预防、诊断到双向转诊等,进行全科医学处理策略的设计和讲解 常见精神障碍的全科医学处理 2学时 从常见精神疾病的预防、诊断到双向转诊等,进行全科医学处理策略的设计和讲解 恶性肿瘤的全科医学处理 2学时 从恶性肿瘤的预防、诊断到双向转诊等,进行全科医学处理策略的设计和讲解 社区急症的全科医学处理 2学时 从社区急症的疾病预防、抢救和转诊等,进行全科医学处理策略的设计和讲解 重点人群的全科医疗服务 2学时 从重点人群的疾病预防、诊断到双向转诊等,进行全科医学处理策略的设计和讲解 实践服务和学科竞赛 健康管理与健康风险评估 2学时 选择某小区目标人群和某种疾病进行健康风险评估和健康管理,进行社会实践 全科医学的科学研究 2学时 针对社区实践中发现的科学研究问题,查阅相关文献资料进一步整合梳理研究方向,教师指导并鼓励学生以团队形式积极参与学科竞赛,从而促进学科建设与发展 全科医学中的医患沟通与法律问题 2学时 培养人文素质和医学法律能力 表 3 《全科医学概论》混合式教学实践过程
Table 3. The blended teaching practice process of Introduction to General Practice course
步骤 形式 教师 学生 课前准备 线上教学 上传重点教学微课、MOOC视频等 获取学习资源进行学习 参与互动答疑 参与互动讨论 查看学生学习时长 记录学习体会 课中教学 线上教学+线下教学 通过预设答疑互动和课本重难点,进行课程重难点讲解 理解课程重难点 组织学生讨论、点评学生发言 参与小组讨论自由发言 进行线上课堂试题发放 学生在有限时间内答题 总结课堂研讨情况布置课后学习任务 了解课堂研讨情况以及课后学习任务 课外学习 线上教学+实践教学 查看学生课后学习任务完成情况 完成课后学习任务 教师制定实践计划 在教师指导下,学生进入社区进行教学实践 总结学生学习情况 反复复习学习内容 -
[1] 鞠香丽, 裴冬梅. 全科医学师资队伍建设的影响因素与对策探讨[J]. 中国继续医学教育, 2020, 12(20): 91-93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9308.2020.20.037JU X L, PEI D M. Discussion on the Influencing factors and countermeasures of the construction of general practice teaching staff[J]. China Continuing Medical Education, 2020, 12(20): 91-93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9308.2020.20.037 [2] 衡甜甜. 我国全科医学发展现状与问题分析[J]. 中医药管理杂志, 2020, 28(8): 8-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYYG202008006.htmHENG T T. Analysis of the development status and problems of general practice in China[J]. Chinese Medicine Management, 2020, 28(8): 8-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYYG202008006.htm [3] 吕淑云, 张超. 疫情期间高校线上教学质量保障困境与对策研究[J]. 中国轻工教育, 2020, 23(3): 14-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QGJY202003003.htmLYU S Y, ZHANG C. The dilemma and countermeasures of university online teaching quality control during the epidemic period[J]. China Education of Light Industry, 2020, 23(3): 14-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QGJY202003003.htm [4] 罗映红. 高校混合式教学模式构建与实践探索[J]. 高教探索, 2019, 35(12): 48-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJTA201912008.htmLUO Y H. On the construction and practice of mixed teaching mode in colleges and universities[J]. Higher Education Exploration, 2019, 35(12): 48-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJTA201912008.htm [5] 李校堃, 李章平, 刘晓冬, 等. 优化医学教育体系加强医学人才培养[J]. 中国高等教育, 2020, 56(6): 25-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDJ202006010.htmLI X K, LI Z P, LIU X D, et al. Optimize the medical education system and strengthen the training of medical talents[J]. China Higher Education, 2020, 56(6): 25-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDJ202006010.htm [6] 王佳, 路宁, 崔曼莉, 等. 新型冠状病毒肺炎疫情防控给全科医学发展带来的思考[J]. 中国全科医学, 2020, 23(9): 1090-1094. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QKYX202009004.htmWANG J, LU N, CUI M L, et al. Prevention and control of COVID-19 epidemic bring thinking to general practice[J]. Chinese General Practice, 2020, 23(9): 1090-1094. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QKYX202009004.htm [7] 刘彦, 张冬青, 黄静, 等. 基于SPOC的《全科医学概论》课程混合式教学模式研究与实践[J]. 中国全科医学, 2021, 24(1): 84-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QKYX202101015.htmLIU Y, ZHANG D Q, HUANG J, et al. Research and practice on blended teaching design of introduction to general practice course based on small private online course curriculum[J]. Chinese General Practice, 2021, 24(1): 84-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QKYX202101015.htm [8] 于歆杰. 论混合式教学的六大关系[J]. 中国大学教学, 2019, 41(5): 14-18, 28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXCY201905004.htmYU X J. On six relations of blended teaching[J]. China University Teaching, 2019, 41(5): 14-18, 28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXCY201905004.htm [9] 闫宝龙, 梁韶晖. 《医学寄生虫学》线上线下混合式课程建设及应用[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2021, 39(3): 376-379. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJSB202103020.htmYAN B L, LIANG S H. Development and application of online-offline mixed teaching mode for medical parasitology[J]. Chinese Journal of Parasitology and Parasitic Diseases, 2021, 39(3): 376-379. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJSB202103020.htm [10] 刘静, 袁中尚, 李秀君, 等. "以学生为中心"理念指导下的《医学统计学》教学综合改革与探索[J]. 山东大学学报(医学版), 2021, 59(7): 119-124. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYB202107021.htmLIU J, SHANG Z S, LI X J, et al. Comprehensive teaching reform and exploration of Medical Statistics under the guidance of "student-centered" concept[J]. Journal of Shandong University (Health Sciences), 2021, 59(7): 119-124. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYB202107021.htm [11] 吴大龙, 王冰, 冯长卓, 等. "双线"混合式教学模式在中医临床实践教学中的应用[J]. 长春中医药大学学报, 2022, 38(6): 687-689. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CZXX202206024.htmWU D L, WANG B, FENG C Z, et al. Discussion on the application of "double-line" blended teaching mode in TCM clinical practice teaching[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, 2022, 38(6): 687-689. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CZXX202206024.htm [12] 董明, 闻梓钧, 陈佳. 雨课堂教学模式在全科医学理论课教学中的应用研究[J]. 中国继续医学教育, 2021, 13(5): 7-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXUY202105003.htmDONG M, WEN Z J, CHEN J. Research on the application of rain classroom teaching mode in the theory of general medical course[J]. China Continuing Medical Education, 2021, 13(5): 7-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXUY202105003.htm [13] 李淑杰, 徐彦辉. 医学微课在全科医学教育模式发展中的作用[J]. 中医药管理杂志, 2020, 28(8): 17-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYYG202008009.htmLI S J, XU Y H. The role of medical micro-course in the development of general practice education model[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine Management, 2020, 28(8): 17-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYYG202008009.htm [14] 赵睿, 刘峰, 朱坤, 等. 本科教育阶段《全科医学概论》课程建设的需求研究[J]. 中华全科医学, 2021, 19(8): 1382-1385. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002066ZHAO R, LIU F, ZHU K, et al. Research of the demand of curriculum construction of general practice medicine in undergraduate education[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2021, 19(8): 1382-1385. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002066 [15] 王慧. 基于任务导向和能力评价的课程考核方式改革研究[J]. 知识经济, 2019, 21(16): 119-120. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZJJ201916069.htmWANG H. Research on the reform of course assessment methods based on task orientation and ability evaluation[J]. Knowledge Economy, 2019, 21(16): 119-120. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZJJ201916069.htm -





 下载:
下载: