Causal relationship between ulcerative colitis and bronchiectasis based on mendelian randomization
-
摘要:
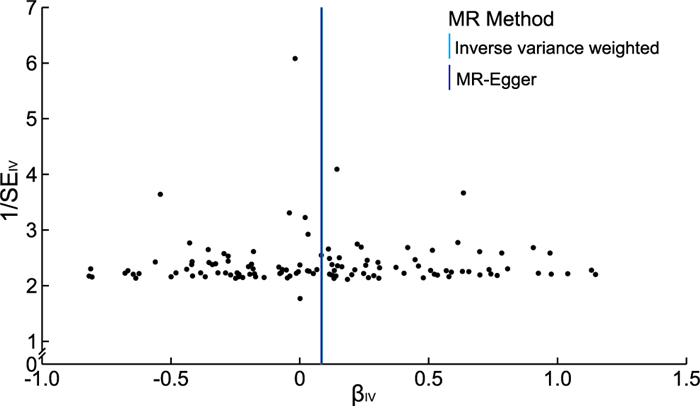
目的 溃疡性结肠炎与支气管扩张之间临床可同时发病,采用两样本孟德尔随机化的方法来探究两者之间是否存在关联,为临床防治提供建议。 方法 在全基因关联研究(GWAS)的汇总数据中提取溃疡性结肠炎密切相关的遗传位点作为工具变量,支气管扩张为结局变量,提取的数据来源于欧洲人种。溃疡性结肠炎数据共包含样本量214 620人,SNPs为16 380 459个,支气管扩张症数据共包含样本量187 824人,SNPs为16 380 375个。分别用IVW、MR-Egger回归和WME进行MR分析,以OR值及95%CI评价溃疡性结肠炎与支气管扩张症之间因果关系,采用Egger-intercept法检验水平多效性,“留一法(leave-one-out)”进行敏感性分析。 结果 共纳入123个SNPs作为工具变量,IVW、MR-Egger、WME结果OR值和95% CI分别为1.089(1.008~1.177)、1.089(0.909~1.305)、1.031(0.918~1.157),IVW的P值小于0.05,表明溃疡性结肠炎与支气管扩张症之间存在因果关系。MR-Egger回归显示截距为3.190×10-5,标准误为0.013,P=0.998,即暴露因素的工具变量不存在水平多效性。异质性检验显示不存在异质性,“leave-one-out”敏感性分析结果稳定。 结论 溃疡性结肠炎对支气管扩张症的发生存在因果关联,会增加支气管扩张症的发病风险。 Abstract:Objective The association between ulcerative colitis and bronchiectasis can be clinically concurrent, and a two-sample mendelian randomization (MR) approach is used to investigate whether there is an association between the two and to provide recommendations for clinical management. Methods Genetic loci closely associated with ulcerative colitis were extracted as instrumental variables and bronchiectasis was the outcome variable in pooled data from the gene-wide association study (GWAS), which was derived from European ethnic groups. The ulcerative colitis data contained a total sample size of 214 620 individuals and 16 380 459 SNPs, and the bronchiectasis data contained a total sample size of 187 824 individuals and 16 380 375 SNPs. MR analysis was performed using the inverse-variance weighted (IVW), MR-Egger regression and the weighted median (WME) respectively, and the causal relationship between ulcerative colitis and bronchiectasis was evaluated by OR and 95% CI, and the Egger-intercept method was used to test for horizontal multiplicity, and the sensitivity analysis was performed using "leave-one-out method". Results A total of 123 SNPs were included as instrumental variables, with OR and 95% CI of 1.089 (1.008-1.177), 1.089 (0.909-1.305), and 1.031 (0.918-1.157) for IVW, MR-Egger, and WME results respectively, and P value of less than 0.05 for IVW, indicating that a causal relationship between ulcerative colitis and bronchiectasis was causally related. MR-Egger regression showed an intercept of 3.190×10-5 with a standard error of 0.013 and P=0.998, there was no horizontal pleiotropy for the instrumental variable of exposure factors. Heterogeneity tests showed no heterogeneity and the results of the "leave-one-out" sensitivity analysis were stable. Conclusion There is a causal association between ulcerative colitis and bronchiectasis, which increases the risk of developing bronchiectasis. -
Key words:
- Ulcerative colitis /
- Bronchiectasis /
- Mendelian randomization
-
表 1 与溃疡性结肠炎关联的SNPs基本信息表
Table 1. Basic information table on SNPs associated with ulcerative colitis
SNPs CHR POS EA OA EAF β SE P值 rs181316459 7 5 473 610 C G 0.047 0.633 0.058 7.43×10-28 rs10807943 7 5 340 664 C T 0.937 -0.367 0.048 2.78×10-14 rs9275160 6 32 652 620 A G 0.297 -0.175 0.025 2.38×10-12 rs10737481 1 20 171 514 G T 0.509 0.157 0.023 2.76×10-12 rs3197999 3 49 721 532 A G 0.393 0.146 0.023 3.14×10-10 rs4676410 2 241 563 739 A G 0.271 0.156 0.026 9.07×10-10 rs12946510 17 37 912 377 T C 0.519 0.127 0.023 1.73×10-8 rs6671847 1 161 478 810 A G 0.454 -0.125 0.023 3.26×10-8 rs10748781 10 101 283 330 A C 0.653 -0.126 0.024 1.18×10-7 rs3024493 1 206 943 968 A C 0.156 0.164 0.031 1.34×10-7 rs10241367 7 4 493 946 C G 0.042 0.293 0.056 1.99×10-7 rs1061537 6 29 937 795 A G 0.394 -0.124 0.024 2.13×10-7 rs139613239 10 67 271 698 G A 0.080 -0.215 0.042 3.67×10-7 rs36051895 9 4 981 866 T G 0.338 0.120 0.024 4.29×10-7 rs2836878 21 40 465 534 A G 0.247 -0.132 0.026 4.79×10-7 注:SNPs为单核苷酸多态性;CHR为染色体;POS为位置;EA为效应等位基因;OA为非效应等位基因;EAF为效应等位基因频率;β为等位基因效应值;SE为β的标准误差。 表 2 溃疡性结肠炎对支气管扩张的MR结果
Table 2. MR results of bronchiectasis in ulcerative colitis
方法 β SE OR(95% CI) P值 IVW 0.086 0.040 1.089(1.008~1.177) 0.031 MR-Egger 0.085 0.009 1.089(0.909~1.305) 0.356 WME 0.030 0.057 1.031(0.918~1.157) 0.596 -
[1] KAENKUMCHORN T, WAHBEH G. Ulcerative colitis: making the diagnosis[J]. Gastroenterol Clin North Am, 2020, 49(4): 655-669. doi: 10.1016/j.gtc.2020.07.001 [2] DU L, HA C. Epidemiology and pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis[J]. Gastroenterol Clin North Am, 2020, 49(4): 643-654. doi: 10.1016/j.gtc.2020.07.005 [3] 许宝才, 陈伟. 雷氏银盏隔姜灸联合补火生土法干预缓解期溃疡性结肠炎的效果评价[J]. 中华全科医学, 2022, 20(5): 844-847, 902. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002469XU B C, CHEN W. Evaluation of the effect of LEI's Yinzhan ginger moxibustion combined with Buhuo Shengtu therapy on ulcerative colitis in the remission stage[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2022, 20(5): 844-847, 902. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002469 [4] 徐峰, 徐琳霞, 刘伟, 等. 盐酸青藤碱介导Hedgehog信号通路治疗小鼠溃疡性结肠炎分子机制的研究[J]. 中华全科医学, 2022, 20(10): 1654-1657, 1723. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002671XU F, XU L X, LIU W, et al. The molecular mechanism of sinomenine hydrochloride treat ulcerative colitis through Hedgehog signalling pathway in mice[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2022, 20(10): 1654-1657, 1723. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002671 [5] SCHAFER J, GRIESE M, CHANDRASEKARAN R, et al. Pathogenesis, imaging and clinical characteristics of CF and non-CF bronchiectasis[J]. BMC Pulm Med, 2018, 18(1): 79. doi: 10.1186/s12890-018-0630-8 [6] GAO L, QIN K R, LI T, et al. The clinical phenotype of bronchiectasis and its clinical guiding implications[J]. Exp Biol Med (Maywood), 2021, 246(3): 275-280. doi: 10.1177/1535370220972324 [7] FENG J, SUN L, SUN X, et al. Increasing prevalence and burden of bronchiectasis in urban Chinese adults, 2013-2017: a nationwide population-based cohort study[J]. Respir Res, 2022, 23(1): 111. doi: 10.1186/s12931-022-02023-8 [8] ALIBERTI S, SOTGIU G, LAPI F, et al. Prevalence and incidence of bronchiectasis in Italy[J]. BMC Pulm Med, 2020, 20(1): 15. doi: 10.1186/s12890-020-1050-0 [9] MASSART A, HUNT D P. Pulmonary manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Am J Med, 2020, 133(1): 39-43. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2019.07.007 [10] PEMMASANI G, LOFTUS E V, TREMAINE W J. Prevalence of pulmonary diseases in association with inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2022, 67(11): 5187-5194. doi: 10.1007/s10620-022-07385-z [11] FREUER D, LINSEISEN J, MEISINGER C. Association between inflammatory bowel disease and both psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: a bidirectional 2-sample mendelian randomization study[J]. JAMA Dermatol, 2022, 158(11): 1262-1268. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.3682 [12] DAVIES N M, HOLMES M V, DAVEY SMITH G. Reading mendelian randomisation studies: a guide, glossary, and checklist for clinicians[J]. BMJ, 2018, 362: k601. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.k601. [13] FREUER D, LINSEISEN J, MEISINGER C. Asthma and the risk of gastrointestinal disorders: a mendelian randomization study[J]. BMC Med, 2022, 20(1): 82. doi: 10.1186/s12916-022-02283-7 [14] WU F, HUANG Y, HU J, et al. Mendelian randomization study of inflammatory bowel disease and bone mineral density[J]. BMC Med, 2020, 18(1): 312. doi: 10.1186/s12916-020-01778-5 [15] CARTER A R, SANDERSON E, HAMMERTON G, et al. Mendelian randomisation for mediation analysis: current methods and challenges for implementation[J]. Eur J Epidemiol, 2021, 36(5): 465-478. doi: 10.1007/s10654-021-00757-1 [16] SHI Y, FENG S, YAN M, et al. Inflammatory bowel disease and celiac disease: a bidirectional mendelian randomization study[J]. Front Genet, 2022, 13: 928944. DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.928944. [17] KEULERS L, DEHGHANI A, KNIPPELS L, et al. Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics to prevent or combat air pollution consequences: the gut-lung axis[J]. Environ Pollut, 2022, 302: 119066. DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119066. [18] TANG Q, LIU R, CHU G, et al. A comprehensive analysis of microflora and metabolites in the development of ulcerative colitis into colorectal cancer based on the lung-gut correlation theory[J]. Molecules, 2022, 27(18): 5838. doi: 10.3390/molecules27185838 [19] KUT C, SABATH B F. A 55-year-old man with cough and hematochezia[J]. Chest, 2020, 157(4): e121-e125. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2019.10.027 [20] CAMUS P, COLBY T V. The spectrum of airway involvement in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Clin Chest Med, 2022, 43(1): 141-155. doi: 10.1016/j.ccm.2021.12.003 -





 下载:
下载: