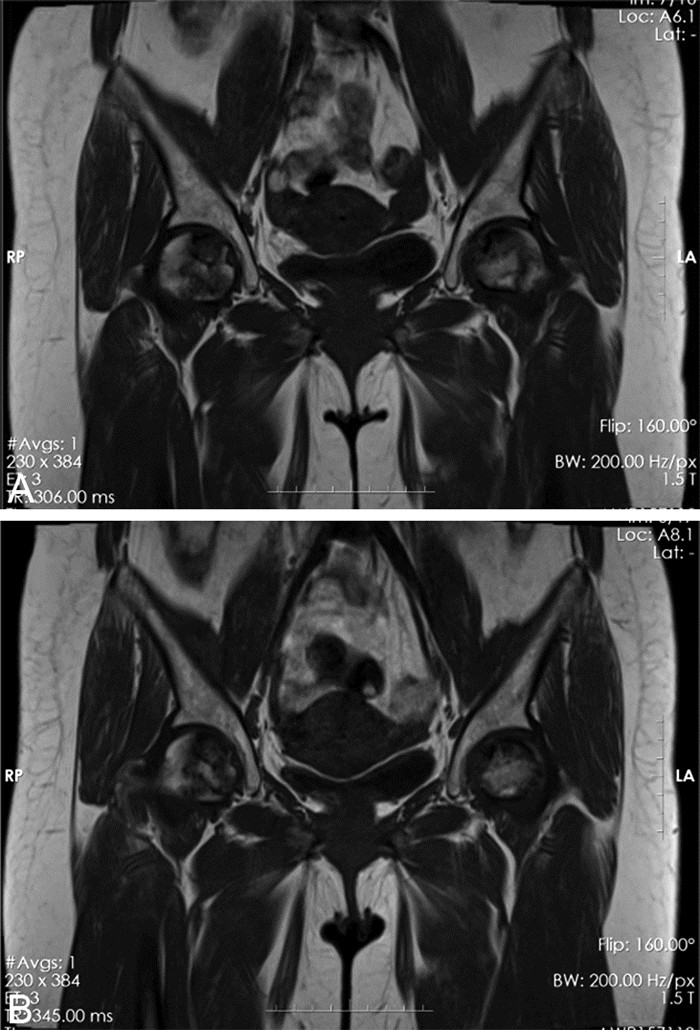
Clinical study of 99Technetium-methylenediphosphonate in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus complicated with osteonecrosis of the femoral head
-
摘要:
目的 探究99锝-亚甲基二膦酸盐(99Tc-MDP)治疗系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)合并股骨头坏死(ONFH)的有效性及安全性。 方法 选取2021年6月—2022年9月蚌埠医学院第一附属医院确诊为SLE合并ONFH(坏死组)及SLE不合并ONFH(对照组)患者共60例。其中坏死组(30例),根据有无使用99Tc-MDP分为常规组(15例)和联合组(15例),对照组为30例;采用ELISA测定联合组与常规组患者治疗1个小疗程前后及对照组血浆骨保护素(OPG)、骨桥蛋白(OPN)浓度并进行比较分析,对联合组及常规组在1个大疗程治疗结束后进行随访,比较患者Harris评分、影像学变化及有无不良反应。 结果 3组治疗前基线资料差异无统计学意义。1个小疗程治疗后:联合组患者治疗后血浆OPG水平较治疗前OPG水平升高、OPN水平较治疗前降低,差异有统计学意义。1个大疗程治疗后:(1)髋关节功能Harris评分联合组较常规组增加,联合组治疗后较治疗前明显增加,差异有统计学意义;常规组治疗后Harris评分较治疗前差异无统计学意义。(2)99Tc-MDP治疗后影像学评价结果较治疗前无明显进展。(3)3组患者均未出现严重不良反应。 结论 99Tc-MDP在常规用药基础上治疗SLE合并ONFH临床效果良好,且具有较高的安全性。 -
关键词:
- 99锝-亚甲基二膦酸盐 /
- 系统性红斑狼疮 /
- 股骨头坏死 /
- 骨保护素 /
- 骨桥蛋白
Abstract:Objective To investigate the efficacy and safety of 99Technetium-methylenediphosphonate (99Tc-MDP) in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) complicated with osteonecrosis of the femoral head (ONFH). Methods A total of 60 patients diagnosed with SLE combined with ONFH (necrosis group) and SLE without ONFH (control group) were selected from June 2021 to September 2022 in the First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College. Among them, the necrosis group (30 cases) was divided into the conventional group (15 cases) and the combined group (15 cases) according to whether 99Tc-MDP was used. The concentrations of plasma osteoprotegerin (OPG) and osteopontin (OPN) were determined by ELISA before and after a short course of treatment between the combined group and the conventional group, and the control group were compared. Follow-up was conducted after a long course of treatment between the combination group and the conventional group, and the Harris score, imaging changes and adverse reactions were compared. Results There was no significant difference in baseline data between the three groups before treatment. After 1 short course of treatment: compared with before treatment, plasma OPG level increased and OPN level decreased in combination group after treatment, the differences were statistically significant. After 1 course of treatment: (1) The Harris score of hip function in the combined group was increased compared with the conventional group, and was significantly increased after treatment in the combined group compared with before treatment, the difference was statistically significant; There was no significant difference in Harris score between the conventional group after treatment and before treatment. (2) There was no significant improvement in imaging evaluation after 99Tc-MDP treatment. (3) No serious adverse reactions were found in the three groups. Conclusion On the basis of routine medication, 99Tc-MDP has good clinical effect and high safety in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus complicated with osteonecrosis of the femoral head. -
表 1 各组系统性红斑狼疮患者基线资料比较
Table 1. Comparison of baseline data of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus in each group
组别 例数 性别(男性/女性,例) 年龄[M(P25, P75),岁] SLE病程[M(P25, P75),年] ONFH病程[M(P25, P75),年] 平均激素用量[M(P25, P75),mg/d] 常规组 15 2/13 37.00(31.00, 49.00) 7.00(4.00, 12.00) 1.00(0.25, 2.00) 10.00(5.00, 15.00) 联合组 15 4/11 32.00(29.00, 47.00) 5.00(3.00, 10.00) 2.00(0.50, 3.00) 10.00(7.50, 10.00) 对照组 30 2/28 37.00(29.00, 50.50) 3.00(0.95, 10.00) 10.00(7.50, 15.00) 统计值 3.462a 1.094b 1.211b -0.861c 4.120b P值 0.177 0.579 0.546 0.389 0.127 组别 例数 胆固醇[M(P25, P75),mmol/L] 甘油三酯[M(P25, P75),mmol/L] 高密度脂蛋白[M(P25, P75),mmol/L] 低密度脂蛋白[M(P25, P75),mmol/L] CRP [M(P25, P75),mg/L] 常规组 15 3.45(2.96, 4.25) 1.16(0.65, 1.90) 1.02(0.93, 1.26) 1.86(1.61, 2.50) 9.10(1.90, 12.90) 联合组 15 4.23(3.33, 4.95) 1.26(0.96, 1.81) 1.04(0.86, 1.20) 2.32(1.74, 3.07) 14.05(2.80, 25.80) 对照组 30 4.14(3.57, 4.92) 1.48(1.13, 1.91) 1.10(0.80, 1.37) 2.62(1.81, 2.98) 6.30(0.98, 24.48) 统计值 2.713b 1.146b 0.056b 2.731b 1.172b P值 0.258 0.564 0.972 0.255 0.556 注:a为χ2值,b为H值,c为Z值。 表 2 联合组和常规组患者治疗前后Harris评分比较(x±s,分)
Table 2. Comparison of Harris scores before and after treatment between combination group and conventional group(x±s, points)
组别 例数 疼痛 功能 畸形、活动度 总分 治疗前 治疗后 治疗前 治疗后 治疗前 治疗后 治疗前 治疗后 联合组 15 26.00±5.07 30.00±5.35a 24.67±6.23 30.67±2.92a 5.47±1.06 6.20±0.78a 56.13±11.10 67.13±7.17a 常规组 15 24.67±5.16 25.33±5.15 22.60±4.88 23.13±4.37 5.13±0.74 5.13±0.83 52.27±9.04 53.60±8.64 t值 1.080 2.779 1.011 4.549 0.997 3.630 1.206 3.758 P值 0.289 0.010 0.321 0.001 0.327 0.001 0.238 0.001 注:与同组治疗前比较,aP < 0.05。 表 3 3组患者治疗前后OPG、OPN水平比较(x±s)
Table 3. Comparison of OPG and OPN levels in 3 groups before and after treatment(x±s)
组别 例数 OPG(ng/mL) OPN(pg/mL) 治疗前 治疗后 治疗前 治疗后 联合组 15 333.31±136.50 405.71±141.26b 19.75±9.70 16.56±10.77b 常规组 15 501.28±197.05 443.13±162.09b 18.32±10.66 21.87±6.34 对照组 30 463.58±219.72 16.229±7.34 统计量 3.151a -0.674c 0.852a -1.645c P值 0.050 0.506 0.432 0.114 注:a为F值,c为t值;与治疗前比较,bP < 0.05。 -
[1] 张莉莉, 张冬梅, 谢长好. 初发系统性红斑狼疮相关血小板减少症的临床特点及治疗随访分析[J]. 中华全科医学, 2021, 19(5): 760-762, 793. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.001910ZHANG L L, ZHANG D M, XIE C H. Clinical characteristics, treatment and follow-up analysis of newly diagnosed systemic lupus erythematosus associated thrombocytopenia[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2021, 19(5): 760-762, 793. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.001910 [2] HISADA R, KATO M, OHNISHI N, et al. Antiphospholipid score is a novel risk factor for idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Rheumatology(Oxford), 2019, 58(4): 645-649. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/key365 [3] KANEKO K, CHEN H, KAUFMAN M, et al. Glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis in systemic lupus erythematosus patients[J]. Clin Transl Med, 2021, 11(10): e526. DOI: 10.1002/ctm2.526. [4] RELLA V, ROTONDO C, ALTOMARE A, et al. Bone involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(10): 5804. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105804 [5] 吴婵媛, 曾小峰. 锝[99Tc]亚甲基二膦酸盐注射液治疗类风湿关节炎专家共识[J]. 中华临床免疫和变态反应杂志, 2019, 13(4): 259-262. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-OZHL201904002.htmWU C Y, ZENG X F. Expert consensus of technetium[99Tc]methylene diphosphonate injection for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Allergy & Clinical Immunology, 2019, 13(4): 259-262. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-OZHL201904002.htm [6] 赵德伟, 胡永成. 成人股骨头坏死诊疗标准专家共识(2012年版)[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2012, 6(3): 479-484. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHGJ201203031.htmZHAO D W, HU Y C. Expert consensus on diagnosis and treatment criteria for adult femoral head necrosis(2012)[J]. Chinese Journal of Joint Surgery (Electronic Edition), 2012, 6(3): 479-484. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHGJ201203031.htm [7] SHAHARIR S S, CHUA S H, MOHD R, et al. Risk factors for symptomatic Avascular Necrosis(AVN) in a multi-ethnic Systemic Lupus Erythematosus(SLE) cohort[J]. PLoS One, 2021, 16(3): e0248845. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248845. [8] 邹瑶, 肖伟, 任翔. 云克治疗类风湿关节炎患者合并骨质疏松的临床疗效观察[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2021, 27(6): 848-850, 861. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2021.06.013ZOU Y, XIAO W, REN X. The clinical observation of 99Tc-MDP in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis patients with osteoporosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Osteoporosis, 2021, 27(6): 848-850, 861. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2021.06.013 [9] 王波, 郭会利. 云克联合股骨头坏死愈胶囊治疗早期非创伤性股骨头坏死的临床效果[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2021, 37(10): 1328-1331. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2021.10.019WANG B, GUO H L. Analysis of clinical effect and safety of Yunke combined with Gugutou Huaisiyu capsule in the treatment of early non-traumatic femoral head necrosis[J]. The Journal of Practical Medicine, 2021, 37(10): 1328-1331. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2021.10.019 [10] 曹盼举, 张晓刚, 曹林忠, 等. 从OPG/RANK/RANKL信号调控机制探讨从瘀论治非创伤性股骨头坏死[J]. 中国中医药信息杂志, 2020, 27(4): 4-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXYY202004002.htmCAO P J, ZHANG X G, CAO L Z, et al. Discussion on Treating Nontraumatic Osteonecrosis of Femoral Head from"Blood Stasis"Based on OPG/RANK/RANKL Signal Regulation Mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Information on Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 27(4): 4-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXYY202004002.htm [11] 李文茜, 郭永昌, 田亮玉, 等. OPG、RANK、RANKL及血液学指标水平变化与股骨头坏死的相关性研究[J]. 现代医药卫生, 2022, 38(10): 1654-1658, 1662. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYWS202210008.htmLI W X, GUO Y C, TIAN L Y, et al. Study on the correlation between the changes of OPG, RANK, RANKL and hematological indexes and osteonecrosis of the femoral head[J]. Journal of Modern Medicine & Health, 2022, 38(10): 1654-1658, 1662. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYWS202210008.htm [12] ZHENG Y, ZHENG Z H, ZHANG K, et al. Osteonecrosis in systemic lupus erythematosus: systematic insight from the epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis and management[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2022, 21(2): 102992. DOI: 10.1016/j.autrev.2021.102992. [13] 曹婷, 韦标方. 骨桥蛋白和趋化素评估非创伤性股骨头坏死的价值[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2021, 29(20): 1853-1857. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJXS202120008.htmCAO T, WEI B F. Clinical value of serum osteopontin and chemerin for evaluating non-traumatic femoral head necrosis[J]. Orthopedic Journal of China, 2021, 29(20): 1853-1857. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJXS202120008.htm [14] MAESTRO-PARAMIO L, GARCIA-REY E, BENSIAMAR F, et al. Osteoblast function in patients with idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head: implications for a possible novel therapy[J]. Bone Joint Res, 2021, 10(9): 619-628. [15] DONG M, YU X X, CHEN W F, et al. Osteopontin promotes bone destruction in periapical periodontitis by activating the NF-kappaB pathway[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2018, 49(3): 884-898. [16] MA M X, TAN Z, LI W Y, et al. Osteoimmunology and osteonecrosis of the femoral head[J]. Bone Joint Res, 2022, 11(1): 26-28. [17] SPINELLI F R, GARUFI C, TRUGLIA S, et al. The role of osteopontin as a candidate biomarker of renal involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Clin Exp Rheumatol, 2019, 37(6): 899-905. -





 下载:
下载: