Analysis of the pathogenic microorganisms and drug treatment of acute pelvic inflammatory disease
-
摘要:
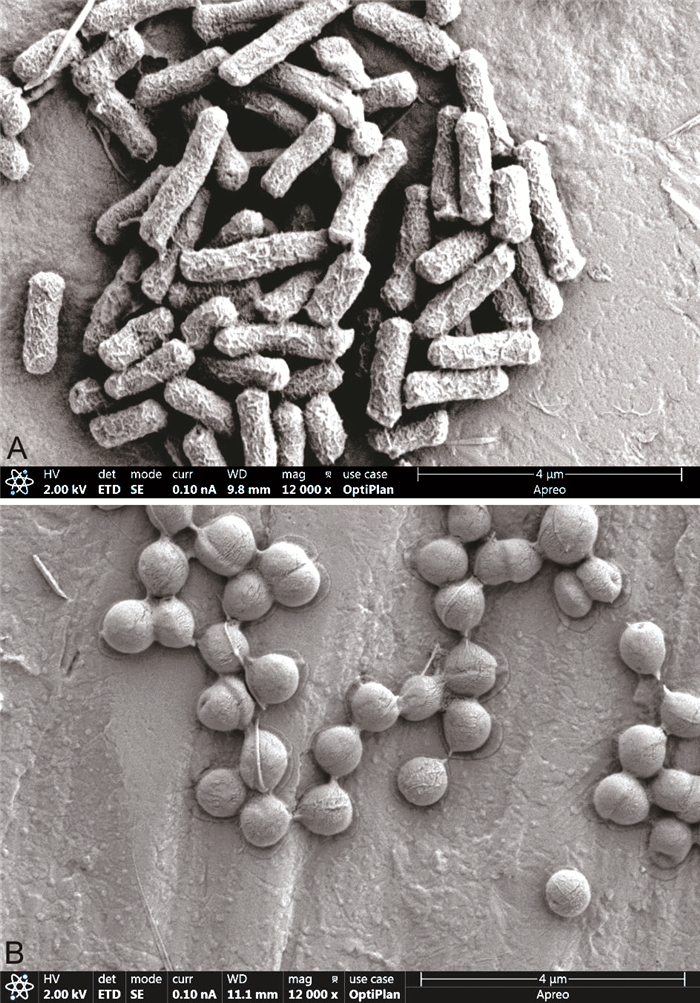
目的 分析急性盆腔炎性疾病患者的致病微生物的特点、种类,抗生素的治疗情况以及致病微生物的耐药情况,希望可以帮助患者找到更合适的治疗方案。 方法 回顾性分析2019年1月—2021年1月于蚌埠医学院第一附属医院妇科就诊的100例患者的资料,基于分析结果,研究致病微生物的耐药情况。 结果 患者的致病因素包括不规则阴道出血、流产等;患者多出现发烧、腹痛、白带增多等症状。致病微生物中大肠杆菌与表皮葡萄球菌最为常见;患者均静脉应用抗生素治疗,患者在使用第三代头孢治疗后,体温以及白细胞恢复正常的时间更短(P < 0.05)。药敏实验表明青霉素类耐药率为56.3%,头孢类耐药率为23.8%;患者在应用致病微生物敏感和耐药的抗生素治疗时血液中白细胞数量比较差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。多次抗生素传代处理致病微生物实验结果表明致病微生物对不同种抗生素产生耐药性的时间有一定的差异,传代培养结束,抗生素抑制90%的致病微生物生长浓度提高至64倍。 结论 急性盆腔炎性疾病致病微生物种类较多,其中占主导地位的是大肠杆菌与表皮葡萄球菌;三代头孢治疗效果优于二代头孢;喹诺酮类和氨基糖甙类抗生素的耐药性更低,可作为临床用药的首选。致病微生物耐药产生的速度较快,具体的抗生素选取应参考细菌培养、药敏实验、临床医生的经验进行综合判断。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the types, characteristics, resistance and treatments of pathogenic microorganisms in patients with acute pelvic inflammatory disease, which will help patients to find an appropriate treatment plan. Methods From January 2019 to January 2021, a retrospective analysis was conducted on the data of 100 patients who visited the gynaecology department of the First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College. Based on the results of the retrospective analysis, the drug resistance of pathogenic microorganisms was investigated. Results Many causes of the disease, including irregular vaginal bleeding, abortion. The main symptoms of the disease are fever, abdominal pain and increased vaginal discharge. Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus epidermidis were the most common pathogenic microorganisms detected in 100 patients. All patients were treated with intravenous antibiotics, and the temperature and white blood cell count returned to normal in a shorter time in patients treated with third-generation cephalosporins (P < 0.05). The drug sensitivity test showed that penicillin had been tested and the drug resistance rate was 56.3%. Cephalosporin had been tested and the drug resistance rate was 23.8%. There was a significant difference (P < 0.05) in the number of white blood cells in the blood when the patients were treated with susceptibility antibiotic compared to the resistant antibiotic. Moreover, the results of serial passage experiment to treat microorganisms showed that there was a clear difference in the time it took bacteria to develop resistance to different antibiotics. At the end of the passages, the concentration that inhibited the growth of 90% of the bacteria had increased 64-fold. Conclusion There are many pathogenic microorganisms in acute pelvic inflammatory disease, the predominant pathogens of acute pelvic inflammatory disease are Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Moreover, third-generation cephalosporins are superior to second-generation cephalosporins in treating patients with antibiotics. In addition, there is less resistance to quinolones and aminoglycosides, which may be the first choice of clinical treatment. Furthermore, Pathogenic microorganism can easily develop resistance, highlighting the importance of the accuracy of empirical medication. Of course, the selection of specific antibiotics should be based on comprehensive identification of bacterial culture, drug sensitivity tests and clinician experiences. -
表 1 致病微生物的种类
Table 1. The species of pathogenic organism
致病微生物 检出数量(株) 检出比例(%) 大肠杆菌 31 27.7 表皮葡萄球菌 29 25.8 粪肠球菌 12 10.7 不动杆菌 9 8.0 棒状杆菌 7 6.3 金黄色葡萄球菌 6 5.4 肺炎克雷白杆菌 5 4.5 中间普雷沃菌 4 3.6 L型菌 3 2.7 其他 6 5.4 表 2 头孢类抗生素使用效果比较(x±s,d)
Table 2. Comparison of the use effect with cephalosporin antibiotics(x±s, d)
组别 例数 体温恢复正常时间 白细胞恢复正常时间 二代头孢类 24 3.5±0.9 4.8±0.8 三代头孢类 11 2.7±0.6 4.1±0.6 t值 2.422 2.377 P值 0.021 0.023 表 3 抗生素的使用情况
Table 3. Instructions on antibiotics use
抗生素 使用人数 占比(%) 头孢类 78 37.7 抗厌氧菌类 63 30.4 喹诺酮类 32 15.5 青霉素类 11 5.3 林可霉素类 9 4.3 氨基糖甙类 7 3.4 四环素类 4 1.9 大环内酯类 3 1.4 表 4 致病菌敏感与耐药抗生素治疗后效果比较(x±s)
Table 4. Comparison of sensitive and resistant pathogens after antibiotic treatment(x±s)
组别 例数 最高体温
(℃)白细胞
(×109/L)中性粒细胞
(%)体温恢复
(d)血象恢复
(d)A组 47 38.6±0.5 13.3±4.9 81.1±7.2 2.1±1.9 3.9±2.2 B组 22 38.7±0.6 16.1±2.1 81.2±3.4 2.0±2.1 4.1±1.2 t值 -0.889 -3.276 -0.064 0.342 -0.374 P值 0.377 0.002 0.950 0.734 0.710 -
[1] 李珂, 李明传, 尹伶, 等. 120例急性盆腔炎症性疾病患者的致病因素及微生物特点的临床分析[J]. 中国性科学, 2018, 27(2): 57-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1993.2018.02.018LI K, LI M C, YIN L, et al. Clinical analysis of pathogenesis and microbial characteristics of 120 patients with acute pelvic inflammatory disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Human Sexuality, 2018, 27(2): 57-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1993.2018.02.018 [2] 彭祥宇, 张丽娟. 慢性盆腔炎患者不同中医证型与细胞免疫学指标、血清炎症指标相关性分析[J]. 河南中医, 2022, 42(6): 887-891. doi: 10.16367/j.issn.1003-5028.2022.06.0191PENG X Y, ZHANG L J. An Analysis of Correlation Between Different TCM Syndrome Types and Cellular Immunologic Indexes and Serum Inflammatory Indexes in Patients with Chronic Pelvic Inflammatory Disease[J]. Henan Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 887-891. doi: 10.16367/j.issn.1003-5028.2022.06.0191 [3] 陈湘宜, 胡欣欣. 当归芍药散加味治疗盆腔炎患者的临床效果[J]. 中华全科医学, 2020, 18(2): 255-257, 261. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.001219CHEN X Y, HU X X. Clinical effect of Danggui Shaoyao powder in the treatment of pelvic inflammation patients[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2020, 18(2): 255-257, 261. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.001219 [4] 赵多爱, 赵晓燕, 周蕾, 等. 金昌市女性盆腔炎病原菌谱及耐药性分析[J]. 国际检验医学杂志, 2020, 41(16): 2024-2027. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4130.2020.16.025ZHAO D A, ZHAO X Y, ZHOU L, et al. Pathogen spectrum and drug resistance analysis of female pelvic inflammatory disease in Jinchang City[J]. International Journal of Laboratory Medicine, 2020, 41(16): 2024-2027. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4130.2020.16.025 [5] 肖飞. 甲硝唑联合左氧氟沙星治疗急性盆腔炎疗效观察[J]. 中国药物与临床, 2020, 20(18): 3109-3110. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YWLC202018063.htmXIAO F. Efficacy of metronidazole combined with levofloxacin in treatment of acute pelvic inflammatory disease[J]. Chinese Remedies & Clinics, 2020, 20(18): 3109-3110. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YWLC202018063.htm [6] 王猛. 康妇消炎栓联合盆腔炎治疗仪对盆腔炎致慢性疼痛患者血液流变学及炎症因子影响研究[J]. 现代医药卫生, 2021, 37(2): 289-290, 330. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5519.2021.02.032WANG M. Effect of Kangfu Xiaoyan Supposal combined with Pelvic inflammation Therapy Instrument on hemorheology and inflammatory factors in patients with chronic pain caused by pelvic inflammation[J]. Journal of Modern Medicine & Health, 2021, 37(2): 289-290, 330. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5519.2021.02.032 [7] SOPER DAVID E, WIESENFELD HAROLD C. The continued challenges in the diagnosis of acute pelvic inflammatory disease: focus on clinically mild disease[J]. J Infect Dis, 2021, 224(12 Suppl 2): S75-S79. [8] 余芳. 临床病例分析盆腔炎性疾病的诊断和治疗方法[J]. 临床医药文献电子杂志, 2019, 6(32): 24-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCWX201932017.htmYU F. Clinical case analysis of the diagnosis and treatment of pelvic inflammatory diseases[J]. Electronic Journal of Clinical Medical Literature, 2019, 6(32): 24-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCWX201932017.htm [9] 阴惠琴. 舒适护理在胃镜检查患者中的应用效果分析[J]. 中国基层医药, 2018, 25(13): 1762-1764. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1008-6706.2018.13.036YIN H Q. Application effect analysis of comfort nursing in gastroscopy patients[J]. : Chinese Journal of Primary Medicine and Pharmacy, 2018, 25(13): 1762-1764. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1008-6706.2018.13.036 [10] WORKOWSKI K A, BACHMANN L H, CHAN P A, et al. Sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines, 2021[J]. MMWR Recomm Rep, 2021, 70(4): 1-187. [11] DE FRANCESCO M A, STEFANELLI P, CARANNANTE A, et al. Management of a case of peritonitis due to neisseria gonorrhoeae infection following pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)[J]. Antibiotics(Basel), 2020, 9(4): 193. [12] 张群先, 梁慧娜. 解脲支原体、沙眼衣原体、淋球菌感染与盆腔炎患者不同发病状态宫颈、盆腔分泌物菌群分布的关系及优势菌敏感性抗菌药物的筛选[J]. 中国性科学, 2022, 31(3): 97-101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XKXZ202203025.htmZHANG Q X, LIANG H N. Relationship between UU, CT, NG infection and distribution of cervical and pelvic secretory flora in patients with pelvic inflammatory disease at different states and antimicrobial susceptibility of dominant bacteria[J]. Chinese Journal of Human Sexuality, 2022, 31(3): 97-101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XKXZ202203025.htm [13] 刘毅, 吴小莉. 淋球菌、衣原体感染与盆腔炎的相关性[J]. 临床与病理杂志, 2019, 39(2): 319-323. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WYSB201902014.htmLIU Y, WU X L. Risk of pelvic inflammatory disease in relation to chlamydia and gonorrhea infection[J]. Journal of Clinical and Pathological Research, 2019, 39(2): 319-323. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WYSB201902014.htm [14] 全国细菌耐药监测网. 全国细菌耐药监测网2014—2019年血标本病原菌耐药性变迁[J]. 中国感染控制杂志, 2021, 20(2): 124-133. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GRKZ202102003.htmNational bacterial resistance monitoring network. Change in antimicrobial resistance of pathogens from blood specimens: surveillance report from China Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System in 2014-2019[J]. Chinese Journal of Infection Control, 2021, 20(2): 124-133. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GRKZ202102003.htm [15] 孙明芬, 王大明, 朱力. 急诊科血培养阳性率与其他科室血培养阳性率对比分析[J]. 当代医学, 2021, 27(12): 164-166. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DDYI202112071.htmSUN M F, WANG D M, ZHU L. Comparative analysis of the positive rate of blood culture in emergency department and other departments[J]. Contemporary Medicine, 2021, 27(12): 164-166. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DDYI202112071.htm [16] YOUNES J A, LIEVENS E, HUMMELEN R, et al. Women and their microbes: the unexpected friendship[J]. Trends Microbiol, 2018, 26(1): 16-32. [17] 张笑, 郭丰. 生殖道微生物与生殖健康[J]. 微生物学通报, 2022, 49(2): 713-723. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSWT202202026.htmZHANG X, GUO F. Reproductive tract microorganisms and reproductive health[J]. Microbiology China, 2022, 49(2): 713-723 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSWT202202026.htm [18] BREIJYEH Z, JUBEH B, KARAMAN R. Resistance of gram-negative bacteria to current antibacterial agents and approaches to resolve it[J]. Molecules, 2020, 25(6): 1340. [19] GUPTA V, DATTA P. Next-generation strategy for treating drug resistant bacteria: antibiotic hybrids[J]. Indian J Med Res, 2019, 149(2): 97-106. [20] 吴晓飞, 吴晨辰. 全科医生如何合理应用抗菌药物[J]. 中华全科医学, 2021, 19(8): 1255-1256. http://www.zhqkyx.net/article/id/7296f45a-0599-4056-b031-76f3b263716eWU X F, WU C C. How to use antibiotics rationally by General Practitioners[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2021, 19(8): 1255-1256. http://www.zhqkyx.net/article/id/7296f45a-0599-4056-b031-76f3b263716e -





 下载:
下载: