Predictive value of eustachian tube function for endoscopic intra tympanic injection in patients with sudden sensorineural deafness
-
摘要:
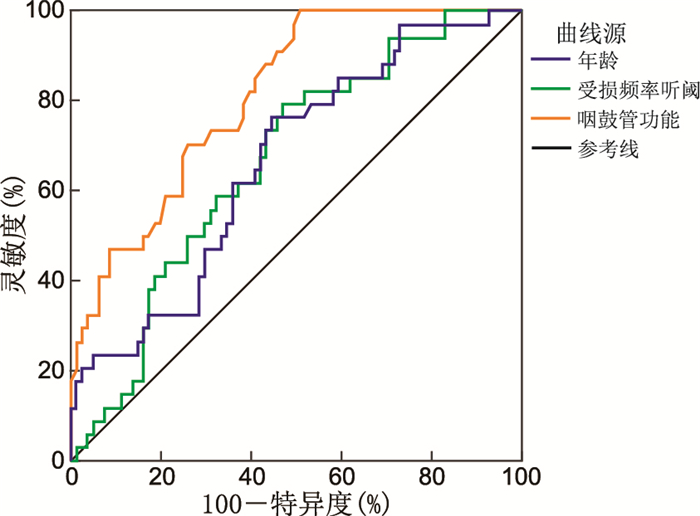
目的 通过检测突发性感音神经性聋患者咽鼓管功能,评估其对内镜下鼓室内注射效果的预测价值。 方法 选取2021年2月—2022年8月于浙江省中西医结合医院接受内镜下鼓室内注射的突发性感音神经性聋患者115例,根据治疗2周后纯音听阈检测结果分为有效组(听力提高≥15 dB)和无效组(听力提高 < 15 dB)。采用多因素logistic回归分析影响突发性感音神经性聋患者内镜下鼓室内注射效果的相关因素,绘制ROC曲线分析咽鼓管功能对内镜下鼓室内注射效果的预测价值。 结果 治疗2周后,81例听力较治疗前提高≥15 dB为有效组,其余34例听力提高 < 15 dB为无效组。无效组年龄、受损频率听阈、咽鼓管功能评分水平较有效组高(P < 0.05);多因素logistic回归分析显示:年龄(OR=1.056,95% CI:1.022~1.155)、受损频率听阈(OR=1.042,95% CI:1.006~1.079)、咽鼓管功能评分(OR=4.412,95% CI:2.247~8.666)为内镜下鼓室内注射效果的影响因素(P < 0.05)。ROC曲线显示,咽鼓管功能评分预测内镜下鼓室内注射效果的AUC为0.812(95% CI:0.728~0.879),显著高于年龄[0.665(95% CI:0.571~0.750)]、受损频率听阈[0.667(95% CI:0.573~0.752),P < 0.05]。 结论 咽鼓管功能对突发性感音神经性聋患者内镜下鼓室内注射效果预测价值相对较高。 Abstract:Objective To evaluate the predictive value of the eustachian tube for the effect of endoscopic intra tympanic injection through detecting the function of the eustachian tube in patients with sudden sensorineural deafness. Methods A total of 115 patients with sudden senineural deafness who received endoscopic tympanic injection in Zhejiang Hospital of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine from February 2021 to August 2022 were selected. According to the pure tone hearing threshold detection results two weeks after treatment, they were divided into effective group (hearing improvement ≥15 dB) and ineffective group (hearing improvement < 15 dB). Multivariate logistic regression was used to analyze the related factors affecting the effect of endoscopic tympanic injection in patients with sudden senineural deafness, and ROC curve was drawn to analyze the predictive value of eustachian tube function on the effect of endoscopic tympanic injection. Results After 2 weeks of treatment, 81 cases of hearing improvement ≥15 dB compared with before treatment were effective group, and the remaining 34 cases of hearing improvement < 15 dB were ineffective group. The age, impaired frequency threshold and eustachian tube function score of ineffective group were higher than those of effective group (P < 0.05). Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that: Age (OR=1.056, 95% CI: 1.022-1.155), impaired frequency threshold (OR=1.042, 95% CI: 1.006-1.079), eustachian tube function score (OR=4.412, 95% CI: 2.247-8.666) were the risk factors for endoscopic tympanic injection effect (P < 0.05). ROC curve showed that the prediction AUC of endoscopic tympanic injection effect was 0.812 (95% CI: 0.728-0.879), which was significantly higher than that of age (0.665, 95% CI: 0.571-0.750) and impaired frequency hearing threshold (0.667, 95% CI: 0.573-0.752), P < 0.05. Conclusion The function of eustachian tube is relatively valuable in predicting the effect of endoscopic tympanic injection in patients with sudden senineural deafness. -
表 1 内镜下鼓室内注射效果单因素分析
Table 1. Single factor analysis of endoscopic intra tympanic injection effect
项目 无效组(n=34) 有效组(n=81) 统计量 P值 年龄(x±s,岁) 53.07±9.72 46.36±9.66 3.384a 0.001 性别(男性/女性,例) 20/14 53/28 0.451b 0.502 体重指数(x±s) 23.56±1.54 23.61±1.49 0.160a 0.873 吸烟史[例(%)] 23(67.65) 52(64.20) 0.126b 0.723 高血压[例(%)] 0.538b 0.463 有 12(35.29) 23(28.40) 无 22(64.71) 58(71.60) 眩晕[例(%)] 0.714b 0.398 有 11(32.35) 20(24.69) 无 23(67.65) 61(75.31) 耳鸣[例(%)] 0.241b 0.624 有 9(26.47) 18(22.22) 无 25(73.53) 63(77.78) 发病侧别[例(%)] 0.016b 0.899 左侧 21(61.76) 49(60.49) 右侧 13(38.24) 32(39.51) 听力类型[例(%)] 0.061b 0.805 低频/平坦型 21(61.76) 52(64.20) 高频/全聋型 13(38.24) 29(35.80) 受损频率听阈(x±s,dB) 63.58±12.73 54.65±16.39 3.141a 0.002 咽鼓管功能评分(x±s,分) 5.48±1.10 4.15±1.00 6.075a <0.001 注:a为t值,b为χ2值。 表 2 内镜下鼓室内注射效果多因素logistic分析
Table 2. Logistic analysis of the effect of intratympanic injection under endoscope
变量 B SE Wald χ2 P值 OR值 95% CI 年龄 0.083 0.031 7.046 0.008 1.086 1.022~1.155 受损频率听阈 0.041 0.018 5.147 0.023 1.042 1.006~1.079 咽鼓管功能评分 1.484 0.344 18.580 <0.001 4.412 2.247~8.666 表 3 内镜下鼓室内注射效果的预测效能
Table 3. Predictive efficacy of endoscopic intra tympanic injection
变量 SE AUC 95% CI 特异度(%) 敏感度(%) 截断值 年龄 0.054 0.665 0.571~0.750 55.65 76.47 46.84 受损频率听阈 0.053 0.667 0.573~0.752 50.62 79.41 53.03 咽鼓管功能评分 0.040 0.812 0.728~0.879 66.67 85.29 4.24 -
[1] PRINCE A D P, STUCKEN E Z. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a diagnostic and therapeutic emergency[J]. J Am Board Fam Med, 2021, 34(1): 216-223. doi: 10.3122/jabfm.2021.01.200199 [2] MARX M, YOUNES E, CHANDRASEKHAR S S, et al. International consensus (ICON) on treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss[J]. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis, 2018, 135(1S): S23-S28. [3] CHEW S C, MD DAUD M K. The efficacy of intratympanic steroid injection for the treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss[J]. Med J Malaysia, 2020, 75(1): 74-77. [4] 王海茹, 王海涛, 郝玲. 耳后与全身应用糖皮质激素治疗突发性耳聋系统评价与meta分析[J]. 中华耳科学杂志, 2018, 16(5): 669-675. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2922.2018.05.015WANG H R, WANG H T, HAO L. Postauricular Injection and Systemic Glucocorticoid Treatment for Sudden Hearing Loss: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Otology, 2018, 16(5): 669-675. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2922.2018.05.015 [5] JOSHI K S, HO V W Q, SMITH M E, et al. The effect of topical xylometazoline on eustachian tube function[J]. J Laryngol Otol, 2020, 134(1): 29-33. doi: 10.1017/S0022215120000158 [6] 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志编辑委员会, 中华医学会耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学分会. 突发性聋诊断和治疗指南(2015)[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2015, 50(6): 443-447. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2015.06.002Chinese Journal of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery Editorial Board, Chinese Medical Association Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery Branch. Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of sudden deafness(2015)[J]. Chinese Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, 2015, 50(6): 443-447. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2015.06.002 [7] 陈彬, 俞晨杰, 沈晓辉, 等. 七项咽鼓管功能障碍症状评分量表的应用分析[J]. 中华耳科学杂志, 2016, 14(5): 582-585. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2922.2016.05.005CHEN B, YU C J, SHEN X H, et al. Application of seven-item symptom scoring scale for Eustachian tube dysfunction[J]. Chinese Journal of Otology, 2016, 14(5): 582-585. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2922.2016.05.005 [8] YOUNG Y H. Contemporary review of the causes and differential diagnosis of sudden sensorineural hearing loss[J]. Int J Audiol, 2020, 59(4): 243-253. doi: 10.1080/14992027.2019.1689432 [9] SUN H C, HU J D, MAO Z Y, et al. Efficacy of combination therapy in adolescent and adult patients with total-deafness sudden sensorineural hearing loss[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2019, 139(3): 258-262. doi: 10.1080/00016489.2018.1554266 [10] 李坤军, 周汝环, 徐明安, 等. 鼻内镜下经咽鼓管鼓室内注药治疗分泌性中耳炎的应用研究[J]. 中国中西医结合耳鼻咽喉科杂志, 2019, 27(3): 171-173, 170. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYJH201903004.htmLI K J, ZHOU R H, XU M A, et al. Application research on the treatment of secretory otitis media by transtympanic injection of drugs through eustachian tube under nasal endoscope[J]. Chinese Journal of Otorhinolaryngology in Integrative Medicine, 2019, 27(3): 171-173, 170. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYJH201903004.htm [11] 韩跃峰, 许彬彬, 刘学宝. 江淮地区128例感音神经性聋患者常见耳聋基因检测结果分析[J]. 中华全科医学, 2019, 17(6): 906-908, 1013. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.000822YUE Y F, XU B B, LIU X B. Analysis of genetic test results of common deafness in 128 cases of sensorineural deafness in Jianghuai region[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2019, 17(6): 906-908, 1013. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.000822 [12] SI J P, JIANG H, LI Y Y. Correlation between effectual time and the curative effect in patients with all frequency descending sudden deafness after treatment[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2020, 41(5): 102621. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2020.102621. [13] HUNG W C, LIN K Y, CHENG P W, et al. Sudden deafness: a comparison between age groups[J]. Int J Audiol, 2021, 60(11): 911-916. doi: 10.1080/14992027.2021.1900611 [14] ZHANG B Y, YOUNG Y H. Geriatric sudden deafness[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2021, 42(4): 102985. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2021.102985. [15] SHIMANUKI M N, SHINDEN S, OISHI N, et al. Early hearing improvement predicts the prognosis of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2021, 278(11): 4251-4258. doi: 10.1007/s00405-020-06532-4 [16] UHM T, LEE J E, YI S, et al. Predicting hearing recovery following treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss with machine learning models[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2021, 42(2): 102858. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2020.102858. [17] TEIXEIRA M S. Understanding Eustachian tube function[J]. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol, 2020, 86(5): 523-524. doi: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2020.02.001 [18] CHO I, LEE H M, CHOI S W, et al. Comparison of two different treatment protocols using systemic and intratympanic steroids with and without hyperbaric oxygen therapy in patients with severe to profound idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a Randomized controlled trial[J]. Audiol Neurootol, 2018, 23(4): 199-207. doi: 10.1159/000493558 -





 下载:
下载: