Diagnostic value of CT combined with serum tumor marker in oral squamous cell carcinoma
-
摘要:
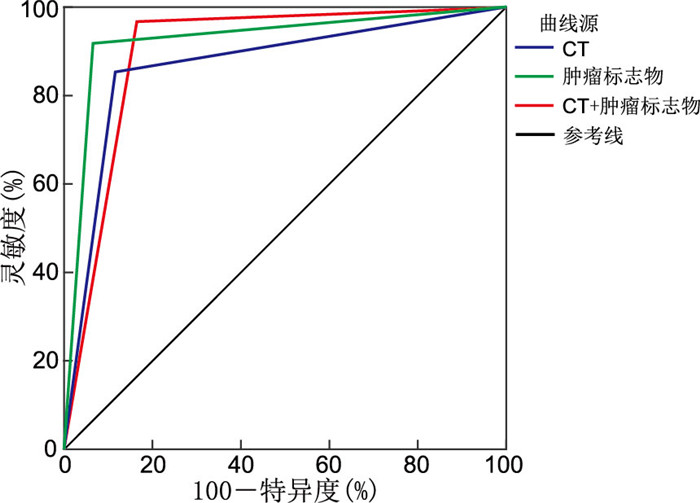
目的 通过观察口腔鳞状细胞癌(简称鳞癌)患者的CT影像学特征及对口腔鳞癌患者血清肿瘤标志物检测,探讨口腔鳞癌的诊断新思路,分析CT联合肿瘤标志物对口腔鳞癌的诊断效能及临床意义。 方法 选取2020年9月—2022年3月于蚌埠医学院第一附属医院行口腔鳞癌根治手术,且术后病理证实为鳞癌的60例患者为实验组,另外选取口腔颌面部良性肿瘤患者60例为对照组。结合患者的术前CT影像,比较2组患者的血清肿瘤标志物水平差异,以术后病理诊断为金标准,采用Kappa检验比较两者与病理结果的一致性,采用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线分析CT和肿瘤标志物单独及联合应用对口腔鳞癌的诊断价值。 结果 实验组血清中肿瘤标志物鳞状细胞癌相关抗原(SCC-Ag)、癌胚抗原(CEA)的水平明显高于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(均P<0.05)。CT联合血清肿瘤标志物检测对口腔鳞癌的诊断与病理结果具有高度一致性(Kappa=0.800,P<0.001),其诊断效能高于CT单独使用。CT联合血清肿瘤标志物对口腔鳞癌具有较高的诊断价值(AUC=0.900), 单独血清肿瘤标志物检测对口腔鳞癌具有较高的诊断价值(AUC=0.925),单独CT检查对口腔鳞癌具有中等诊断价值(AUC=0.867),肿瘤标志物检测诊断效能最高,二者联合应用诊断效能高于CT单独诊断。 结论 相比于传统的术前CT影像检查,血清肿瘤标志物检测具有更高的诊断准确率,考虑患者术前影像的重要性,必要时可采取CT联合血清肿瘤标志物检测,二者联合应用能提高口腔鳞癌的筛查,且2种方法均对患者伤害较小,可广泛应用。 Abstract:Objective To explore the new diagnostic ideas of oral squamous cell carcinoma, and analyze the diagnostic efficacy and clinical significance of CT combined with tumor markers by observing the CT imaging features of patients and detecting the serum tumor markers of patients. Methods A total of 60 patients who underwent radical operation for oral squamous cell carcinoma in the First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College from September 2020 to March 2022 and pathologically confirmed as squamous cell carcinoma were selected as the experimental group. In addition, 60 patients with oral and maxillofacial benign tumors were selected as the control group. Combined with preoperative CT images of patients, the differences in serum tumor markers between the two groups were compared. Postoperative pathological diagnosis was taken as the gold standard. Kappa test was used to compare the consistency between the two groups and pathological findings. Results Serum levels of tumor markers of squamous cell carcinoma associated antigen (SCC-Ag) and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) in experimental group were significantly higher than those in control group (all P < 0.05). CT combined with serum tumor marker detection showed high consistency with pathological results (Kappa=0.800, P < 0.001), and its diagnostic efficacy was higher than that of CT alone. CT combined with serum tumor markers had a high diagnostic value (AUC=0.900), serum tumor markers alone had a high diagnostic value (AUC=0.925), and CT alone had a medium diagnostic value (AUC=0.867). Tumor marker testing has the highest diagnostic efficacy, and the combination of the two has higher diagnostic efficacy than CT alone. Conclusion Compared with traditional preoperative CT imaging, serum tumor marker detection has a higher diagnostic accuracy. Considering the importance of patients ' preoperative imaging, CT combined with serum tumor marker detection can be used when necessary. The combined application of the two methods can improve the screening of oral squamous cell carcinoma, and both methods have less harm to patients, so they can be widely used. -
Key words:
- CT /
- Oral squamous cell carcinoma /
- Tumor markers /
- Diagnostic efficacy /
- Diagnostic value
-
表 1 实验组与对照组肿瘤标志物水平比较[M(P25, P75),ng/mL]
Table 1. Comparison of tumor biomarker levels between the experimental group and the control group[M(P25, P75), ng/mL]
组别 例数 CEA SCC-Ag 对照组 60 2.83(1.60, 4.07) 0.00(0.00, 0.00) 实验组 60 3.91(1.66, 6.65) 5.51(2.36, 11.10) Z值 -2.265 -9.506 P值 0.024 < 0.001 表 2 CT和肿瘤标志物单独应用及联合应用与病理结果比较及Kappa检验(例)
Table 2. Comparison of CT scan and tumor marker application alone and in combination with pathological results, and Kappa test (cases)
诊断方法 结果 病理结果 Kappa值 P值 阴性 阳性 CT 阴性 53 9 0.733 < 0.001 阳性 7 51 肿瘤标志物 阴性 56 5 0.850 < 0.001 阳性 4 55 CT联合肿瘤标志物 阴性 50 2 0.800 < 0.001 阳性 10 58 表 3 CT和肿瘤标志物单独应用及联合应用对口腔鳞癌的诊断效能(%)
Table 3. Diagnostic performance of CT, tumor markers, and their combination in the diagnosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma (%)
诊断方法 灵敏度 特异度 准确性 CT 85.0(51/60) 88.3(53/60) 86.7(104/120) 肿瘤标志物 91.7(55/60) 93.3(56/60) 92.5(111/120) CT联合肿瘤标志物 96.7(58/60) 83.3(50/60) 90.0(108/120) -
[1] TANG J F, FANG X D, CHEN J, et al. Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) in oral squamous cell carcinoma: biological function and clinical application[J]. Cancers, 2021, 13(23): 5944. doi: 10.3390/cancers13235944 [2] ECKERT A W, KAPPLER M, GROE I, et al. Current understanding of the HIF-1-dependent metabolism in oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(17): 6083. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176083 [3] KESHAVARZI M, DARIJANI M, MOMENI F, et al. Molecular imaging and oral cancer diagnosis and therapy[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2017, 118(10): 3055-3060. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26042 [4] 袁川淑, 杨凯, 唐洪, 等. 血清肿瘤标志物Cyfra 21-1、SCCAg、Ferritin、CEA、CA19-9和AFP对口腔/口咽鳞癌的诊断价值[J]. 重庆医科大学学报, 2017, 42(9): 1066-1071. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYK201709003.htmYUAN C S, YANG K, TANG H, et al. Diagnostic values of serum tumor markers Cyfra 21-1, SCCAg, Ferritin, CEA, CA19-9 and AFP for oral/oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas[J]. Journal of Chongqing Medical University, 2017, 42(9): 1066-1071. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYK201709003.htm [5] 邹剑, 许蕾, 王超. 血清TPS、CEA及CA125对口腔癌的诊断价值分析[J]. 中国煤炭工业医学杂志, 2022, 25(5): 539-543. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZMGY202205020.htmZOU J, XU L, WANG C. ANALYSIS OF DIAGNOSTIC VALUE OF SERUM TPS, CEA AND CA125 in oral cancer[J]. Chinese Journal of Coal Industry Medicine, 2022, 25(5): 539-543. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZMGY202205020.htm [6] 习兴龙, 杨洋, 尹亮, 等. 18F-FDG PET/CT对口腔癌颈部淋巴结转移诊断价值的Meta分析[J]. 海南医学院学报, 2019, 25(12): 951-956. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNYY201912018.htmXI X L, YANG Y, YIN L, et al. The diagnostic value of 18F-FDG PET/CT in cervical lymph node metastasis of oral cancer: meta-analysis[J]. Journal of Hainan Medical University, 2019, 25(12): 951-955. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNYY201912018.htm [7] 魏卓, 郭骏, 黄怡, 等. 股前外侧皮瓣修复口腔恶性肿瘤切除术后缺损的临床疗效分析[J]. 口腔疾病防治, 2021, 29(5): 328-333. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDYB202105007.htmWEI Z, GUO J, HUANG Y, et al. Clinical effect of anterolateral thigh flap repair on postoperative defects in oral malignant tumors[J]. Journal of Prevention and Treatment for Stomatological Diseases, 2021, 29(5): 328-333. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDYB202105007.htm [8] WONG H M. Oral complications and management strategies for patients undergoing cancer therapy[J]. Sci World J, 2014: 581795. DOI: 10.1155/2014/581795. [9] 刘骁蕾, 侯栋梁, 冯芝恩, 等. 口腔鳞癌患者外周血CD57+细胞表达水平变化和预后的相关性[J]. 标记免疫分析与临床, 2022, 29(5): 795-800, 828. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJMY202205016.htmLIU X L, HOU D L, FENG Z E, et al. Expression patterns and clinical significance of peripheral blood CD57-Positive cells in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Labeled Immunoassays and Clinical Medicine, 2022, 29(5): 795-800. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJMY202205016.htm [10] 周彩然, 刘焕磊, 孙莹莹, 等. 口腔鳞癌患者血清骨膜素、巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子和畸胎瘤衍生生长因子-1表达水平及其临床预后的关系[J]. 现代口腔医学杂志, 2022, 36(2): 83-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDKY202202003.htmZHOU C R, LIU H L, SUN Y Y, et al. The relationship between the expression levels of serum periostin, macrophage migration inhibitory factor, Cripto-1 and clinical prognosis in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Journal of Modern Stomatology, 2022, 36(2): 83-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDKY202202003.htm [11] 项洋, 陈辉, 李雪莲, 等. 手术治疗口腔颌面部肿瘤患者的临床疗效评价[J]. 当代医学, 2020, 26(22): 60-62. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DDYI202022024.htmXIANG Y, CHEN H, LI X L, et al. Clinical evaluation of surgical treatment of oral and maxillofacial tumors[J]. Contemporary Medicine, 2020, 26(22): 60-62. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DDYI202022024.htm [12] SHAMIM T. Bibliometric analysis of oral and maxillofacial cytology-related articles published in a cytology journal from India[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol, 2018, 22(1): 121-127. doi: 10.4103/jomfp.JOMFP_178_16 [13] 袁焕初, 郑晓林, 邹玉坚, 等. 肺磨玻璃样病变高分辨率CT的质地分析及其对早期肺癌的诊断价值[J]. 临床放射学杂志, 2018, 37(2): 252-256. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCFS201802020.htmYUAN H C, ZHENG X L, ZOU Y J, et al. The textural analyzing of lung ground-glass opacity at high resolution CT and the diagnosing values for early stage lung cancer[J]. Journal of Clinical Radiology, 2018, 37(2): 252-256. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCFS201802020.htm [14] 李迎春. CT检查对良恶性骨肿瘤和肿瘤样病变的鉴别诊断价值[J]. 中国医疗器械信息, 2020, 26(20): 107-109. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGQX202020058.htmLI Y C. The value of CT in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant bone tumors and tumor-like lesions[J]. Chinese Medical Device Information, 2020, 26(20): 107-109. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGQX202020058.htm [15] 边勤疆, 多力昆·吾甫尔. 5种肿瘤标志物联合检测在口腔鳞状细胞癌中的诊断价值[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2020, 28(19): 3330-3333. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXZL202019012.htmBIAN Q J, DUOLIKUN·WUFUER. Diagnostic value of combined detection of five tumor markers in oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Journal of Modern Oncology, 2020, 28(19): 3330-3333. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXZL202019012.htm [16] 徐飞, 段峰, 李美景, 等. 口腔鳞癌患者血清及唾液中AFP、CEA的表达及临床意义[J]. 齐齐哈尔医学院学报, 2016, 37(16): 2015-2017. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QQHB201616004.htmXU F, DUAN F, LI M J, et al. Expression and clinical significance of AFP and CEA in serum and saliva of patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Journal of Qiqihar University of Medicine, 2016, 37(16): 2015-2017. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QQHB201616004.htm [17] 周艳刚, 刘朝敏, 王少龙. 不同肿瘤标志物检测在口腔癌等恶性肿瘤不同阶段的诊断价值[J]. 北华大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 17(2): 217-221. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZLYY201602016.htmZHOU Y G, LIU Z M, WANG S L. Diagnostic values of detections on individual tumor markers in oral cancer at different stages[J]. Journal of Beihua University(Natural Science), 2016, 17(2): 217-221. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZLYY201602016.htm [18] 王政书. 食管癌患者血清SCC-Ag的检测及临床意义[J]. 国际检验医学杂志, 2015, 36(24): 3643-3644. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWSQ201524068.htmWANG Z S. Detection and clinical significance of serum SCCAg in patients with esophageal cancer[J]. International Journal of Laboratory Medicine, 2015, 36(24): 3643-3644. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWSQ201524068.htm -





 下载:
下载: