Correlation between gut microbiota metabolites and coronary heart disease combined with chronic heart failure and its predictive role in patient prognosis
-
摘要:
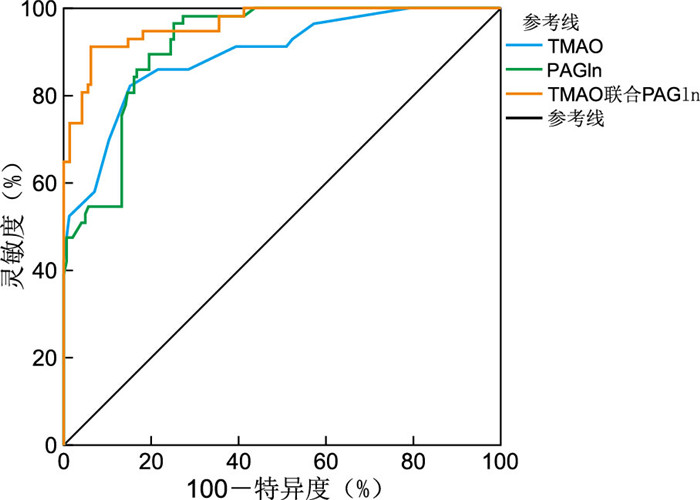
目的 探讨肠道菌群代谢物氧化三甲胺(TMAO)和苯乙酰谷氨酰胺(PAGln)与稳定性冠心病(SCAD)合并慢性心力衰竭(CHF)患者心功能指标的相关性,分析其联合预测SCAD合并CHF患者主要不良心血管事件(MACE)的临床价值。 方法 选取2018年4月—2021年4月温州市中西医结合医院心血管内科门诊收治的200例SCAD合并CHF和200例单纯SCAD患者为研究对象,分析SCAD合并CHF患者TMAO和PAGln含量与心功能指标的相关性,评估TMAO联合PAGln预测MACE的诊断效能。 结果 SCAD合并CHF患者左室收缩末内径(LVESD)、左室舒张末内径(LVEDD)、基质金属蛋白酶-9(MMP-9)、脑钠肽(BNP)、TMAO和PAGln均高于单纯SCAD患者,而左室射血分数(LVEF)和脂联素(APN)均低于单纯SCAD患者(均P < 0.05)。SCAD合并CHF患者TMAO和PAGln与LVESD、LVEDD、MMP-9和BNP均呈正相关关系(均P < 0.05),而与LVEF和APN均呈负相关关系(均P < 0.05)。出现MACE的SCAD合并CHF患者血清TMAO和PAGln均高于非MACE患者(均P < 0.05)。TMAO联合PAGln预测SCAD合并CHF患者MACE的ROC曲线下面积、灵敏度和特异度分别为0.964、91.20%和93.70%,均高于两者单独预测。 结论 SCAD合并CHF患者肠道菌群代谢物TMAO和PAGln含量均呈现升高趋势,两者联合预测SCAD合并CHF患者MACE具有较高的临床价值。 Abstract:Objective To explore of the correlation between intestinal microbiota metabolites trimethylamine oxide (TMAO) and phenylacetylglutamine (PAGln) and cardiac function indicators in patients with stable coronary heart disease (SCAD) and chronic heart failure (CHF), and analyze the clinical value of their combined use in predicting major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in patients with SCAD and CHF. Methods A total of 200 patients with SCAD combined with CHF and 200 patients with SCAD alone admitted to the Cardiovascular Department of Wenzhou Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Hospital from April 2018 to April 2021 were selected as the study subjects. The correlation between the contents of TMAO and PAGln and cardiac function indexes in SCAD patients with CHF were analyzed. The diagnostic efficacy of TMAO combined with PAGln in predicting MACE were analyzed. Results The left ventricular end systolic diameter (LVESD), left ventricular end diastolic diameter (LVEDD), matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), brain natriuretic peptide (BNP), TMAO, and PAGln values in patients with SCAD combined with CHF were significantly higher than those in simple SCAD patient, while left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and adiponectin (APN) values were significantly lower than those in patients with simple SCAD (all P < 0.05). TMAO and PAGln in patients with SCAD combined with CHF were positively correlated with LVESD, LVEDD, MMP-9, and BNP detection values (all P < 0.05), while they were negatively correlated with LVEF and APN detection values (all P < 0.05). Serum TMAO and PAGln levels in SCAD patients with MACE combined with CHF were significantly higher than those in non-MACE patients (all P < 0.05). TMAO combined with PAGln predicted the area, sensitivity and specificity under the receiver operating characteristic of MACE in patients with SCAD and CHF (0.964, 91.20% and 93.70%), which were higher than those predicted by both alone. Conclusion The levels of intestinal microbiota metabolites TMAO and PAGln in SCAD combined with CHF patients show an increasing trend, and the combination of the two has high clinical value in predicting MACE in SCAD combined with CHF patients. -
表 1 SCAD合并CHF与单纯SCAD患者心功能指标及肠道菌群代谢物含量比较(x±s)
Table 1. Comparison of cardiac functional parameters and gut microbial metabolite levels between patients with SCAD and concurrent CHF, and patients with isolated SCAD (x±s)
组别 例数 LVEF (%) LVESD (mm) LVEDD (mm) APN (μg/mL) MMP-9 (μg/mL) BNP (μg/mL) TMAO (μmol/L) PAGln (ng/mL) SCAD合并CHF组 200 41.82±3.62 42.96±4.01 55.73±4.73 9.27±1.13 174.16±16.21 526.39±42.85 7.19±0.70 176.52±16.23 单纯SCAD组 200 45.53±3.74 38.75±3.82 51.29±4.46 10.84±1.26 156.82±14.63 451.64±40.73 5.83±0.64 148.74±14.56 t值 10.080 10.750 9.659 13.119 11.231 17.881 20.278 18.018 P值 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 表 2 SCAD合并CHF患者TMAO和PAGln与心功能指标相关性分析
Table 2. Correlation analysis of TMAO and PAGln with cardiac functional parameters in patients with SCAD and concurrent CHF
心功能超声指标 TMAO PAGln r值 P值 r值 P值 LVEF -0.852 <0.001 -0.864 <0.001 LVESD 0.743 0.024 0.751 0.021 LVEDD 0.762 0.011 0.773 0.009 APN -0.771 0.008 -0.782 0.005 MMP-9 0.816 <0.001 0.824 <0.001 BNP 0.831 <0.001 0.856 <0.001 表 3 不同预后SCAD合并CHF患者TMAO和PAGln含量比较(x±s)
Table 3. Comparison of TMAO and PAGln levels in SCAD patients with concurrent CHF of different prognosis (x±s)
组别 例数 TMAO(μmol/L) PAGln(ng/mL) MACE组 57 7.89±0.63 182.84±8.92 非MACE组 143 6.91±0.50 167.72±7.33 t值 11.573 12.354 P值 <0.001 <0.001 表 4 TMAO和PAGln预测SCAD合并CHF患者MACE的诊断效能
Table 4. The diagnostic performance of TMAO and PAGln in predicting MACE in patients with SCAD and CHF
检测指标 ROC曲线下面积 灵敏度(%) 特异度(%) 95% CI TMAO 0.894 82.50 84.60 0.843~0.944 PAGln 0.916 89.50 80.40 0.879~0.953 TMAO联合PAGln 0.964 91.20 93.70 0.938~0.989 -
[1] HAO G, WANG X, CHEN Z, et al. Prevalence of heart failure and left ventricular dysfunction in China: the China Hypertension Survey, 2012-2015[J]. Eur J Heart Fail, 2019, 21(11): 1329-1337. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1629 [2] YAN J L, PAN Y B, HE Y Q, et al. The effects of serum iron level without anemia on long-term prognosis of patients with coronary heart disease complicated with chronic heart failure: a retrospective cohort study[J]. Heart Vessels, 2020, 35(10): 1419-1428. doi: 10.1007/s00380-020-01613-0 [3] 刘继轩, 兰翔, 赵晓静, 等. 心力衰竭分期和肠道菌群组成相关性研究[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志, 2022, 14(9): 1056-1060. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-PZXX202209007.htmLIU J X, LAN X, ZHAO X J, et al. Correlation between heart failure stage and gut microbiota composition[J]. Chinese Journal of Evidence-Bases Cardiovascular Medicine, 2022, 14(9): 1056-1060. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-PZXX202209007.htm [4] NEMET I, SAHA P P, GUPTA N, et al. A Cardiovascular disease-linked gut microbial metabolite acts via adrenergic receptors[J]. Cell, 2020, 180(5): 862-877. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.016 [5] 沈迎, 张瑞岩, 沈卫峰. 稳定性冠心病血运重建策略进展: 2018中国稳定性冠心病诊断与治疗指南解读[J]. 心脑血管病防治, 2019, 19(2): 107-111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXFZ201902001.htmSHEN Y, ZHANG R Y, SHEN W F. Progress in strategies for stable coronary heart disease revascularization: interpretation of the 2018 China guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of stable coronary heart disease[J]. Prevention and Treatment of Cardio-Cerebral-Vascular Disease, 2019, 19(2): 107-111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXFZ201902001.htm [6] 张建军. 接轨国际指南、彰显中国特色: 《中国心力衰竭诊断和治疗指南2018》解读[J]. 中国临床医生杂志, 2019, 47(4): 398-402. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-8552.2019.04.006ZHANG J J. Integrating with international guidelines and highlighting Chinese characteristics: interpretation of Chinese guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of heart failure 2018[J]. Chinese Journal for Clinicians, 2019, 47(4): 398-402. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-8552.2019.04.006 [7] MAYERHOFER C, KUMMEN M, HOLM K, et al. Low fibre intake is associated with gut microbiota alterations in chronic heart failure[J]. ESC Heart Fail, 2020, 7(2): 456-466. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.12596 [8] 邹云法, 余文华, 徐丽君, 等. NO、ET-1、Hcy联合检测在冠心病中的诊断价值[J]. 中华全科医学, 2019, 17(7): 1178-1180. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.000895ZOU Y F, YU W H, XU L J, et al. The diagnostic value of combined detection of NO, ET-1 and Hcy in coronary heart disease[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2019, 17(7): 1178-1180. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.000895 [9] 张芳, 陈国藩, 王明伟, 等. 冠心病合并高血压患者血浆同型半胱氨酸水平与血压变异性的相关性[J]. 中华全科医学, 2022, 20(7): 1106-1108, 1138. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002534ZHANG F, CHEN G P, WANG M W, et al. Correlation between plasma homocysteine and blood pressure variability in patients with coronary heart disease complicated with hypertension[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2022, 20(7): 1106-1108, 1138. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002534 [10] 王亚丽, 程艳丽, 商丽华. 肠道菌群在冠心病发病机制中的研究进展[J]. 中国研究型医院, 2023, 10(1): 59-62. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJXU202301013.htmWANG Y L, CHENG Y L, GAO L H. Research advance in gut microbiota in the pathogenesis of coronary artery disease[J]. Journal of Chinese Research Hospitals, 2023, 10(1): 59-62. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJXU202301013.htm [11] 杨芾, 王淙玉, 王琳, 等. 心力衰竭与肠道菌群失调的研究进展[J]. 临床内科杂志, 2020, 37(2): 142-144. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCLZ202002026.htmYANG F, WANG C Y, WANG L, et al. Research progress on heart failure and intestinal microbiota imbalance[J]. Journal of Clinical Internal Medicine, 2020, 37(2): 142-144. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCLZ202002026.htm [12] 何卫斌, 段新杰, 王耀辉. 肠道菌群代谢产物氧化三甲胺联合左室射血分数在慢性心力衰竭患者预后中的价值[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志, 2021, 13(4): 443-446. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-PZXX202104016.htmHE W B, DUAN X J, WANG Y H. Prognostic value of trimethylamine oxide combined with left ventricular ejection fraction in patients with chronic heart failure[J]. Chinese Journal of Evidence-Bases Cardiovascular Medicine, 2021, 13(4): 443-446. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-PZXX202104016.htm [13] 郭攀, 冯津萍, 冯超, 等. 肠道菌群及其代谢产物氧化三甲胺与心力衰竭关系的研究进展[J]. 天津医药, 2019, 47(4): 440-444. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJYZ201904027.htmGUO P, FENG J P, FENG C, et al. Research advances on trimethylamine N-oxide of metabolite of gut flora and heart failure[J]. Tianjin Medical Journal, 2019, 47(4): 440-444. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJYZ201904027.htm [14] 李亚梦, 魏秋阳, 刘明宇, 等. 肠道菌群及其代谢产物氧化三甲胺与冠心病的关系及相关技术方法的研究进展[J]. 中国微生态学杂志, 2022, 34(10): 1222-1227. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWS202210021.htmLI Y M, WEI Q Y, LIU M Y, et al. The relationship between gut microbiota and its metabolites trimethylamine-N-oxide and coronary artery disease and the progress of research on related technical methods[J]. Chinese Journal of Microecology, 2022, 34(10): 1222-1227. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWS202210021.htm [15] OTTOSSON F, BRUNKWALL L, SMITH E, et al. The gut microbiota-related metabolite phenylacetylglutamine associates with increased risk of incident coronary artery disease[J]. J Hypertens, 2020, 38(12): 2427-2434. [16] 任良强, 侯晓晓, 乔平, 等. 灯盏生脉胶囊结合沙库巴曲缬沙坦钠片对冠心病合并慢性心衰患者血清APN、MMP-9和BNP水平的影响[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2022, 40(1): 180-183. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYHS202201043.htmREN L Q, HOU X X, QIAO P, et al. Effects of Dengzhan Shengmai Capsule combined with salkubatroxartan sodium tablet on serum levels of APN, MMP-9 and BNP in patients with coronary heart disease complicated with chronic heart failure[J]. Chinese Archives of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 40(1): 180-183. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYHS202201043.htm -





 下载:
下载: