Analysis of factors influencing liver injury caused by long-term use of second-generation antipsychotics in patients with schizophrenia
-
摘要:
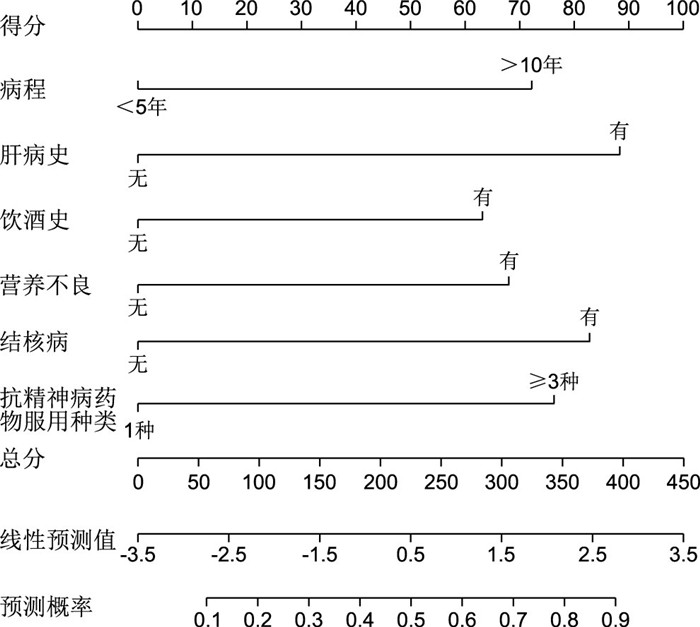
目的 通过回顾性研究,探讨精神分裂症患者长期服用帕利哌酮、齐拉西酮等第二代抗精神病药物相关肝功能受损的危险因素。 方法 选择2021年4月—2023年4月杭州市第七人民医院收治的长期服用第二代抗精神病药物的120例精神分裂症患者进行回顾性研究,根据是否发生肝损伤将其分为2组,36例发生肝损伤的患者为观察组,84例未发生肝损伤的患者为对照组,采用单因素、多因素logistic回归分析研究肝损伤的危险因素。结合logistic回归分析结果,通过R软件构建预测精神分裂症患者长期服用第二代抗精神病药物导致肝损伤的列线图预测模型,绘制受试者工作曲线(ROC),计算曲线下面积(AUC),分析该模型的预测区分度。 结果 Logistic回归分析显示,病程>10年、肝病史、饮酒史、营养不良、结核病、抗精神病药物服用种类≥3种是精神分裂症患者长期服用第二代抗精神病药物导致肝损伤的危险因素(均P<0.05)。Hosmer-Lemeshow拟合优度检验,χ2=3.049,P=0.405;C-index=0.910;AUC为0.910(95% CI:0.804~0.946)。 结论 精神分裂症患者长期服用第二代抗精神病药物引发肝损伤的影响因素是病程,危险因素包括肝病史、饮酒史、营养不良、结核病、抗精神病药物服用种类≥3种,构建预测模型的预测效能较高。 Abstract:Objective A retrospective study was conducted to investigate the risk factors for liver dysfunction associated with long-term use of paliperidone, ziprasidone and other second-generation antipsychotics in patients with schizophrenia. Methods A retrospective study was conducted on 120 patients with schizophrenia who were on long-term second-generation antipsychotics in Hangzhou Seventh People's Hospital from April 2021 to April 2023. They were divided into 2 groups according to whether they had liver injury or not. Thirty-six patients with liver injury were set as the observation group, and 84 patients without liver injury were set as the control group. The risk factors of liver injury were investigated by univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis. Combined with the results of logistic regression analysis results, R software was used to build a nomogram prediction model for predicting liver injury caused by long-term use of second-generation antipsychotics in schizophrenia patients, and the receiver operating curve (ROC) was plotted, the area under the curve (AUC) was calculated, and the predictive ability of this model was analyzed. Results Logistic regression analysis showed that disease duration >10 years, history of liver disease, history of alcohol consumption, malnutrition, tuberculosis and type of antipsychotic drugs ≥3 were risk factors for long-term use of second-generation antipsychotics in schizophrenia patients (P < 0.05). Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness of fit test, χ2=3.049, P=0.405; C-index=0.910; AUC was 0.910 (95% CI: 0.804-0.946). Conclusion Influencing factors for liver injury induced by long-term use of second-generation antipsychotics in schizophrenia patients were disease duration, and risk factors included liver disease history, alcohol consumption, malnutrition, tuberculosis and type of antipsychotics ≥3 types. The prediction model had a high predictive power. -
Key words:
- Schizophrenia /
- Antipsychotic drugs /
- Liver injury /
- Influencing factor
-
表 1 精神分裂症患者长期服用第二代抗精神病药物引发肝损伤的单因素分析[例(%)]
Table 1. Univariate analysis of liver injury induced by long-term use of second-generation antipsychotics in patients with schizophrenia[case(%)]
项目 类别 观察组(n=36) 对照组(n=84) 统计量 P值 项目 类别 观察组(n=36) 对照组(n=84) 统计量 P值 性别 男性 17(47.22) 40(47.62) 0.002a 0.968 吸烟史 有 25(69.44) 61(72.62) 0.125a 0.724 女性 19(52.78) 44(52.38) 无 11(30.56) 23(27.38) 年龄 < 45岁 18(50.00) 48(57.14) 0.520a 0.471 肝病史 有 16(44.44) 9(10.71) 17.384a < 0.001 ≥45岁 18(50.00) 36(42.86) 无 20(55.56) 75(89.29) 病程 < 5年 2(5.56) 22(26.19) 3.422b 0.001 饮酒史 有 26(72.22) 39(46.43) 6.753a 0.009 5~10年 13(36.11) 38(45.24) 无 10(27.78) 45(53.57) >10年 21(58.33) 24(28.57) 营养不良 有 28(77.78) 41(48.81) 8.653a 0.003 BMI < 18.5 16(44.44) 40(47.62) 0.976b 0.329 无 8(22.22) 43(51.19) 18.5~24.0 11(30.56) 35(41.67) 贫血 有 17(47.22) 34(40.48) 0.469a 0.493 >24.0 9(25.00) 9(10.71) 无 19(52.78) 50(59.52) 诊断分型 单纯型 15(41.67) 36(42.86) 0.015a 0.904 心功能不全 有 12(33.33) 32(38.10) 0.246a 0.620 偏执型 21(58.33) 48(57.14) 无 24(66.67) 52(61.90) 家族遗传史 有 29(80.56) 70(83.33) 0.135a 0.714 结核病 有 13(36.11) 6(7.14) 15.868a < 0.001 无 7(19.44) 14(16.67) 无 23(63.89) 78(92.86) 糖尿病 有 8(22.22) 24(28.57) 0.520a 0.471 抗精神病药物服用种类 1种 4(11.11) 25(29.76) 3.598b 0.001 无 28(77.78) 60(71.43) 2种 15(41.67) 46(54.76) 高血压 有 7(19.44) 20(23.81) 0.275a 0.600 ≥3种 17(47.22) 13(15.48) 无 29(80.56) 64(76.19) 注:a为χ2值,b为Z值。 表 2 长期服用第二代抗精神病药物引发肝损伤的危险因素变量赋值情况
Table 2. Assignment of risk factor variables for liver injury induced by long-term use of second-generation antipsychotic medications
变量 赋值方法 病程 < 5年=0,5~10年=1,>10年=2 肝病史 无=0,有=1 饮酒史 无=0,有=1 营养不良 无=0,有=1 结核病 无=0,有=1 抗精神病药物服用种类 1种=0,2种=1,≥3种=2 表 3 精神分裂症患者长期服用第二代抗精神病药物引发肝损伤的多因素分析
Table 3. Multivariable analysis of liver injury induced by long-term use of second-generation antipsychotic medications in patients with schizophrenia
因素 B SE Wald χ2 P值 OR值 95%CI 病程>10年 0.216 0.075 8.158 < 0.001 1.224 1.101~1.418 肝病史 0.286 0.077 13.794 < 0.001 1.329 1.146~1.511 饮酒史 0.180 0.061 7.019 < 0.001 1.164 0.986~1.207 营养不良 0.198 0.061 9.518 < 0.001 1.206 1.038~1.328 结核病 0.234 0.059 15.758 < 0.001 1.286 1.135~1.482 抗精神病药物服用种类≥3种 0.231 0.072 10.284 < 0.001 1.256 1.113~1.462 -
[1] 黄锦, 朱丞. 帕利哌酮缓释片联合阿立哌唑对精神分裂症精神病性症状、认知功能和催乳素的影响[J]. 中华全科医学, 2022, 20(10): 1688-1690, 1791. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002680HUANG J, ZHU C. Effects of paliperidone sustained-release tablets combined with aripiprazole on psychotic symptoms, cognitive function and prolactin in schizophrenia[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2022, 20(10): 1688-1690, 1791. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002680 [2] 刘世昌, 张黎明, 高晓玲, 等. 非典型抗精神病药物引起精神分裂症患者糖脂代谢异常及其机制的研究进展[J]. 现代药物与临床, 2022, 37(12): 2911-2916. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWZW202212044.htmLIU S C, ZHANG L M, GAO X L, et al. Research progress of abnormal glucose and lipid metabolism induced by atypical antipsychotic drugs in patients with schizophrenia and its mechanism[J]. Modern Medicine and Clinic, 2022, 37(12): 2911-2916. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWZW202212044.htm [3] 杨松, 张丽丽, 张云淑, 等. MTHFR基因多态性与非典型抗精神病药物治疗精神分裂症患者疗效的关系研究[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志, 2023, 39(5): 625-629. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLYZ202305004.htmYANG S, ZHANG L L, ZHANG Y S, et al. Study on the relationship between MTHFR gene polymorphism and the efficacy of atypical antipsychotic drugs in the treatment of schizophrenia[J]. Chinese clinical pharmacology magazine, 2023, 39(5): 625-629. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLYZ202305004.htm [4] 李聪颖, 杨占江, 杜广清. 还原型谷胱甘肽联合多烯磷脂酰胆碱对急性药物性肝损害患者CRP IL-6 PCT及肝功能的影响[J]. 河北医学, 2021, 27(7): 1076-1081. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HCYX202107004.htmLI C Y, YANG Z J, DU G Q. Effects of reduced glutathione combined with polyene phosphatidylcholine on CRP IL-6 PCT and liver function in patients with acute drug-induced liver injury[J]. Hebei Medicine, 2019, 27(7): 1076-1081. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HCYX202107004.htm [5] CSNP精神病性障碍研究联盟全体成员. 中国精神病临床高危综合征早期识别和干预: CSNP精神病性障碍研究联盟专家共识(2020版)[J]. 中国神经精神疾病杂志, 2020, 46(4): 193-199. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0152.2020.04.001Members of the CSNP Psychiatric Disorders Research Consortium. Early identification and Intervention of clinical high-risk syndrome of Psychosis in China: Expert consensus of CSNP Psychiatric Disorders Research Consortium (2020 edition)[J]. Chinese Journal of Neuropsychiatric Diseases, 2020, 46(4): 193-199. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0152.2020.04.001 [6] 中华医学会, 中华医学会杂志社, 中华医学会消化病学分会, 等. 药物性肝损伤基层诊疗指南(2019年)[J]. 中华全科医师杂志, 2020, 19(10): 868-875.Chinese Medical Association, Journal of Chinese Medical Association, Branch of Gastroenterology of Chinese Medical Association, et al. Guideline for primary care of drug-induced liver injury(2019)[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practitioners, 2020, 19(10): 868-875. [7] YASUI-FURUKORI N, MURAOKA H, HASEGAWA N, et al. Association between the examination rate of treatment-resistant schizophrenia and the clozapine prescription rate in a nationwide dissemination and implementation study[J]. Neuropsychopharmacol Rep, 2022, 42(1): 3-9. doi: 10.1002/npr2.12218 [8] 张敏, 李星星, 何霞, 等. 抗结核治疗中药物肝损伤相关因素的Logistic回归分析[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志, 2021, 37(18): 2387-2389, 2393. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLYZ202118001.htmZHANG M, LI X X, HE X, et al. Logistic regression analysis of related factors of secondary drug-induced liver injury during anti-tuberculosis treatment[J]. The Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 2021, 37(18): 2387-2389, 2393. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLYZ202118001.htm [9] 易文英, 吴海波, 佘生林, 等. 住院未成年精神疾病患者抗精神病药物使用情况调查[J]. 国际精神病学杂志, 2021, 48(4): 615-619. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWYJ202104012.htmYI W Y, WU H B, SHE S L, et al. The use of antipsychotics in child and adolescent inpatients with mental disorders[J]. Journal Of International Psychiatry, 2021, 48(4): 615-619. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWYJ202104012.htm [10] 赵滨. 长期服用抗精神病药物患者肝胆B超检查结果分析[J]. 中国药物与临床, 2020, 20(5): 726-727. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YWLC202005018.htmZHAO B. Analysis of liver and bile B-ultrasound in patients taking antipsychotic drugs for a long time[J]. Chinese Remedies & Clinics, 2020, 20(5): 726-727. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YWLC202005018.htm [11] 巢楠, 陈颖, 王莹, 等. 198例抗精神失常药物致肝损害回顾性分析[J]. 解放军药学学报, 2023, 36(1): 57-59.CHAO N, CHEN Y, WANG Y, et al. Retrospective Analysis of 198 Cases of Liver Injury Caused by Antipsychotic Drugs[J]. Pharmaceutical Journal of Chinese People's Liberation Army, 2023, 36(1): 57-59. [12] 牛春燕, 张强, 赵向阳. 饮酒对非酒精性脂肪性肝病的影响[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2020, 36(11): 2593-2596. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCGD202011058.htmNIU C Y, ZHANG Q, ZHAO X Y. Influence of drinking on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Journal of Clinical Hepatology, 2020, 36(11): 2593-2596. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCGD202011058.htm [13] 谢佛添, 王冬梅, 吕翼. 自噬在酒精性肝病中的作用[J]. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2020, 36(10): 1151-1158. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWHZ202010004.htmXIE F T, WANG D M, LYU Y. Role of autophagy in alcoholic liver disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2020, 36(10): 1151-1158. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWHZ202010004.htm [14] 黄瑶, 黄文湧, 杨敬源, 等. 贵州省少数民族地区男性人群吸烟、饮酒及乙肝感染对肝功能异常影响的现况研究[J]. 现代预防医学, 2020, 47(9): 1673-1677, 1698. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDYF202009034.htmHUANG Y, HUANG W Y, YANG J Y, et al. Smoking, drinking and hepatitis B infection in male population in minority areas of Guizhou Province: a cross-sectional study[J]. Modern Preventive Medicine, 2020, 47(9): 1673-1677, 1698. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDYF202009034.htm [15] 陈显荣, 肖兵容, 成浩. B超与血清D-二聚体、白蛋白和总胆红素水平评价肝硬化和向原发性肝癌转化时的临床价值[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志, 2020, 30(20): 2489-2491. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWJZ202020017.htmCHEN X R, XIAO B R, CHENG H. Clinical value of predicting liver cirrhosis severity and translating primary liver cancer by B ultrasonography, serum D-D, ALB and TBil levels determination[J]. Chinese Journal of Health Laboratory Technology, 2020, 30(20): 2489-2491. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWJZ202020017.htm [16] 宋晓婷, 许文涛, 陈煜, 等. 《2021年美国肝病学会实践指导: 肝硬化患者营养不良、衰弱和肌肉减少症》摘译[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2021, 37(12): 2787-2789. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCGD202112047.htmSONG X T, XU W T, CHEN Y, et al. An excerpt of malnutrition, frailty, and sarcopenia in patients with cirrhosis: 2021 practice guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases[J]. Journal of Clinical Hepatology, 2021, 37(12): 2787-2789. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCGD202112047.htm [17] 赵鹏, 陈静, 杨光红, 等. 住院结核患者抗结核药物性肝损伤的Nomogram风险预测模型构建[J]. 中华结核和呼吸杂志, 2022, 45(2): 171-176.ZHAO P, CHEN J, YANG G H, et al. Nomogram model for predicting risk of anti-tuberculosis drug-induced liver injury among inpatients with tuberculosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases, 2022, 45(2): 171-176. [18] 户彦龙, 梁长华, 窦文广, 等. 抗结核药物所致脂肪肝的临床转归及影像学特征分析[J]. 中华传染病杂志, 2020, 38(7): 416-421.HU Y L, LIANG C H, DOU W G, et al. Clinical outcome and imaging characteristics of fatty liver caused by anti-tuberculosis drugs[J]. Chinese Journal of Infectious Diseases, 2020, 38(7): 416-421. [19] 王建辉, 郭红丹, 孔晶晶, 等. 抗结核药物致药物性肝损伤患者临床特点及其危险因素分析[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2020, 23(1): 58-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GBSY202001019.htmWANG J H, GUO H D, KONG J J, et al. Clinical characteristics and risk factors ofdrug-induced liver injury caused by antituberculosis therapy[J]. Journal of Practical Hepatology, 2020, 23(1): 58-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GBSY202001019.htm [20] 王翠荣, 成芳梅, 黄斌, 等. 柿叶水提物对异烟肼和利福平联用所致小鼠肝损伤的保护作用及机制研究[J]. 广西医科大学学报, 2020, 37(1): 37-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXYD202001006.htmWANG C R, CHENG F M, HUANG B, et al. Protective effect and mechanism of water extract from persimmon leaves on liver injury induced by isoniazid and rifampicin in mice[J]. Journal of Guangxi Medical University, 2020, 37(1): 37-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXYD202001006.htm -





 下载:
下载: