Early identification and correlation analysis of infectious mononucleosis and acute suppurative tonsillitis in children
-
摘要:
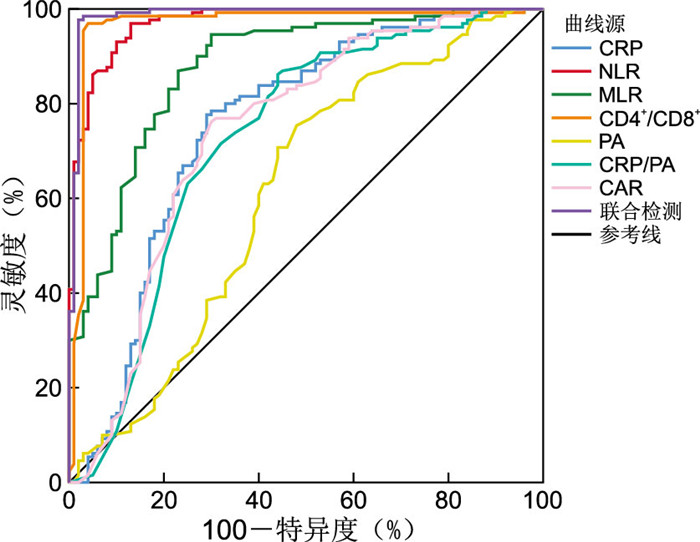
目的 探讨儿童传染性单核细胞增多症(IM)与急性化脓性扁桃体炎(AST)的早期鉴别指标及相关性,为临床诊断提供参考依据。 方法 选取2021年1月—2022年6月温州医科大学附属第二医院收治的IM儿童130例(IM组)和AST儿童100例(对照组)作为研究对象。对2组患儿的临床资料及实验室相关检测指标水平进行分析比较,通过ROC曲线分析联合多个指标对IM早期诊断的价值,使用Spearman相关性分析分析各实验室指标之间的相关性。 结果 临床表现上,IM组体温 < 39 ℃、眼睑浮肿、颈部淋巴结肿大、扁桃体分泌物占比均明显高于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(均P < 0.05)。感染早期,IM组CRP、中性粒细胞与淋巴细胞比值(NLR)、单核细胞与淋巴细胞比值(MLR)、CD4+/CD8+值、前白蛋白(PA)、C反应蛋白与前白蛋白比值(CRP/PA)、C反应蛋白与白蛋白比值(CAR)均低于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(均P < 0.05)。IM治疗后,CRP、WBC、MLR、CRP/PA及CAR水平均下降,NLR与PA水平升高,与治疗前比较差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),而ALB水平治疗前后差异无统计学意义。ROC曲线显示,联合检测的AUC为0.988,均高于单独检测。NLR与CRP、CAR呈正相关关系(r=0.431、0.433,均P < 0.05);CRP/PA与NLR呈正相关关系(r=0.443,P < 0.05),与PA呈负相关关系(r=-0.340,P < 0.05)。 结论 IM与AST的早期鉴别难度较大,易出现误诊情况,可通过CRP、NLR、MLR、CD4+/CD8+、PA、CRP/PA和CAR等实验室指标及临床表现(体温 < 39 ℃、眼睑浮肿、颈部淋巴结肿大、扁桃体分泌物)进行评估与比较,联合运用各指标对IM早期诊断与疗效评估具有较大的应用价值,可为临床提供辅助。 -
关键词:
- 传染性单核细胞增多症 /
- 急性化脓性扁桃体炎 /
- 临床表现 /
- 相关性
Abstract:Objective To explore the early differential diagnosis and correlation between pediatric infectious mononucleosis (IM) and acute suppurative tonsillitis (AST), and to provide reference for clinical diagnosis. Methods A total of 130 children with IM (IM group) and 100 children with AST (control group) admitted between January 2021 and June 2022 were selected as study subjects. The clinical data and laboratory indicators of the two groups were analyzed and compared. The receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC curve) was used to analyze the predictive ability of multiple indicators for the early diagnosis of IM. Spearman correlation was used to analyze the correlation between laboratory indicators. Results In terms of clinical manifestations, body temperature < 39 ℃, eyelid edema, neck lymph node enlargement and tonsil secretions were significantly higher in IM group than in the control group, with statistical significance (all P < 0.05). At the early stage of infection, the levels of CRP, neutrophil lymphocyte ratio (NLR), monocyte lymphocyte ratio (MLR), CD4+/CD8+, prealbumin (PA), CRP/PA and C-reactive protein/albumin ratio (CAR) levels were lower in IM group than in the control group, with statistical significance (all P < 0.05). After IM treatment, the levels of CRP, WBC, MLR, CRP/PA and CAR were decreased, while the levels of NLR and PA were increased with statistical significance compared with before treatment (P < 0.05), while the level of ALB was not statistically significant. The ROC curve showed that the AUC of combined detection was 0.988, both higher than that of single detection. NLR was positively correlated with CRP and CAR (r=0.431, 0.433, all P < 0.05). CRP/PA was positively correlated with NLR (r=0.443, P < 0.05), and negatively correlated with PA (r=-0.340, P < 0.05). Conclusion Early identification of IM and AST is difficult and misdiagnosis is easy. Laboratory indicators such as CRP, NLR, MLR, CD4+/CD8+, PA, CRP/PA, CAR and clinical manifestations (body temperature < 39 ℃, eyelid edema, cervical lymph node enlargement, amygdala secretion) can be evaluated and compared. The combined application has great application value to improve the early diagnosis and efficacy evaluation of IM, and provides clinical assistance. -
表 1 2组患儿一般资料与临床表现比较
Table 1. Comparison of general information and clinical manifestations between two groups of pediatric patients
项目 IM组(n=130) 对照组(n=100) 统计量 P值 性别[例(%)] 3.735a 0.053 男 60(46.15) 59(59.00) 女 70(53.85) 41(41.00) 年龄[例(%)] 1.121a 0.290 ≤6岁 102(78.46) 84(84.00) >6岁 28(21.54) 16(16.00) 体重(x±s, kg) 20.18±10.02 9.20±8.77 0.714b 0.243 发热[例(%)] 5.860a 0.015 < 39 ℃ 58(44.62) 29(29.00) ≥39 ℃ 72(55.38) 71(71.00) 眼睑浮肿[例(%)] 134.699a < 0.001 有 101(77.69) 1(1.00) 无 29(22.31) 99(99.00) 颈部淋巴结肿大[例(%)] 147.922a < 0.001 有 127(97.69) 20(20.00) 无 3(2.31) 80(80.00) 扁桃体肿大程度[例(%)] 2.090a 0.148 ≤Ⅱ度 115(88.46) 94(94.00) >Ⅱ度 15(11.54) 6(6.00) 扁桃体分泌物[例(%)] 6.457a 0.011 有 89(68.46) 52(52.00) 无 41(31.54) 48(48.00) 注:a为χ2值,b为t值。 表 2 2组患儿血常规与生化指标比较
Table 2. Comparison of blood routine and biochemical parameters between two groups of pediatric patients
组别 例数 CRP [M(P25, P75), mg/L] WBC (x±s, ×109/L) NLR [M(P25, P75)] MLR (x±s) CD4+/CD8+ (x±s) PA (x±s, mg/L) ALB (x±s, g/L) CRP/PA [M(P25, P75)] CAR [M(P25, P75)] IM组 130 5.70(3.20, 11.33) 16.88±7.06 0.42(0.29, 0.59) 0.15±0.09 0.27±0.26 107.52±28.56 41.08±3.06 0.06(0.03, 0.12) 0.14(0.08, 0.27) 对照组 100 17.90(9.25, 45.95) 14.65±8.18 2.94(1.53, 6.41) 0.46±0.41 1.50±0.64 124.35±45.00 44.30±3.23 0.19(0.08, 0.42) 0.43(0.21, 1.04) 统计量 3.661a 2.214b 6.309a -7.351b -18.046b -3.267b -7.724b 3.169a 3.470a P值 < 0.001 0.061 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 0.999 < 0.001 < 0.001 注:a为Z值,b为t值。 表 3 IM组患儿治疗前后血常规与生化指标比较
Table 3. Comparison of complete blood count and biochemical parameters before and after treatment in the IM group of pediatric patients
组别 例数 CRP [M(P25, P75), mg/L] WBC (x±s, ×109/L) NLR (x±s) MLR [M(P25, P75)] PA (x±s, mg/L) ALB (x±s, g/L) CRP/PA [M(P25, P75)] CAR [M(P25, P75)] 治疗前 130 5.70(3.20, 11.33) 16.88±7.06 0.48±0.30 0.14(0.08, 0.19) 107.52±28.56 41.08±3.06 0.06(0.03, 0.12) 0.14(0.08, 0.27) 治疗后 130 1.03(0.25, 3.03) 8.90±3.36 0.69±0.65 0.11(0.08, 0.15) 187.76±53.96 43.33±3.25 0.01(0.00, 0.02) 0.02(0.01, 0.07) 统计量 4.465a 11.634b -3.416b 1.923a -14.985b -5.738b 4.651a 4.465a P值 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 0.001 < 0.001 0.462 < 0.001 < 0.001 注:a为Z值,b为t值。 表 4 CRP、NLR、MLR、CD4+/CD8+、PA、CRP/PA及CAR诊断IM的ROC曲线分析结果
Table 4. ROC curve analysis for CRP, NLR, MLR, CD4+/CD8+, PA, CRP/PA, and CAR as diagnostic markers for IM
项目 AUC 阈值 约登指数 灵敏度(%) 特异度(%) CRP 0.754 43.10 0.487 77.7 71.0 NLR 0.973 1.07 0.839 96.9 87.0 MLR 0.877 0.25 0.646 94.6 70.0 CD4+/CD8+ 0.967 0.63 0.929 96.9 96.0 PA 0.612 123.00 0.274 75.4 52.0 CRP/PA 0.726 0.17 0.422 86.2 56.0 CAR 0.740 0.29 0.462 76.2 70.0 联合检测 0.988 0.957 97.7 98.0 表 5 IM患儿NLR、MLR、CD4+/CD8+、PA与CRP、CRP/PA、CAR的相关性
Table 5. Correlation of NLR, MLR, CD4+/CD8+, PA with CRP, CRP/PA, and CAR in pediatric patients with IM
项目 CRP CRP/PA CAR r值 P值 r值 P值 r值 P值 NLR 0.431 < 0.001 0.443 < 0.001 0.433 < 0.001 MLR 0.108 0.221 0.058 0.509 0.105 0.236 CD4+/CD8+ 0.073 0.410 0.039 0.659 0.061 0.490 PA -0.084 0.344 -0.340 < 0.001 -0.115 0.193 -
[1] NIQUELLE B W, CHANG C M, CONTI D, et al. Correction to infectious mononucleosis, immune genotypes, and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL): an inter Lymph consortium study[J]. Cancer Causes Control, 2020, 31(6): 47-49. [2] 陈新敏, 梁华, 郭燕, 等. 异型淋巴细胞比例联合EB病毒抗体及核酸检测在儿童传染性单核细胞增多症辅助诊断中的应用[J]. 国际检验医学杂志, 2021, 42(4): 501-503. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4130.2021.04.027CHEN X M, LIANG H, GUO Y, et al. Application of allotypic lymphocyte proportion combined with Epstein-Barr virus antibody and nucleic acid detection in the auxiliary diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis in children[J]. International Journal of Laboratory Medicine, 2021, 42(4): 501-503. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4130.2021.04.027 [3] 刘锋. 外周血细胞形态学检查在小儿传染性单核细胞增多症早期诊断中的应用及临床意义分析[J]. 中国药物与临床, 2020, 20(23): 3892-3895. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YWLC202023002.htmLIU F. The role of peripheral blood cells morphology in early diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis in children and its clinical significance[J]. Chinese Remedies & Clinics, 2020, 20(23): 3892-3895. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YWLC202023002.htm [4] SALGADO C, GARCIA A M, RUBIO C, et al. Infectious mononucleosis and cholestatic hepatitis: a rare association[J]. Acta Med Port, 2017, 30(12): 886-888. doi: 10.20344/amp.8715 [5] 幸红军, 朱明路. 原发传染性单核细胞增多症患儿血清sHLA-G水平与EBV-DNA载量的相关性分析[J]. 检验医学与临床, 2021, 18(9): 1193-1195. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYYL202109003.htmXING H J, ZHU L M. Correlation analysis between serum sHLA-G level and EBV-DNA load in children with primary infectious mononucleosis[J]. Laboratory Medicine and Clinic, 2021, 18(9): 1193-1195. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYYL202109003.htm [6] 刘秀静, 陈华乐, 余坚, 等. 新型EB病毒全自动核酸定量检测系统在儿童传染性单核细胞增多症快速诊断中的价值[J]. 中华全科医学, 2021, 19(7): 1191-1195. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002018LIU X J, CHEN H L, YU J, et al. The value of a novel automatic nucleic acid system in detecting Epstein-Barr virus for the rapid diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis in children[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2021, 19(7): 1191-1195. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002018 [7] 胡亚美, 江载芳. 诸福棠实用儿科学[M]. 8版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2015: 919.HU Y M, JIANG Z F. Zhu Futang Practical pediatrics[M]. 8 Edition. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2015: 919. [8] 中国医师协会儿科医师分会儿童耳鼻咽喉专业委员会. 儿童急性扁桃体炎诊疗: 临床实践指南(2016年制定)[J]. 中国实用儿科杂志, 2017, 32(3): 161-164. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSEK201703001.htmCommittee of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology, Pediatrician Society of Chinese Medical Doctor Association. Diagnosis and treatment in children with acute tonsillitis: clinical practice guideline(2016)[J]. Chinese Journal of Practical Pediatrics, 2017, 32(3): 161-164. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSEK201703001.htm [9] 陈若红, 冯业成, 黄慧敏, 等. EBV感染患儿临床特征及血清免疫因子水平[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2021, 31(3): 463-467. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHYY202103032.htmCHEN R H, FENG Y C, HUANG H M, et al. Clinical features and serum immune factors in children with EB virus infection[J]. Chinese Journal of Nosocomiology, 2021, 31(3): 463-467. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHYY202103032.htm [10] WANG J, ZHU Q W, CHENG X Y, et al. Clinical significance of neutron-phil-lymphocyte ratio and monocyte-lymphocyte ratio in women with hyperglycemia[J]. Postgrad Med, 2020, 132(8): 702-708. [11] 李海霞, 陶永明, 赵秋霞, 等. 传染性单核细胞增多症患儿调节性T细胞与EB病毒DNA浓度的相关性研究[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2021, 25(15): 98-101, 105. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYZL202115022.htmLI H X, TAO Y M, ZHAO Q X, et al. Study on the correlation between regulatory T cells and EB virus DNA concentration in children with infectious mononucleosis[J]. Journal of Clinical Medicine in Practice, 2021, 25(15): 98-101, 105. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYZL202115022.htm [12] LIN J, CHEN X, WU H, et al. Peripheral blood lymphocyte counts in patients with infectious mononucleosis or chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection and prognostic risk factors of chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2021, 13(11): 12797-12806. [13] 黄彬晓, 何敏菲, 孔元梅, 等. 儿童EB病毒相关淋巴组织增殖性疾病临床分析[J]. 国际儿科学杂志, 2021, 48(2): 137-141. https://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZJKX202010002005.htmHUANG B X, HE M F, KONG Y M, et al. Clinical analysis of Epstein-Barr virus-associated lymphoproliferative disease in children[J]. International Journal of Pediatrics, 2021, 48(2): 137-141. https://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZJKX202010002005.htm [14] 梁杰增, 吴涛, 詹桂兰. C反应蛋白前白蛋白及降钙素原在儿童烧伤感染中的表达水平及诊断效能[J]. 山西医药杂志, 2019, 48(5): 579-581. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXYY201905084.htmLIANG J Z, WU T, ZHAN G L. CRP?PA and PCT expression level in children burn infection and the diagnosis efficiency[J]. Shanxi Medical Journal, 2019, 48(5): 579-581. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXYY201905084.htm [15] 秦小菀, 朱萍, 惠晓霞, 等. PCT与CRP和WBC及前白蛋白联合检测对儿科感染性疾病早期诊断的价值[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2019, 29(1): 146-148, 156. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHYY201901040.htmQIN X W, ZHU P, HUI X X, et al. Value of joint detection of PCT, CRP, WBC and prealbumin in early diagnosis of children with infectious diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Nosocomiology, 2019, 29(1): 46-148, 156. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHYY201901040.htm [16] SAYAR S, KURBUZ K, KAHRAMAN R, et al. A practical marker to determining acute severe ulcerative colitis: CRP/albumin ratio[J]. North Clin Istanb, 2020, 7(1): 49-55. [17] 符传铰, 夏鹰, 陈华澎, 等. 外周血白细胞计数、C反应蛋白/白蛋白比值与动脉瘤性蛛网膜下腔出血患者短期预后相关性研究[J]. 创伤与急危重病医学, 2021, 9(2): 101-104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSJB202102006.htmFU C J, XIA Y, CHEN H P, et al. Correlation between peripheral blood white blood cell count, C-reactive protein/albumin ratio and short-term prognosis in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage[J]. Trauma and Critical Care Medicine, 2021, 9(2): 101-104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSJB202102006.htm [18] STEFANESCU S, COCO瘙塁R, TURCU-STIOLICA A, et al. Prediction of treatment outcome with inflammatory biomarkers after 2 months of therapy in pulmonary tuberculosis patients: preliminary results[J]. Pathogens, 2021, 10(7): 789. [19] 胡岩岩, 潘家华, 周浩泉. 儿童传染性单核细胞增多症临床及实验室检查特点分析[J]. 中华全科医学, 2021, 19(9): 1510-1513. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002099HU Y Y, PAN J H, ZHOU H Q. Analysis of clinical and laboratory characteristics of infectious mononucleosis in children[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2021, 19(9): 1510-1513. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002099 [20] 梁栋, 王全楚. 传染性单核细胞增多症临床特点及误诊分析[J]. 临床误诊误治, 2020, 33(2): 1-3. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCWZ202002002.htmLIANG D, WANG Q C. Clinical characteristics and misdiagnosis of infectious mononucleosis[J]. Clinical Misdiagnosis & Mistherapy, 2020, 33(2): 1-3. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCWZ202002002.htm -





 下载:
下载: