Application value of HINE combined with skull Gesell in early recognition of high risk infants with cerebral palsy
-
摘要:
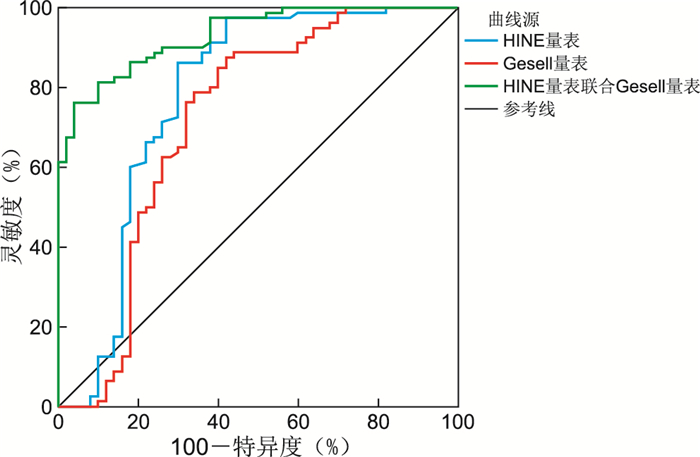
目的 将Hammersmith婴儿神经学检查量表(HINE)和Gesell发育量表联合应用于脑瘫高危儿的早期筛查,旨在开发出更完善更高效的早期筛查方案。 方法 选择台州市妇女儿童医院及台州市中心医院于2020年10月—2021年12月就诊的脑瘫高危儿80例为脑瘫高危组;另选择同期健康婴幼儿50例为对照组。比较脑瘫高危儿和健康婴幼儿HINE量表和Gesell发育量表评分;分析HINE联合Gesell发育量表对脑瘫高危儿早期识别价值。 结果 脑瘫高危组颅神经[(12.94±1.81)分]、运动[(4.59±1.04)分]、姿势[(15.91±1.86)分]、反射和反应[(12.91±1.94)分]、肌张力[(21.38±2.73)分]及量表总分[(67.71±8.61)分]均低于对照组[(13.62±1.11)分、(5.32±0.62)分、(16.78±1.25)分、(13.96±1.12)分、(23.30±0.88)分、(72.98±3.36)分,均P < 0.05]。脑瘫高危组应物、精细动作、粗大运动和应人DQ值低于对照组(均P < 0.05),而脑瘫高危组语言DQ值比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。经ROC曲线分析,HINE联合Gesell量表对脑瘫高危儿早期预测灵敏度(96.3%)和特异度(96.0%)高于HINE量表(86.3%、70.0%)与Gesell量表(87.5%、58.0%,P < 0.05)。 结论 HINE量表联合Gesell发育量表对脑瘫高危儿早期识别价值显著,灵敏度和特异度良好。 -
关键词:
- Hammersmith婴儿神经学检查量表 /
- Gesell发育量表 /
- 脑瘫高危儿 /
- 早期识别
Abstract:Objective The combined application of the Hammersmith infant neurological examination scale (HINE) and the Gesell developmental scale in early screening of high-risk infants with cerebral palsy aims to develop a more comprehensive and efficient early screening plan. Methods Select Taizhou Women's and Children's Hospital and Taizhou Central Hospital to study 80 high-risk children with cerebral palsy from October 2020 to December 2021; another 50 healthy infants and young children in the same period were selected as the control group. To compare the scores of the HINE scale and the Gesell developmental scale scores between high-risk infants with cerebral palsy and healthy infants; to analyze the early recognition value of HINE combined with Gesell developmental scale in high-risk infants with cerebral palsy. Results The high-risk cerebral palsy group had lower scores in cranial nerves [(12.94±1.81) points], motor [(4.59±1.04) points], posture [(15.91±1.86) points], reflexes and reactions [(12.91±1.94) points], muscle tone [(21.38±2.73) points] and total scale score [(67.71±8.61) points] compared to the control group [(13.62±1.11) points, (5.32±0.62) points, (16.78±1.25) points, (13.96±1.12) points, (23.30±0.88) points, and (72.98±3.36) points], the differences were statistically significant (all P < 0.05). The DQ scores of reaction, fine motor, gross motor, and response were lower in the high-risk cerebral palsy group than control group (all P < 0.05); while the DQ values of language in the high-risk cerebral palsy group had no statistical significance (P>0.05). By receiver operating characteristic analysis, the sensitivity (96.3%) and specificity (96.0%) of HINE combined with Gesell scale for early prediction of high risk infants with cerebral palsy were higher than those of HINE scale (86.3%, 70.0%), Gesell scale (87.5%, 58.0%, P < 0.05). Conclusion HINE combined with the Gesell Scales of Brain Development is of great value in the early recognition of high-risk infants with cerebral palsy and can improve the diagnostic sensitivity and specificity. -
表 1 2组婴幼儿HINE量表评分比较(x ±s,分)
Table 1. Comparison of HINE scale scores between two groups of infants (x ±s, points)
组别 例数 颅神经 运动 姿势 反射和反应 肌张力 量表总分 脑瘫高危组 80 12.94±1.81 4.59±1.04 15.91±1.86 12.91±1.94 21.38±2.73 67.71±8.61 对照组 50 13.62±1.11 5.32±0.62 16.78±1.25 13.96±1.12 23.30±0.88 72.98±3.36 t值 2.655 5.013 2.889 3.878 5.820 4.906 P值 0.009 <0.001 0.005 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 表 2 2组婴幼儿Gesell量表检查结果比较(x ±s)
Table 2. Comparison of Gesell scale results between two groups of infants (x ±s)
组别 例数 应物 语言 精细动作 粗大运动 应人 脑瘫高危组 80 81.97±12.51 90.03±6.36 84.46±11.32 84.27±9.32 86.14±7.84 对照组 50 88.64±5.31 91.40±5.40 89.12±4.65 89.47±6.59 90.10±5.46 t值 4.201 1.265 3.268 3.435 3.119 P值 <0.001 0.208 0.001 0.001 0.002 表 3 HINE联合Gesell量表对脑瘫高危儿的早期识别价值分析
Table 3. Analysis of early identification value of HINE combined with Gesell scale for high-risk infants with cerebral palsy
项目 曲线下面积 灵敏度(%) 特异度(%) 95% CI HINE量表 0.777 86.3 70.0 0.679~0.875 Gesell量表 0.716 87.5 58.0 0.612~0.820 HINE联合Gesell量表 0.931 96.3 96.0 0.891~0.970 -
[1] HARNIESSS P A, GIBBS D, BEZEMER J, et al. Parental engagement in early intervention for infants with cerebral palsy-A realist synthesis[J]. Child Care Health Dev, 2022, 48(3): 359-377. doi: 10.1111/cch.12916 [2] ZHANG Q F, HU Y S, DONG X, et al. Predictive value of electroencephalogram, event-related potential, and general movements quality assessment in neurodevelopmental outcome of high-risk infants[J]. Appl Neuropsychol Child, 2022, 11(3): 438-443. doi: 10.1080/21622965.2021.1879085 [3] JACKMAN M, SAKZEWSKI L, MORGAN C, et al. Interventions to improve physical function for children and young people with cerebral palsy: international clinical practice guideline[J]. Dev Med Child Neurol, 2022, 64(5): 536-549. doi: 10.1111/dmcn.15055 [4] 黄金容, 张峰, 温芳芳, 等. 任务导向结合生物反馈训练对痉挛型脑瘫患儿手功能、Gesell量表评分及平衡能力的影响[J]. 四川大学学报(医学版), 2020, 51(3): 428-433. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYK202003029.htmHUANG J R, ZHANG F, WEN F F, et al. Effect of Biofeedback Combined with Task-oriented Training on Hand Function, Gesell Scale Score and Balance Ability in Children with Spastic Cerebral Palsy[J]. Journal of Sichuan University(Medical Science Edition), 2020, 51(3): 428-433. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYK202003029.htm [5] 徐艳, 吴锋锋, 何凤翔. 肌内效贴扎对小儿脑瘫核心肌群的影响及异常步态的预防作用[J]. 中华全科医学, 2021, 19(10): 1737-1741. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002155XU Y, WU F F, HE F X. Effect of kinesio taping on the core muscle groups of children with cerebral palsy and the prevention of abnormal gait[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2021, 19(10): 1737-1741. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002155 [6] ELSHAFEY M A, ABDRABO M S, EINAGGAR R K. Effects of a core stability exercise program on balance and coordination in children with cerebellar ataxic cerebral palsy[J]. J Musculloskelet Neuronal Interact, 2022, 22(2): 172-178. [7] HAATAJA L, MERCURI E, REGEV R, et al. Optimality score for the neurologic examination of the infant[J]. J Pediatr, 1999, 135(2): 153-161. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3476(99)70016-8 [8] 唐久来, 秦炯, 邹丽萍, 等. 中国脑性瘫痪康复指南(2015): 第一部分[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2015, 30(7): 747-754. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1242.2015.07.028TANG J L, QIN J, ZOU L P, et al. Guidelines for Rehabilitation of Cerebral Palsy in China(2015): Part Ⅰ[J]. Chinese Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine, 2015, 30(7): 747-754. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1242.2015.07.028 [9] SELPH S S, SKELLY A C, WASSON N, et al. Physical activity and the health of wheelchair users: a systematic review in multiple sclerosis, cerebral palsy, and spinal cord injury[J]. Arch Phsy Med Rehabil, 2021, 102(12): 2464-2481. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2021.10.002 [10] 张鸿雁, 赵云霞. 听性脑干反应中枢性损害分类对脑瘫高危儿的诊断价值[J]. 中国实用神经疾病杂志, 2021, 24(14): 1246-1252. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNSJ202114009.htmZHANG H Y, ZHAO Y X. Analysis of the diagnostic value the classification of central lesion by ABR in infants at high risk of cerebral palsy[J]. Chinese Journal of Practical Nervous Diseases, 2021, 24(14): 1246-1252. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNSJ202114009.htm [11] WILSON Y A, SMITHERS-SHEEDY H, OSTOJIC K, et al. Cerebral palsy and sex differences in children: a narrative review of the literature[J]. Dev Med Child Neurol, 2022, 64(12): 1470-1476. doi: 10.1111/dmcn.15245 [12] 屈克丽, 高美哲, 王春霞, 等. 基于健康宣教与保健的早期干预在脑瘫高危儿中的应用价值及预后随访观察[J]. 广东医学, 2020, 41(13): 1340-1343. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GAYX202013009.htmQU K L, GAO M Z, WANG C X, et al. Application value and prognosis of early intervention based on health education and health care in high-risk infants with cerebral palsy[J]. Guangdong Medical Journal, 2020, 41(13): 1340-1343. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GAYX202013009.htm [13] 范忠媛, 鄢毅, 张光梅. 0~6个月龄脑瘫高危儿血清NSE、IL-6水平及临床价值[J]. 热带医学杂志, 2020, 20(12): 1565-1568. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDYZ202012008.htmFAN Z Y, YAN Y, ZHANG G M. Levels of serum NSE and IL-6 in high-risk cerebral palsy of 0-6 months old infants and their clinical value[J]. Journal of Tropical Medicine, 2020, 20(12): 1565-1568. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDYZ202012008.htm [14] ADIGUZEL H, SARIKABADAYI Y, APAYDIN U, et al. Turkish validity and reliability of the Hammersmith infant neurological examination (HINE) with high-risk infant group: a preliminary study[J]. Turk Arch Pediatr, 2022, 57(2): 151-159. doi: 10.5152/TurkArchPediatr.2022.21231 [15] ROMEO D, COWAN F M, HAATAJA L, et al. Hammersmith infant neurological examination in infants born at term: predicting outcomes other than cerebral palsy[J]. Dev Med Child Neurol, 2022, 64(7): 871-880. [16] ROMEO D M, VENRZIA I, PEDA E, et al. Cerebral palsy and sex differences in children: a narrative review of the literature[J]. J Neurosci Res, 2023, 101(5): 783-795. [17] ELLIOTT A M, GUIMOND C. Genetic counseling considerations in cerebral palsy[J]. Mol Genet Metab, 2022, 137(4): 428-435. [18] DEMONT A, GEDDA M, LAGER C, et al. Evidence-based, implementable motor rehabilitation guidelines for individuals with cerebral palsy[J]. Neurology, 2022, 99(7): 283-297. [19] NOVAK I, MORGAN C, ADDE L, et al. Early, accurate diagnosis and early intervention in gerebral palsy: advances in diagnosis and treatment[J]. JAMA Pediatr, 2017, 171(9): 897-907. [20] ROMEO D M, RICCI D, BROGNA C, et al. Use of the hammersmith infant neurological examination in infants with cerebral palsy: a critical review of the literature[J]. Dev Med Child Neurol, 2016, 58(3): 240-245. [21] ROMEO D M, COWAN F M, HAATAJA L, et al. Hammersmith Infant Neurological Examination for infants born preterm: predicting outcomes other than cerebral palsy[J]. Dev Med Child Neurol, 2021, 63(8): 939-946. [22] 陈艳艳, 陈奕江, 梁彬. 脑瘫患儿血清瘦素、IGF-1水平变化与DQ、GMFM-88量表评分的关系[J]. 标记免疫分析与临床, 2022, 29(3): 392-396. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJMY202203007.htmCHEN Y Y, CHEN Y J, LIANG B. The Correlation of Serum Leptin and IGF-1 levels and DQ, GMFM-88 scores in children with cerebral palsy[J]. Labeled Immunoassays and Clinical Medicine, 2022, 29(3): 392-396. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJMY202203007.htm -





 下载:
下载: