A systematic review of factors influencing utilization of primary medical service at home and abroad based on the Andersen model
-
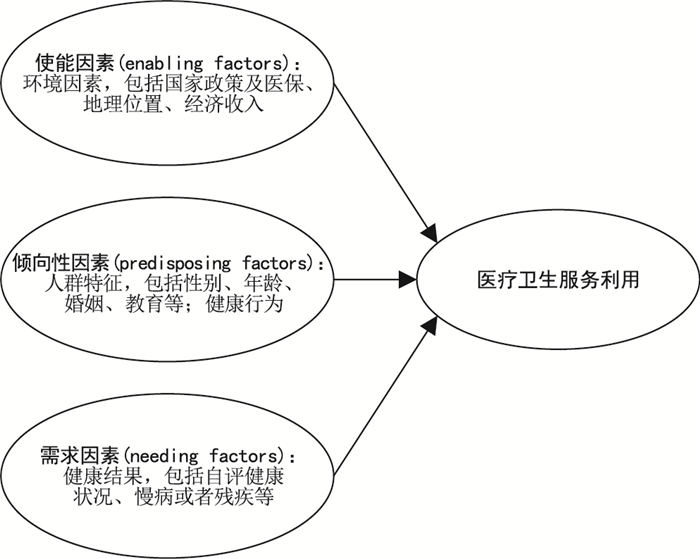
摘要: 随着“健康中国”战略的推进,分析基层医疗服务利用影响因素对医疗资源合理分配至关重要。目前尚无针对国内外基层医疗服务利用影响因素的综述研究,文章基于Andersen医疗服务利用行为模型对基层医疗服务利用影响因素进行系统化梳理。研究发现需求因素是影响医疗服务利用的最显著因素,患有慢性病、患慢性病数量、残疾失能及疾病程度显著影响医疗服务利用;使能因素中,人口健康政策、医疗保险普及以及经济收入增加是影响医疗服务利用的积极因素;倾向性因素中,性别、年龄、婚姻状况、受教育程度对医疗服务利用的影响,结论不一致,可能与研究对象的选择、研究地区的选择有关系,但各个因素都对医疗服务利用产生不同程度的影响;另外健康行为和正确的诊疗观念对医疗服务利用有积极影响。既往研究多从地域、经济、医保等方面分析和比较医疗服务利用情况,结合患者健康结局、满意度的因素较少,致使在分析影响因素过程中研判证据不足;且对于基层医疗服务利用的关注度低,数据少且不全面,未来研究中需要重点关注我国各个地区基层医疗服务利用及其影响因素,开展科学系统的数据分析,为基层医疗服务的均衡发展与政策的精准干预提供科学可靠的证据支持与切实可行的政策建议。
-
关键词:
- 医疗服务利用 /
- Andersen医疗服务利用行为模型 /
- 影响因素
Abstract: With the promotion of the "Healthy China" strategy, analyzing the factors affecting the utilization of primary healthcare services is crucial for the rational allocation of healthcare resources. At present, there is no review study on the influencing factors of primary healthcare service utilization at home and abroad, and this article is based on Andersen ' s behavioral model of healthcare service utilization to systematically sort out the influencing factors of primary healthcare service utilization. The study finds that the needing factor is the most significant factor influencing the utilization of healthcare services, having chronic diseases, number of chronic diseases, disability and degree of illness significantly influenced the utilization of healthcare services. Among the enabling factors, population health policies, universal health insurance coverage, and increased economic income are positive factors affecting the utilization of healthcare services. Among the predisposing factors, the effect of gender, age, marital status, and education on health service utilization, the findings are inconsistent and may be related to the selection of the study population and the selection of the study area, but each factor has a varying degree of influence on health service utilization. In addition, health behaviors and correct treatment concepts have a positive impact on the use of health services. Previous studies have analyzed and compared healthcare service utilization in terms of geography, economy, healthcare insurance, etc., with fewer factors incorporating patient health outcomes and satisfaction, resulting in insufficient evidence for judgement in analyzing the influencing factors. Moreover, previous studies have paid little attention to the utilization of primary healthcare services, and the data are scarce and incomplete. In future studies, we need to focus on the utilization of primary healthcare services and its influencing factors in different regions of China, and carry out scientific and systematic data analysis, so that we can provide scientific and reliable evidence support and practical policy recommendations for the balanced development of primary healthcare services and precise policy interventions. -
表 1 安德森模型与医疗服务利用的相关性
Table 1. Relevance of the Anderson ' s model to healthcare utilization
医疗服务利用影响因素 参考文献 P<0.05 相关性(正相关/负相关) 使能因素 国内政策 [7-8] 是 正相关 医疗保险 [5-6, 9-17] 是 正相关 地理位置 东部地区 [18-19] 是 正相关 城镇地区 [15-20] 是 正相关 农村地区 [16-17] 是 正相关 经济状况好地区 [13] 是 正相关 家庭经济收入(高) [6, 9, 14, 17, 21-23] 是 正相关 [15, 24] 否 不相关 倾向性因素 人群特征 性别(女性) [6, 13, 16, 20, 25-27] 是 正相关 [28, 29] 否 不相关 年龄(大) [5, 6, 12-14, 16, 25, 30-32] 是 正相关 年龄(<5岁) [14] 是 正相关 婚姻状况(已婚) [6, 12, 16-17, 33] 是 正相关 [20] 是 负相关 受教育程度(高) [12-13, 15, 23, 32] 是 正相关 [6, 14] 是 负相关 [29] 否 不相关 健康行为(戒烟、体检) [27, 32-34] 是 正相关 [29] 否 不相关 需求因素 自评健康状况(差)、患有慢病(多重) [6, 15, 17, 20, 25, 29-30, 35] 是 正相关 [13] 是 负相关 [27] 否 不相关 -
[1] 《关于印发全国医疗卫生服务体系规划纲要(2015—2020年)的通知》[R]. 国务院办公厅. 2015.《Notice on Printing and Distributing the Outline of the National Medical and Health Service System Planning (2015—2020)》[R]. General Office of the State Council of the People's Republic of China. 2015. [2] 李莹. 流动老人医疗卫生服务利用研究[D]. 石家庄: 河北经贸大学, 2019.LI Y. Research on the utilization of medical services for mobile elderly[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei University of Economics and Business, 2019. [3] 杜本峰, 曹桂, 许锋. 流动老年人健康状况及医疗服务利用影响因素分析[J]. 中国卫生政策研究, 2018, 11(5): 10-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWZ201805002.htmDU B F, CAO G, XU F. Analysis on health status and medical service utilization among the migrant elderly in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Health Policy, 2018, 11(5): 10-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWZ201805002.htm [4] ANDERSON J G. A social systems model of hospital utilization[J]. Health Serv Res, 1976, 11(3): 271-287. [5] 王权. 医疗保险对北京市老年人医疗机构选择行为的影响研究[D]. 北京: 首都经济贸易大学, 2018.WANG Q. Research on the influence of medical insurance in the selecting behavior of medical institution in the elderly in Beijing[D]. Beijing: Capital University of Economics and Business, 2018. [6] GIL M, CHOI C G. Factors affecting the choice of national and public hospitals among outpatient service users in South Korea[J]. Inquiry, 2019, 56: 46958019833256. DOI: 10.1177/0046958019833256. [7] 陈昊, 陈建伟, 马超. 助力健康中国: 精准扶贫是否提高了医疗服务利用水平[J]. 世界经济, 2020, 43(12): 76-101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJJJ202012005.htmCHEN H, CHEN J W, MA C. For a Healthy China: has targeted poverty alleviation improved the utilisation of medical services?[J]. The Journal of World Economy, 2020, 43(12): 76-101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJJJ202012005.htm [8] 李昕嫄. 分级诊疗制度背景下患者对医疗卫生服务利用的满意度及其影响因素研究[D]. 南昌: 江西中医药大学, 2021.LI X Y. Study on patients' satisfaction with medical service utilization its influencing factors under the background of hierarchical diagnosis[D]. Nanchang: Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, 2021. [9] 刘亚平. 异质性医疗保险对我国中老年人医疗需求及健康水平的影响[D]. 成都: 西南财经大学, 2016.LIU Y P. The Effect of heterogeneous medical Insurance on medical demands and health of the elderly[D]. Chengdu: Southwestern University of Finance and Economics, 2016. [10] CHEN C, SONG J L, XU X L, et al. Analysis of influencing factors of economic burden and medical service utilization of diabetic patients in China[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(10): e0239844. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0239844. [11] WANG Z H, LI X J, CHEN M S, et al. Social health insurance, healthcare utilization, and costs in middle-aged and elderly community-dwelling adults in China[J]. Int J Equity Health, 2018, 17(1): 17-28. doi: 10.1186/s12939-018-0733-0 [12] 苏敏艳, 王紫红, 高山, 等. 分级诊疗制度下居民选择就诊医疗机构的影响因素研究[J]. 中国农村卫生事业管理, 2021, 41(12): 854-858. doi: 10.19955/j.cnki.1005-5916.2021.12.004SU M Y, WANG Z H, GAO S, et al. Influencing factors forresidents' choice of healthinstitutions under the hierarchical diagnosis andtreatment system[J]. Chinese Rural Health Service Administration, 2021, 41(12): 854-858. doi: 10.19955/j.cnki.1005-5916.2021.12.004 [13] BIBIANO A M B, DE LIMA SILVA V, DA SILVEIRA MOREIRA R. Factors associated with the use of health services by elderly men in Brazil: a cross-sectional study[J]. BMC Public Health, 2019, 19(1): 859-870. doi: 10.1186/s12889-019-7232-0 [14] NOURAEI MOTLAGH S, SABERMAHANI A, HADIAN M, et al. Factors affecting health care utilization in Tehran[J]. Glob J Health Sci, 2015, 7(6): 240-249. [15] QUINTAL C, ANTUNES M. Equity in usage of medical appointments in Portugal: in sickness and in health, in poverty and in wealth?[J]. Acta Med Port, 2020, 33(2): 93-100. doi: 10.20344/amp.12278 [16] NOH J W, KIM K B, PARK H, et al. Gender differences in outpatient utilization: a pooled analysis of data from the korea health panel[J]. J Womens Health (Larchmt), 2017, 26(2): 178-185. doi: 10.1089/jwh.2016.5771 [17] KURPAS D, BUJNOWSKA-FEDAK M M, ATHANASIADOU A, et al. Factors influencing utilization of primary health care services in patients with chronic respiratory diseases[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2015, 866: 71-81. [18] 谢荷, 刘芳. 我国医疗卫生资源配置与服务利用研究[J]. 现代医院管理, 2021, 19(4): 12-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLYY202104005.htmXIE H, LIU F. Research on medical and health resource allocation and service utilization in China[J]. Modern Hospital Management, 2021, 19(4): 12-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLYY202104005.htm [19] 刘曼玲, 姚文柱, 冯巩. 建国70年以来我国社区卫生服务的发展[J]. 中华全科医学, 2019, 17(8): 1251-1254, 1311. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.000914LIU M L, YAO W Z, FENG G. The development of community health service in 70 years since the foundation of the People's Republic of China[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2019, 17(8): 1251-1254, 1311. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.000914 [20] 张建芳. 我国居民利用医疗服务的影响因素与对策研究: 基于2018年CFPS数据[J]. 保定学院学报, 2021, 34(5): 8-14, 35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BDSZ202105002.htmZHANG J F. On the Influencing Factors and Countermeasures of Residents'Medical Service Utilization: based on the 2018 CFPS Data[J]. Journal of Baoding University, 2021, 34(5): 8-14, 35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BDSZ202105002.htm [21] 许敏, 王小万, 王增武, 等. 社区高血压患者门诊服务利用的公平性分析[J]. 中南大学学报(医学版), 2018, 43(6): 668-678. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNYD201806017.htmXU M, WANG X W, WANG Z W, et al. Equity of outpatient service utilization for hypertensive patients in community[J]. Journal of Central South University(Medical Science), 2018, 43(6): 668-678. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNYD201806017.htm [22] HU C Q, YU W Y, LV Y P, et al. Study on the health status and health service utilization of the elderly of a remote and poor village in a mountainous area in Jinzhai, Anhui[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2017, 14(4): 408. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14040408 [23] AGUNWA C C, OBI I E, NDU A C, et al. Determinants of patterns of maternal and child health service utilization in a rural community in south eastern Nigeria[J]. BMC Health Serv Res, 2017, 17(1): 715. [24] SAMSUDIN S, ABDULLAH N. Healthcare utilization by older age groups in Northern States of Peninsular Malaysia: the role of predisposing, enabling and need factors[J]. J Cross Cult Gerontol, 2017, 32(2): 223-237. [25] 贺梦璐, 王春霞, 王海鹏, 等. 山东省农村多重慢病患者卫生服务利用现状及影响因素分析[J]. 中国卫生事业管理, 2021, 38(12): 922-925, 935. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWSG202112010.htmHE M L, WANG C X, WANG H P, et al. Analysis of the utilization of health services for patients with multimorbidity in rural Shandong and its influencing factors[J]. Chinese Health Service Management, 2021, 38(12): 922-925, 935. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWSG202112010.htm [26] 丰志鹏. 基于安德森行为模型探究慢性病患者卫生服务利用情况及影响因素[D]. 大连: 大连医科大学, 2019.FENG Z P. Exploring the utilization and influencing factors of health services for chronic disease patients based on Andersen Behavioral Model[D]. Dalian: Dalian Medical University, 2019. [27] 栗佳. 分级诊疗视角下基于Andersen模型的慢性病患者就医选择影响因素研究[D]. 北京: 北京协和医学院, 2020.LI J. Study on influencing factors of chronic disease patients' medical choice based on Andersen Behavioral Model from the perspective of hierarchical medical system[D]. Beijing: Peking Union Medical College, 2020. [28] 王蕊琪, 周郁秋, 贾红红. 慢性病患者就医行为影响因素研究进展[J]. 护理学报, 2018, 25(3): 24-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NFHL201803009.htmWANG R Q, ZHOU Y Q, JIA H H. Research progress on the influencing factors of medical behavior in patients with chronic diseases[J]. Journal of Nursing, 2018, 25(3): 24-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NFHL201803009.htm [29] HAJEK A, BOCK J O, KÖNIG H H. Which factors affect health care use among older Germans? Results of the German ageing survey[J]. BMC Health Serv Res, 2017, 17(1): 30. [30] 马春燕, 高博, 张敏. 成都市老年人住院服务利用研究[J]. 中国医院, 2021, 25(11): 46-48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYU202111014.htmMA C Y, GAO B, ZHANG M. Research on utilization of hospitalization services among the aged people in Chengdu[J]. Chinese Hospitals, 2021, 25(11): 46-48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYU202111014.htm [31] 郝爱华, 陈楚天, 郎玲玲, 等. 老年人自评健康与卫生服务利用的关系研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2021, 24(7): 818-823. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QKYX202107019.htmHAO A H, CHEN C T, LANG L L, et al. Self-rated health status and utilization of health services in the elderly[J]. Chinese General Practice, 2021, 24(7): 818-823. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QKYX202107019.htm [32] PATHAK P, SHRESTHA S, DEVKOTA R, et al. Factors associated with the utilization of institutional delivery service among mothers[J]. J Nepal Health Res Counc, 2018, 15(3): 228-234. [33] 赵骎骎, 冯祥, 钱东福, 等. "健康中国"背景下某市中老年居民就医方式及其影响因素研究[J]. 中国农村卫生事业管理, 2020, 40(3): 160-165. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNWS202003006.htmZHAO Q Q, FENG X, QIAN D F, et al. Medical consultation approaches and influencing factors of middle-aged and elderly residents in a city under the background of"Healthy China"strategy[J]. Chinese Rural Health Service Administration, 2020, 40(3): 160-165. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNWS202003006.htm [34] 宋晨晓, 徐爱军. 高血压患者基层医疗机构就诊情况及其影响因素分析[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2018, 34(8): 1140-1142. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGW201808019.htmSONG C X, XU A J. Status and influencing factors of health care seeking at grassroots medical institutions among hypertensive patients[J]. Chinese Journal of Public Health, 2018, 34(8): 1140-1142. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGW201808019.htm [35] KONG N Y, KIM D H. Factors influencing health care use by health insurance subscribers and medical aid beneficiaries: a study based on data from the Korea welfare panel study database[J]. BMC Public Health, 2020, 20(1): 1133. [36] JI M M, ZHANG Y F, ZOU J J, et al. Study on the status of health service utilization among caregivers of left-behind children in poor rural areas of hunan province: a baseline survey[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2017, 14(8): 910. [37] SHAO S, WANG M R, JIN G H, et al. Analysis of health service utilization of migrants in Beijing using Anderson health service utilization model[J]. BMC Health Serv Res, 2018, 18(1): 462. [38] 周良, 郝雨, 杨永华, 等. 中青年人群对家庭医生楼宇服务认知及影响因素分析[J]. 中华全科医学, 2021, 19(7): 1163-1166. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002011ZHOU L, HAO Y, YANG Y H, et al. Young and middle-aged people's awareness of family doctor building services and influencing factor analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2021, 19(7): 1163-1166. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002011 -





 下载:
下载: