Refractory hypertension caused by bilateral renal artery stenosis: a case report and literature review
-
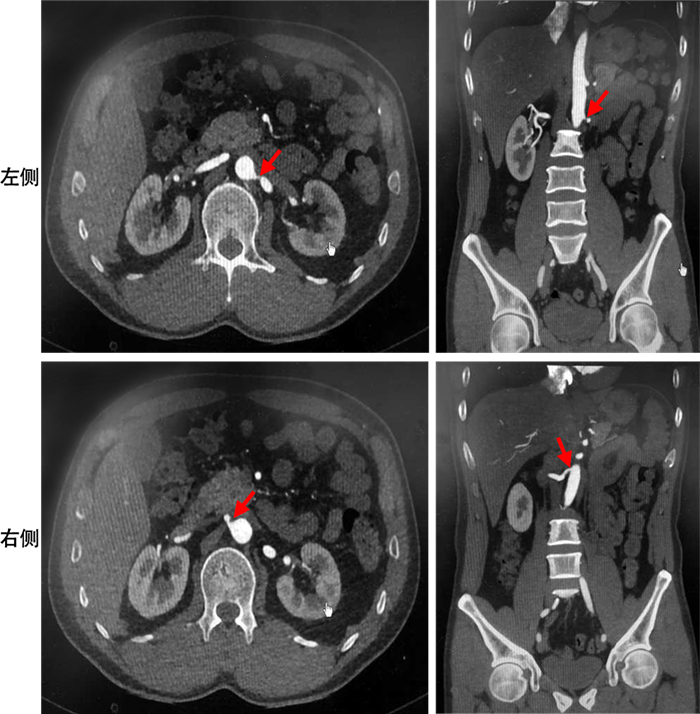
摘要: 由双侧肾动脉狭窄(RAS)所致的难治性高血压,发病率较低,临床诊治较为困难。首都医科大学宣武医院全科医学科收治1例48岁男性患者,近期出现严重的高血压病史。考虑患者的年龄及高血压的严重程度,笔者筛查了继发性高血压的常见原因,进一步行腹主动脉CT血管成像,提示双侧肾动脉开口处中-重度狭窄,为双侧肾动脉狭窄导致的难治性高血压。联合血管外科分期实施双侧肾动脉支架植入术,术后随访患者血压逐渐控制稳定。本文对该患者具体诊治经过进行回顾性分析,并复习相关文献。Abstract: Refractory hypertension caused by bilateral renal artery stenosis (RAS) has a low incidence and is difficult to diagnose and treat clinically. The Department of General Medicine of Xuanwu Hospital Capital Medical University admitted a 48-year-old male patient with a recent history of severe hypertension. Considering the patient's age and severity of hypertension, we screened for common causes of secondary hypertension. Further abdominal aortic CTangiography showed moderate to severe stenosis at the openings of the bilateral renal arteries, which led to refractory hypertension. Therefore, angioplasty of both renal arteries was performed as a staged procedure, and the patient's blood pressure was gradually controlled and stabilized during postoperative follow-up. This article reviews the specific diagnosis and treatment process and reviews relevant literature.
-
Key words:
- Refractory hypertension /
- Bilateral renal artery stenosis
-
表 1 患者肾素-醛固酮检测动态试验情况
Table 1. Dynamic test of renin aldosterone detection in patients
项目 8点
(服药)9点 10点 11点 术后1个月 醛固酮(pg/mL) 108.55 182.99 147.97 180.89 - 肾素(uIU/mL) 284.71 562.31 4 436.01 4 798.98 29.33 醛固酮/肾素 0.38 0.33 0.03 0.04 - 注:“-”为未查该项目。 表 2 SCAI、AHA/ACC、ESC指南关于RAS患者治疗建议
Table 2. Recommendations for Stenting Treatment of RAS Patients in SCAI, AHA/ACC, and ESC Guidelines
临床表现 SCAI AHA/ACC建议 ESC 推荐等级 证据水平 推荐等级 证据水平 难治性高血压(联用三种降压药物至最大剂量控制不佳,包括使用利尿剂)双侧或单功能肾重度RAS 适用 Ⅱa B Ⅲ A 难治性高血压(联用三种降压药物至最大剂量控制不佳,包括使用利尿剂)单侧重度RAS 可能适用 Ⅱa B Ⅲ A 无症状、单侧、双侧或单功能肾,血流动力学显著的RAS 可能适用 Ⅱa B Ⅲ A 注:SCAI为美国心血管造影与介入学会;ACC为美国心脏病学会;AHA为美国心脏病学会;ESC为欧洲心脏病学会;RAS为肾动脉狭窄。Ⅱa级推荐为存在相互矛盾的证据和/或意见分歧,但大量证据证明有效;Ⅲ级推荐为有证据表明该治疗无效或某些情况下有害,不推荐。A级为对随机临床试验的系统回顾或荟萃分析;B级为随机或非随机的临床试验。 -
[1] 蒋雄京, 邹玉宝. 肾动脉狭窄的诊断和处理中国专家共识[J]. 中国循环杂志, 2017, 32(9): 835-844. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2017.09.002JIANG X J, ZOU Y B. Chinese expert consensus on the diagnosis and management of renal artery stenosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Circulation, 2017, 32(9): 835-844. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2017.09.002 [2] DOBREK L. An outline of renal artery stenosis pathophysiology-A narrative review[J]. Life (Basel), 2021, 11(3): 208. DOI: 10.3390/life11030208. [3] SARAFIDIS P, THEODORAKOPOULOU M, ORTIZ A, et al. Atherosclerotic renovascular disease: a clinical practice document by the European Renal Best Practice (ERBP) board of the European Renal Association (ERA) and the Working Group Hypertension and the Kidney of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH)[J]. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2023, 38(12): 2835-2850. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfad095 [4] HIREMATH S, SAPIR-PICHHADZE R, NAKHLA M, et al. Hypertension Canada ' s 2020 evidence review and guidelines for the management of resistant hypertension[J]. Can J Cardiol, 2020, 36(5): 625-634. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2020.02.083 [5] 李妮, 孟琦. 肾动脉狭窄漏诊报告1例并文献复习[J]. 中华全科医学, 2023, 21(5): 900-902. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.003010LI N, MENG Q. Missed diagnosis of renal artery stenosis: a case report and literature review[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2023, 21(5): 900-902. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.003010 [6] EDGR B, PEARSON R, KASTHURI R, et al. The impact of renal artery stenting on therapeutic aims[J]. J Hum Hypertens, 2023, 37(4): 265-272. [7] 杨德业, 赵连友, 李玉明, 等. 中国继发性高血压临床筛查多学科专家共识(2023)[J]. 心脑血管病防治, 2023, 23(1): 1-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-816x.2023.01.001YANG D Y, ZHAO L Y, LI Y M, et al. Multidisciplinary expert consensus on clinical screening of secondary Hypertension in China (2023)[J]. Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Diseases, 2023, 23(1): 1-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-816x.2023.01.001 [8] WILLIAMS B, MANCIA G, SPIERING W, et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension[J]. J Hypertens, 2018, 36(12): 2284-2309. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000001961 [9] PRIMUS C, AUER J. Bilateral renal artery stenosis in a young man[J]. BMJ Case Reports, 2021, 14(8): e237608. DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2020-237608. [10] BAILEY S, BECKMAN J, DAO T, et al. ACC/AHA/SCAI/SIR/SVM 2018 appropriate use criteria for peripheral artery intervention: a report of the American College of Cardiology Appropriate Use Criteria Task Force, American Heart Association, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, Society of Interventional Radiology, and Society for Vascular Medicine[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2019, 73(2): 214-237. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.10.002 [11] ABOYANS V, RICCO J, BARTELINK M, et al. 2017 ESC Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Peripheral Arterial Diseases, in collaboration with the European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS): document covering atherosclerotic disease of extracranial carotid and vertebral, mesenteric, renal, upper and lower extremity arteries endorsed by: the European Stroke Organization (ESO)The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Peripheral Arterial Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and of the European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS)[J]. Eur Heart J, 2018, 39(9): 763-816. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx095 [12] IWASHIMA Y, ISHIMITSU T. How should we define appropriate patients for percutaneous transluminal renal angioplasty treatment?[J]. Hypertens Res, 2020, 43(10): 1015-1027. doi: 10.1038/s41440-020-0496-z [13] LENZ T. Treatment of renal artery stenosis in the year 2021[J]. Internist (Berl), 2021, 62(3): 252-262. doi: 10.1007/s00108-020-00935-5 [14] THEODORAKOPOULOU M, KARAGIANNIDIS A, FERRO C, et al. Renal artery stenting in the correct patients with atherosclerotic renovascular disease: time for a proper renal and cardiovascular outcome study?[J]. Clin Kidney J, 2022, 16(2): 201-204. [15] CHEN Y, PAN H, LUO G, et al. Use of percutaneous transluminal renal angioplasty in atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Int Med Res, 2021, 49(1): 300060520983585. DOI: 10.1177/0300060520983585. [16] IWASHIMA Y, KUSUNOKI H, TANIYAMA A, et al. Impact of percutaneous transluminal renal angioplasty on autonomic nervous system and natriuresis in hypertensive patients with renal artery stenosis[J]. J Am Heart Assoc, 2022, 11(6): e23655. DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.121.023655. -





 下载:
下载: