Changes in inflammatory factors in children with allergic rhinitis before and after allergen-specific immunotherapy: expression spectrum and clinical significance
-
摘要:
目的 检测过敏性鼻炎患儿变应原皮下特异性免疫治疗(SCIT)前后炎症因子表达水平,并分析这些炎症因子在评估SCIT疗效中的应用价值。 方法 纳入2021年2月—2023年7月于浙江省人民医院淳安分院儿科接受标准SCIT的80例过敏性鼻炎(AR)患儿,根据疗效情况将其分为应答组(48例)和无应答组(32例)。对比2组患儿基线炎症因子水平,选取P<0.05的变量构建单因素logistic回归模型,并绘制ROC曲线分析其预测SCIT应用于AR患儿的疗效。 结果 治疗后,80例患儿C反应蛋白(CRP)、白细胞介素(IL)-1β、IL-6及IL-13水平降低,肿瘤坏死因子-β(TNF-β)、IL-10及IL-33水平升高(P<0.05)。应答组患儿基线IL-10及IL-33水平低于无应答组(P<0.05)。单因素logistic回归分析显示,IL-10(OR=0.344)、IL-33(OR=0.963)是SCIT疗效的影响因素(P<0.05)。ROC曲线结果显示,IL-10(AUC=0.836)、IL-33(AUC=0.833)预测SCIT疗效的价值较高。 结论 AR患儿经SCIT治疗后, TNF-β、IL-10、IL-33水平上升,CRP、IL-1β、IL-6及IL-13水平下降;基线IL-10及IL-33水平对SCIT疗效有较好的预测价值。 -
关键词:
- 过敏性鼻炎 /
- 变应原特异性免疫治疗 /
- 炎症因子 /
- 儿童
Abstract:Objective To detect the expression levels of inflammatory factors in children with allergic rhinitis before and after subcutaneous specific immunotherapy (SCIT) and to analyze the application value of these inflammatory factors in evaluating the efficacy of SCIT. Methods Eighty children with allergic rhinitis (AR) who received standard SCIT at the pediatric department of Chun'an Branch of Zhejiang Provincial People's Hospital from February 2021 to July 2023 were divided into a response group (n=48) and a non-response group (n=32) according to the curative effect. The baseline levels of inflammatory factors were compared between the two groups. The variables with P < 0.05 were selected for univariate logistic regression model, and the ROC curves were drawn to analyze the predictive effect of SCIT on AR children. Results After treatment, the levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, and IL-13 decreased, while the levels of tumor necrosis factor-β (TNF-β), IL-10, and IL-33 increased (P < 0.05).The baseline levels of IL-10 and IL-33 in children in the response group were lower than those in the non-response group (P < 0.05). Univariate logistic regression analysis showed that IL-10 (OR=0.344) and IL-33 (OR=0.963) significantly affected SCIT outcomes (P < 0.05). ROC curve showed that IL-10 (AUC=0.836) and IL-33 (AUC=0.833) have good predictive value for SCIT efficacy. Conclusion After SCIT treatment, the levels of TNF-β, IL-10, and IL-33 increased, while the levels of CRP, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-13 decreased. Baseline levels of IL-10 and IL-33 are valuable predictors of efficacy. -
Key words:
- Allergic rhinitis /
- Subcutaneous specific immunotherapy /
- Inflammatory factors /
- Children
-
表 1 80例AR患儿治疗前后炎症因子水平比较(x±s)
Table 1. Comparison of levels of inflammatory factors before and after treatment in 80 children(x±s)
时间 CRP (mg/L) TNF-β (pg/mL) IL-1β (ng/L) IL-6 (ng/L) IL-10 (pg/mL) IL-13 (ng/L) IL-33 (ng/mL) 治疗前 22.76±2.03 14.26±3.20 14.69±2.16 17.66±2.19 6.72±1.85 45.20±7.69 97.65±13.24 治疗后 12.65±1.78 21.23±3.28 6.33±1.05 7.32±1.65 10.51±1.76 24.15±6.42 154.30±20.34 t值 35.576 13.907 32.573 36.822 13.307 20.071 21.243 P值 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 表 2 应答组与无应答组AR患儿一般资料比较
Table 2. Comparison of general data of children in the response group and the non-response group
组别 例数 性别[例(%)] 年龄(x±s,岁) 病程(x±s,年) BMI (x±s) 基线TNSS (x±s,分) VAS (x±s,分) 男 女 应答组 48 22(45.83) 26(54.17) 9.20±2.75 2.14±0.97 20.14±2.06 9.32±3.05 7.12±2.05 无应答组 32 17(53.12) 15(46.88) 9.26±2.64 2.16±0.95 20.08±2.12 9.28±314 7.09±2.01 统计量 0.409a 0.098b 0.091b 0.125b 0.001b 0.065b P值 0.523 0.922 0.927 0.901 0.999 0.948 注:a为χ2值,b为t值。 表 3 应答组与无应答组AR患儿基线炎症因子水平比较(x±s)
Table 3. Comparison of baseline inflammatory factors between children in the response group and the non-response group(x±s)
组别 例数 CRP (mg/L) TNF-β (pg/mL) IL-1β (ng/L) IL-6 (ng/L) IL-10 (pg/mL) IL-13 (ng/L) IL-33 (ng/mL) 应答组 48 23.23±2.45 15.02±3.05 15.03±2.14 17.26±2.22 6.54±1.66 43.69±7.52 90.23±20.13 无应答组 32 22.43±2.18 14.01±2.97 14.26±2.14 17.81±2.25 8.23±2.02 46.23±7.41 116.20±22.30 t值 1.530 1.474 1.577 1.077 3.930 1.493 5.303 P值 0.131 0.145 0.120 0.286 <0.001 0.140 <0.001 表 4 AR患儿SCITL疗效影响因素的单因素logistic回归分析
Table 4. Univariate logistic regression analysis of factors influencing SCITL efficacy in children with AR
变量 B SE Waldχ2 P值 OR值 95%CI IL-10 -1.067 0.267 15.974 0.000 0.344 0.204~0.581 IL-33 -0.038 0.013 8.580 0.003 0.963 0.939~0.988 表 5 基线IL-10及IL-33水平的准确性与预测值
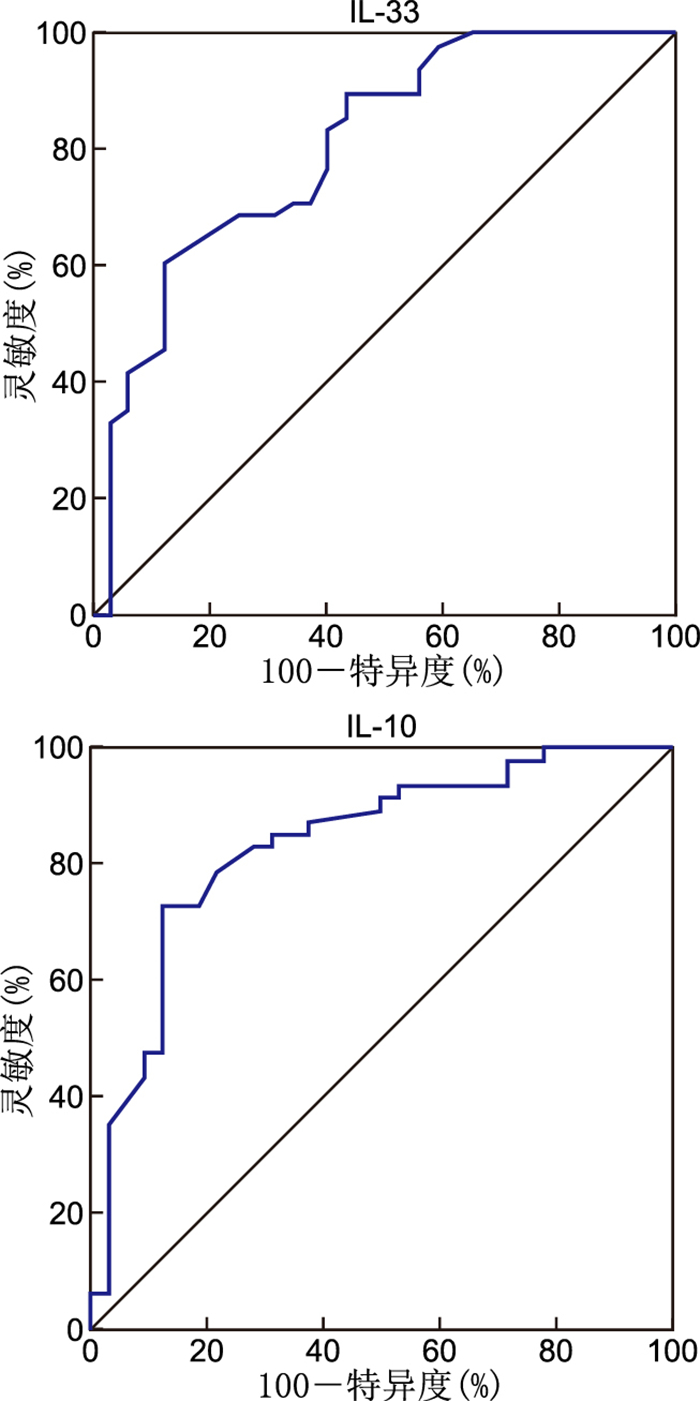
Table 5. Accuracy and predictive value of baseline levels of IL-10 and IL-33
指标 AUC 95% CI 灵敏度(%) 特异度(%) IL-10 0.836 0.737~0.910 72.92 87.50 IL-33 0.833 0.733~0.907 97.92 62.50 -
[1] RAPIEJKO P, JURKIEWICZ D, PIETRUSZEWSKA W, et al. Treatment strategy of allergic rhinitis in the face of modern world threats[J]. Otolaryngol Pol, 2018, 72(2): 1-12. doi: 10.5604/01.3001.0011.8057 [2] SCHULER Ⅳ C F, MONTEJO J M. Allergic rhinitis in children and adolescents[J]. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am, 2021, 41(4): 613-625. doi: 10.1016/j.iac.2021.07.010 [3] PAPADOPOULOS N G, AGGELIDES X, STAMATAKI S, et al. New concepts in pediatric rhinitis[J]. Pediatr Allergy Immunol, 2021, 32(4): 635-646. doi: 10.1111/pai.13454 [4] SULTÉSZ M, HORVÁTH A, MOLNÁR D, et al. Prevalence of allergic rhinitis, related comorbidities and risk factors in schoolchildren[J]. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol, 2020, 16(1): 98. DOI: 10.1186/s13223-020-00495-1. [5] OKUBO K, KURONO Y, ICHIMURA K, et al. Japanese guidelines for allergic rhinitis 2020[J]. Allergol Int, 2020, 69(3): 331-345. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2020.04.001 [6] LI H B, CHEN S, CHENG L, et al. Chinese guideline on sublingual immunotherapy for allergic rhinitis and asthma[J]. J Thorac Dis, 2019, 11(12): 4936-4950. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2019.12.37 [7] LIU Z, LU H, FENG X, et al. Predictive methods for efficacy of house dust mite subcutaneous immunotherapy in allergic rhinitis patients: a prospective study in a Chinese population[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2020, 10(3): 314-319. doi: 10.1002/alr.22508 [8] LICARI A, CASTAGNOLI R, BRAMBILLA I, et al. Biomarkers of immunotherapy response in patients with allergic rhinitis[J]. Expert Rev Clin Immunol, 2018, 14(8): 657-663. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2018.1504679 [9] KIM J Y, RHEE C S, MUN S J, et al. Early response of specific IgE can predict satisfaction with sublingual immunotherapy[J]. Laryngoscope, 2021, 131(3): 467-472. doi: 10.1002/lary.28762 [10] XIE S B, ZHANG H, WANG F J, et al. Circulating MIF associated with disease severity and clinical response of sublingual immunotherapy in house dust mite-induced allergic rhinitis[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12(1): 681724. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.681724. [11] JOUDI M, FARID HOSSEINI R, KHOSHKHUI M, et al. Effects of serum vitamin D and efficacy of subcutaneous immunotherapy in adult patients with allergic rhinitis[J]. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res, 2019, 11(6): 885-893. doi: 10.4168/aair.2019.11.6.885 [12] 付晴, 米光熙, 李建涛, 等. 变应性鼻炎的诊治进展[J]. 牡丹江医学院学报, 2018, 39(1): 119-122.FU Q, MI G X, LI J T, et al. Progress in diagnosis and treatment of allergic rhinitis[J]. Journal of Mudanjiang Medical University, 2018, 39(1): 119-122. [13] XIE S, JIANG S, ZHANG H, et al. Prediction of sublingual immunotherapy efficacy in allergic rhinitis by serum metabolomics analysis[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2021, 90(1): 107211. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107211. [14] XIE S, ZHANG H, WANG F, et al. Activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule as a biomarker for disease severity and efficacy of sublingual immunotherapy in allergic rhinitis[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2020, 88(1): 106975. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106975. [15] 田亮, 张伟. 白三烯受体拮抗剂对过敏性鼻炎模型大鼠血清IL-6、IL-10及TNF-α表达的影响[J]. 河北医药, 2019, 41(19): 2889-2893. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7386.2019.19.002TIAN L, ZHANG W. Effects of leukotriene receptor antagonists on the expressions of IL-6, IL-10 and TNF-α in serum of rats with allergic rhinitis[J]. Hebei Medical Journal, 2019, 41(19): 2889-2893. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7386.2019.19.002 [16] 尤宏银. 过敏性鼻炎患者血清中Treg细胞含量及炎症因子水平与患者病情的关系[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志, 2017, 27(6): 845-847.YOU H Y. The relationship between serum levels of Treg cells and inflammatory factors in patients with allergic rhinitis and severity[J]. Chinese Journal of Health Laboratory Technology, 2017, 27(6): 845-847. [17] 刘宇萌, 安东. 淋巴细胞亚群检测在肾病综合征患儿免疫功能评价中的意义[J]. 中华全科医学, 2022, 20(4): 661-664, 672. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002424LIU Y M, AN D. Significance of lymphocyte subset detection in immune function evaluation of children with nephrotic syndrome[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2022, 20(4): 661-664, 672. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002424 [18] ERKAN K, BOZKURT M K, ARTAÇ H, et al. The role of regulatory T cells in allergic rhinitis and their correlation with IL-10, IL-17 and neopterin levels in serum and nasal lavage fluid[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2020, 277(4): 1109-1114. doi: 10.1007/s00405-020-05811-4 [19] ZISSLER U M, JAKWERTH C A, GUERTH F M, et al. Early IL-10 producing B-cells and coinciding Th/Tr17 shifts during three year grass-pollen AIT[J]. EBioMedicine, 2018, 36(1): 475-488. [20] EL-MAGHRABY H M, RABIE R A. Serum level of IL-10 is significantly increased in allergic rhinitis patients on subcutaneous immunotherapy and vitamin D supplementation[J]. Egypt J Immunol, 2019, 26(2): 87-93. [21] SHARIF H, ACHARYA S, DHONDALAY G, et al. Altered chromatin landscape in circulating T follicular helper and regulatory cells following grass pollen subcutaneous and sublingual immunotherapy[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2021, 147(2): 663-676. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.10.035 [22] POINTNER L, BETHANIS A, THALER M, et al. Initiating pollen sensitization -complex source, complex mechanisms[J]. Clin Transl Allergy, 2020, 10(1): 36. doi: 10.1186/s13601-020-00341-y [23] HACCURIA A, VAN MUYLEM A, MALINOVSCHI A, et al. Increased expression of IL-33 is found in the lower airways of patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis and is not related to natural allergen exposure[J]. Clin Exp Allergy, 2021, 51(6): 845-848. doi: 10.1111/cea.13819 [24] WANG Y M, LI C L, XU Y X, et al. Sublingual immunotherapy decreases expression of interleukin-33 in children with allergic rhinitis[J]. Indian J Pediatr, 2018, 85(10): 872-876. doi: 10.1007/s12098-018-2703-3 [25] GLÜCK J, RYMARCZYK B, JURA-SZOŁTYS E, et al. Serum levels of interleukin 33 and its receptor ST2 in patients treated with subcutaneous allergen immunotherapy in intermittent allergic rhinitis[J]. Cent Eur J Immunol, 2019, 44(2): 214-217. doi: 10.5114/ceji.2019.87075 -





 下载:
下载: