The predictive value of MRI-DWI-IVIM multiparameter imaging in tumor infiltrating lymphocyte levels after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for invasive breast cancer
-
摘要:
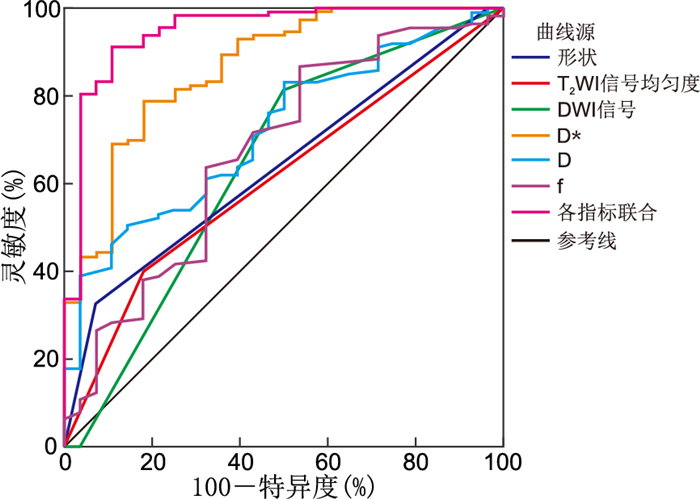
目的 探究浸润性乳腺癌新辅助化疗中采用磁共振(MRI)-扩散加权成像(DWI)-体素内不相干运动(IVIM)多参数成像对患者治疗后浸润淋巴细胞(TILs)水平的预测价值。 方法 选择2021年12月—2022年12月河北北方学院附属第一医院收治的140例浸润性乳腺癌患者作为研究对象,均行MRI-DWI-IVIM检查,患者给予新辅助化疗,治疗后评估TILs。分析MRI-DWI-IVIM多参数成像对TILs水平的预测价值。 结果 治疗后患者TILs阳性率(80.71%)显著高于治疗前(63.57%,χ2=10.236,P<0.05);TILs阳性与TILs阴性患者边界、T2WI信号、DWI信号比较差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05);TILs阳性患者伪扩散系数(D*)低于TILs阴性,而单纯扩散系数(D)、微血管内容量分数(f)等参数高于TILs阴性(P<0.05);ROC曲线显示,边界、T2WI信号、DWI信号、D*、D、f预测TILs水平的AUC分别为0.640、0.610、0.640、0.866、0.720、0.674,各指标联合预测的AUC为0.948。 结论 浸润性乳腺癌新辅助化疗后TILs水平上升,采用MRI-DWI-IVIM多参数成像可以评估患者化疗后TILs水平,各指标联合可以提高对于TILs水平的预测价值。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the potential of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and intravoxel incoherence motion (IVIM) multiparameter imaging in predicting tumour infiltrating lymphocyte (TILs) levels in patients with invasive breast cancer who have undergone neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Methods A total of 140 patients with invasive breast cancer admitted to the hospital between December 2021 and December 2022 were selected as the study subjects. All patients underwent an MRI-DWI-IVIM examination, received neoadjuvant chemotherapy, and had their TILs evaluated after treatment. The utility of MRI-DWI-IVIM multiparameter imaging in predicting TIL levels was evaluated. Results The positive rate of TILs after treatment (80.71%) was significantly higher than that before treatment (63.57%, χ2=10.236, P < 0.05). Furthermore, there was a statistically significant difference in the boundary, T2WI signal and DWI signal between TILs positive and TILs negative patients (P < 0.05). The pseudo-diffusion coefficient (D*) of TILs-positive patients was observed to be lower than that of TILs-negative patients, while the simple diffusion coefficient (D) and microvascular volume fraction (f) were found to be higher than those of TILs-negative patients (P < 0.05). Receiver operating characteristic curves demonstrated that the area under the curve (AUC) predicted by the boundary, T2WI signal, DWI signal, D*, D and f on TILs were 0.640, 0.610, 0.640, 0.866, 0.720 and 0.674, respectively. Furthermore, the combined AUC of all indicators was 0.948. Conclusion The level of TILs was observed to increase following the administration of neoadjuvant chemotherapy for invasive breast cancer. Multiparameter imaging by MRI-DWI-IVIM can be used to evaluate the level of TILs after chemotherapy. Furthermore, the combination of all indicators can improve the predictive value of the TILs level. -
表 1 治疗后不同TILs水平浸润性乳腺癌患者MRI表现比较
Table 1. Comparison of MRI findings in patients with invasive breast cancer with different TILs levels after treatment
组别 例数 肿瘤最大直径
(x±s, cm)肿瘤形状 边界[例(%)] T2WI信号强度[例(%)] T2WI信号均匀度[例(%)] 圆形或者卵圆形 不规则 光滑 粗糙 较高 稍高 等信号 不均匀 均匀 TILs阳性 113 2.12±0.52 29(25.66) 84(74.34) 37(32.74) 76(67.26) 14(13.59) 64(62.14) 25(24.27) 68(60.18) 45(39.82) TILs阴性 27 2.26±0.49 5(18.52) 22(81.48) 2(7.41) 25(92.59) 6(22.22) 18(66.67) 3(11.11) 23(85.19) 4(14.81) 统计量 1.270a 0.605b 6.961b 2.826b 5.991b P值 0.506 0.437 0.008 0.244 0.014 注:a为t值,b为χ2值。 表 2 治疗后不同TILs水平浸润性乳腺癌患者DWI表现比较
Table 2. Comparison of DWI performance in invasive breast cancer patients with different TILs levels after treatment
组别 例数 DWI信号[例(%)] ADC值(x±s,×10-3mm2) 低信号 等信号 高信号 b=500 s/mm2 b=1 000 s/mm2 TILs阳性 113 20(17.70) 72(63.72) 21(18.58) 1.02±0.23 0.88±0.15 TILs阴性 27 3(11.11) 10(37.04) 14(51.85) 1.04±0.19 0.89±0.14 统计量 12.872a 0.419b 0.315b P值 <0.001 0.676 0.753 注:a为χ2值,b为t值。 表 3 治疗后不同TILs水平浸润性乳腺癌患者IVIM表现比较(x±s)
Table 3. Comparison of IVIM performance in invasive breast cancer patients with different TILs levels after treatment(x±s)
组别 例数 D*
(×10-3mm2/s)D
(×10-3mm2/s)f(%) TILs阳性 113 3.16±0.92 1.17±0.26 59.26±13.51 TILs阴性 27 5.53±1.67 0.97±0.24 51.09±15.24 t值 4.512 5.663 7.214 P值 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 表 4 MRI-DWI-IVIM多参数成像对TILs水平的预测价值分析
Table 4. Predictive value of MRI-DWI-IVIM multi-parameter imaging on TILs level
项目 截断值 AUC 95% CI 灵敏度(%) 特异度(%) P值 边界 0.640 0.535~0.745 32.71 92.89 0.022 T2WI信号均匀度 0.610 0.500~0.720 39.83 82.07 0.073 DWI信号 0.640 0.513~0.767 81.37 50.72 0.022 D* 4.62 ×10-3mm2/s 0.866 0.790~0.942 78.67 82.06 <0.001 D 1.06 ×10-3mm2/s 0.720 0.624~0.815 50.36 85.66 <0.001 f 56.00% 0.674 0.558~0.790 86.67 46.37 0.004 各指标联合 0.948 0.898~0.999 91.17 89.28 <0.001 -
[1] TAURIN S, ALKHALIFA H. Breast cancers, mammary stem cells, and cancer stem cells, characteristics, and hypotheses[J]. Neoplasia, 2020, 22(12): 663-678. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2020.09.009 [2] CHEN W, WEI W, YU L, et al. Mammary development and breast cancer: a notch perspective[J]. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia, 2021, 26(3): 309-320. doi: 10.1007/s10911-021-09496-1 [3] IWAMOTO T, KAJIWARA Y, ZHU Y, et al. Biomarkers of neoadjuvant/adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer[J]. Chin Clin Oncol, 2020, 9(3): 27-38. doi: 10.21037/cco.2020.01.06 [4] FERNANDES I, SCORSATO A, KALIKS R, et al. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in HER2-Low breast cancer[J]. Clin Breast Cancer, 2023, 23(7): 470-479. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2023.07.007 [5] SU GH, XIAO Y, JIANG L, et al. Radiomics features for assessing tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes correlate with molecular traits of triple-negative breast cancer[J]. J Transl Med, 2022, 20(1): 471-483. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03688-x [6] 韩佳雯, 苏婷婷, 徐元兵, 等. 肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞在三阴性乳腺癌新辅助化疗预测价值中的研究进展[J]. 中国肿瘤临床, 2023, 50(19): 1011-1016. doi: 10.12354/j.issn.1000-8179.2023.20230567HAN J W, SU T T, XU Y B, et al. Research progress of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in predicting the efficacy of neo-adjuvant chemotherapy for triple negative breast cancer[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2023, 50(19): 1011-1016. doi: 10.12354/j.issn.1000-8179.2023.20230567 [7] 李崇, 杨勇, 徐成春, 等. DCE-MRI在乳腺良性病变与乳腺癌诊断中的应用价值[J]. 保健医学研究与实践, 2024, 21(3): 82-88.LI C, YANG Y, XU C C, et al. The value of DCE-MRI in the diagnosis of benign breast lesions and breast cancer[J]. Health Medicine Research and Practice, 2024, 21(3): 82-88. [8] DIECI M V, RADOSEVIC-ROBIN N, FINEBERG S, et al. Update on tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) in breast cancer, including recommendations to assess TILs in residual disease after neoadjuvant therapy and in carcinoma in situ: a report of the International Immuno-Oncology Biomarker Working Group on Breast Cancer[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2018, 52(Pt 2): 16-25. [9] CHEN Y, KLINGEN T A, AAS H, et al. CD47 and CD68 expression in breast cancer is associated with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, blood vessel invasion, detection mode, and prognosis[J]. J Pathol Clin Res, 2023, 9(3): 151-164. doi: 10.1002/cjp2.309 [10] 王希梅, 蒲倩, 耿文文, 等. 肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞比例与乳腺癌临床病理特征和预后的关系[J]. 中国现代普通外科进展, 2022, 25(10): 782-785, 789.WANG XM, PU Q, GENG WW, et al. Relationship between tumor infiltrating lymphocytes and clinicopathological features and prognosis in patients with breast cancer[J]. Chinese Journal of Current Advances in General Surgery, 2022, 25(10): 782-785, 789. [11] 贺松, 李娇娇, 张斌, 等. 分析NAC治疗乳腺癌的MRI成像变化及其参数对预测浸润性乳腺癌TILs水平的效能[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志, 2023, 21(7): 87-89, 92.HE S, LI JJ, ZHANG B, et al. To Analyze the MRI Changes of NAC in Breast Cancer Treatment and the Efficacy of Its Parameters in Predicting TILs Level in Invasive Breast Cancer[J]. Chinese Journal of CT and MRI, 2023, 21(7): 87-89, 92. [12] 陈翠, 金叶, 王琳, 等. 30例乳腺化生性癌的多种影像学对比分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(1): 70-76.CHEN C, JIN Y, WANG L, et al. Comparative analysis of 30 cases of metaplastic carcinoma of the breast[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University(Medical Science), 2022, 42(1): 70-76. [13] 康锋, 代凤霞. 乳腺癌组织中孕激素受体、人表皮生长因子受体-2检测联合动态增强磁共振成像对乳腺癌术后复发时间的预测价值[J]. 陕西医学杂志, 2022, 51(11): 1437-1440, 1452.KANG F, DAI F X. Prediction value of progesterone receptor and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 detection combined with dynamic enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for postoperative recurrence of breast cancer[J]. Shaanxi Medical Journal, 2022, 51(11): 1437-1440, 1452. [14] KANG H S, KIM J Y, KIM J J, et al. Diffusion kurtosis MR imaging of invasive breast cancer: correlations with prognostic factors and molecular subtypes[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2022, 56(1): 110-120. doi: 10.1002/jmri.27999 [15] 孟庆涛, 李军, 蒋会东, 等. VI-RADS联合IVIM序列在膀胱癌肌层侵犯评估中的价值[J]. 中华全科医学, 2022, 20(12): 2096-2100. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002778MENG QT, LI J, JIANG HD, et al. Value of vesical imaging reporting and data system combined with intravoxel incoherent motion sequences in the evaluation of muscle invasion in bladder cancer[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2022, 20(12): 2096-2100. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002778 [16] HONDA M, IIMA M, KATAOKA M, et al. Biomarkers predictive of distant disease-free survival derived from diffusion-weighted imaging of breast cancer[J]. Magn Reson Med Sci, 2023, 22(4): 469-476. [17] LIU Y, LUO H, WANG C, et al. Diagnostic performance of T2-weighted imaging and intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MRI for predicting metastatic axillary lymph nodes in T1 and T2 stage breast cancer[J]. Acta Radiol, 2022, 63(4): 447-457. [18] JIN Y N, ZHANG Y, CHENG J L, et al. The role of histogram analysis in diffusion-weighted imaging in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant breast lesions[J]. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak, 2020, 20(1): 239-249. [19] 蒋伟, 邓虹, 张翔, 等. 体素内不相干运动扩散加权成像在乳腺癌腋窝转移性小淋巴结中的研究价值[J]. 磁共振成像, 2023, 14(9): 70-75, 80.JIANG W, DENG H, ZHANG X, et al. Clinical value of intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging in the diagnosis of small metastatic axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2023, 14(9): 70-75, 80. -





 下载:
下载: